עמוד 1 מתוך 10 נסוי מס` 1 – תגובות גריניאר והתמרות ארומטיות נוקלאופיליות
advertisement
10 מתוך1 עמוד
– תגובות גריניאר והתמרות ארומטיות נוקלאופיליות1 'נסוי מס
לימוד,מתכתיים-ביצוע תגובות גריניאר באמצעות מגיבים אורגנו
– מטרת הנסוי
.השימושים הסינתטיים של התגובה
הבדלים עם התמרות,ביצוע תגובות התמרה במערכות ארומטיות
.sp3 נוקלאופיליות על פחמני
.ספרי למוד בכימיה אורגנית
– חומר רקע
Grignard Reaction
V. Grignard, Compt. Rend. 130, 1322 (1900).
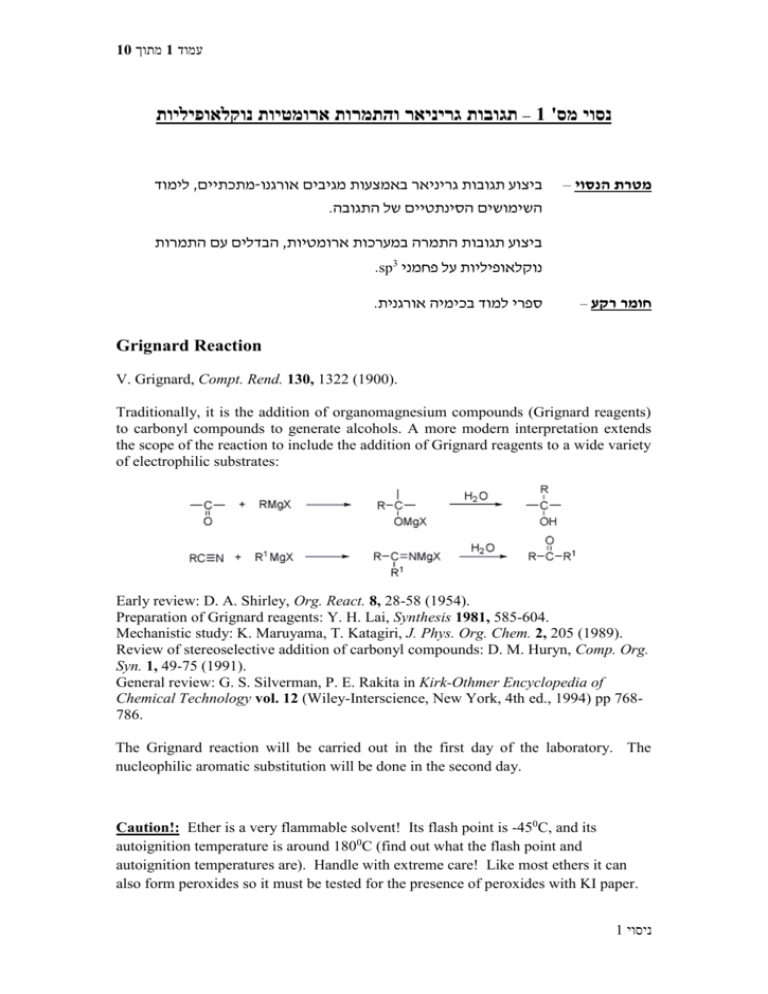
Traditionally, it is the addition of organomagnesium compounds (Grignard reagents)
to carbonyl compounds to generate alcohols. A more modern interpretation extends
the scope of the reaction to include the addition of Grignard reagents to a wide variety
of electrophilic substrates:
Early review: D. A. Shirley, Org. React. 8, 28-58 (1954).
Preparation of Grignard reagents: Y. H. Lai, Synthesis 1981, 585-604.
Mechanistic study: K. Maruyama, T. Katagiri, J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2, 205 (1989).
Review of stereoselective addition of carbonyl compounds: D. M. Huryn, Comp. Org.
Syn. 1, 49-75 (1991).
General review: G. S. Silverman, P. E. Rakita in Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of
Chemical Technology vol. 12 (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 4th ed., 1994) pp 768786.
The Grignard reaction will be carried out in the first day of the laboratory. The
nucleophilic aromatic substitution will be done in the second day.
Caution!: Ether is a very flammable solvent! Its flash point is -450C, and its
autoignition temperature is around 1800C (find out what the flash point and
autoignition temperatures are). Handle with extreme care! Like most ethers it can
also form peroxides so it must be tested for the presence of peroxides with KI paper.
1 ניסוי
10 מתוך2 עמוד
For the reaction to succeed it is imperative that all glassware be absolutely dry (the
best way is to flame dry the equipment, but flames are not allowed in the students lab
so keep the glassware in the oven before use and protect the assembled system with a
CaCl2 guard tube). Do not start the Grignard reaction (halide addition) before the
authorization of the instructor.
Notes:
1. When preparing samples for GCMS don’t forget to dry your sample with a small
amount of MgSO4 (ask your instructor for help). Water will damage the GC column!
2. Do not make concentrated samples for GCMS!
Grignard reactions
Track A (')מסלול א: Benzoic acid from bromobenzene and dry ice
From Vogel 3rd p 756.
Into a dry 3-neck 100 mL RB-flask with stirring magnet, reflux condenser with CaCl2
trap and a dropping funnel place 2.00 gr of dry magnesium turnings, 1 crystal of
iodine and 5-10 mL dry ether. Into the dropping funnel add 9 mL of bromobenzene
and 40 mL dry ether. Add ca. 10 drops from the funnel. Warm gently until the
magnesium starts to react (disappearance of iodine color and cloudiness). Add the
bromobenzene solution dropwise over a period of 30 minutes, maintaining a gentle
reflux. Reflux the mixture for 30 minutes Cool the mixture to room temperature.
Into a dry 250 mL flask beaker with a dropping funnel and CaCl2 trap, add 20gr of dry
ice and add the Grignard solution slowly while stirring, keep the unreacted
magnesium in the flask. Stir until the dry ice evaporates. Add 50 gr of crushed ice and
then 15 mL hydrochloric acid (1:1v/v). Stir until the solid has decomposed. Transfer
the mixture to a separatory funnel, wash the beaker with ether and add to the funnel.
Remove the aqueous layer and wash the organic phase twice with 15 mL of ether.
Wash the combined organic phase twice with water, and then extract with two
portions of 50 mL 5% NaOH. Treat the aqueous phase with ~1gr of activated
charcoal and a Whatman ashlet tablet, and filter on a Büchner funnel. Acidify with 1:1
hydrochloric acid; collect the solid benzoic acid on a Büchner funnel. Recrystalize
from water. Record the yield and M.P. Prepare samples for GCMS with DCM as
solvent and for NMR with CDCl3.
1 ניסוי
10 מתוך3 עמוד
Track B (')מסלול ב: Benzhydrol from bromobenzene and benzaldehyde
Fit a 250 mL dry three necked flask with a magnetic stirrer, dropping funnel and a
condenser, equipped with a calcium chloride drying tube. Add 2.0 g of magnesium
and a 10 mL of anhydrous ether (just enough to cover the Mg surface). Prepare a
solution of 8.6 mL bromobenzene in 40 mL anhydrous ether in the dropping funnel.
Add a small crystal of iodine (if your system is dry enough you probably do not need
the iodine) to the flask, and then add 10 drops of your bromobenzene solution.
Observe the flask for signs of reaction (bubbles and haziness). A vigorous reaction
should start in a few minutes. You may need to heat your reaction slightly with a
heating fan to help the reaction. Have a beaker with ice water ready in case the
reaction is too vigorous and needs to be quenched a little. Do not kill your reaction by
excessive cooling! When the reaction has started continue adding your
bromobenzene solution to keep a gentle reflux. At the end of the reaction add 20 mL
of anhydrous ether. After nearly all the magnesium has reacted begin adding,
dropwise, a solution of 8.6 gr benzaldehyde in 10 mL anhydrous ether. After addition
is complete reflux the mixture for 15 minutes on warm water (do NOT boil the water).
Decompose the complex by careful addition of 100 mL of cold 20% sulphuric acid
dropwise over 20 minutes. Cool the flask in ice and stir continuously while adding
the acid. Transfer the mixture to a separatory funnel and separate the layers. Keep
both layers. Extract the aqueous layer with two 30 mL portions of ether (not
anhydrous of course). Combine all the ether extracts and wash them with a solution
of sodium bicarbonate. Dry the organic phase with potassium carbonate, filter and
evaporate in a 250 mL round-bottom flask. After evaporating add 120 mL hot water.
Cool the flask in an ice bath. Solid benzhydrol will precipitate. After drying
recrystallize from hexane. Record the melting point and yield. Prepare samples for
with DCM as solvent and for NMR with CDCl3.
1 ניסוי
10 מתוך4 עמוד
Track C (')מסלול ג: 2-methylhexan-2-ol from bromopentane and acetone
From Vogel 3rd, p257.
Into a dry 3-neck 100 mL RB-flask with stirring magnet, reflux condenser with CaCl2
trap and a dropping funnel place 1.5 gr of dry magnesium turnings, 1 crystal of iodine
and 5-10 mL dry ether. Into the dropping funnel add 6.7 mL of n-butyl bromide and
20 mL dry ether. Add 10 drops of the bromide solution from the funnel. Warm gently
until the magnesium starts to react (disappearance of iodine color and cloudiness).
Add the bromide solution dropwise over a period of 30 minutes, maintaining a gentle
reflux. Reflux the mixture for 30 minutes. Cool the mixture to room temperature.
Add 4.8 mL of dry acetone in 10 mL anhydrous ether dropwise, while cooling the
flask. Decompose the remaining magnesium with 50 mL of 10% sulphuric acid.
Transfer the mixture to a separatory funnel, separate the two phases. Extract the
aqueous phase twice with ether. Wash the combined organic phases with NaHCO3
solution, dry with potassium carbonate and filter the solution. Remove the ether by
evaporation and distill the product. Record the yield and B.P. Prepare samples for
with DCM as solvent and for NMR with CDCl3.
1 ניסוי
10 מתוך5 עמוד
Track D (')מסלול ד: Triphenyl carbinol from bromobenzene and methyl benzoate
From Vogel 3rd p 756.
Into a dry 3-neck 250 mL RB-flask with stirring magnet, reflux condenser with CaCl2
trap and a dropping funnel place 4 gr of dry magnesium turnings, 1 crystal of iodine
and 5-10 mL dry ether. Into the dropping funnel add 18 mL of bromobenzene and
80 mL dry ether. Add ca. 10 drops from the funnel. Warm gently until the magnesium
starts to react (disappearance of iodine color and cloudiness). Add the bromobenzene
solution dropwise over a period of 30 minutes, maintaining a gentle reflux. Reflux the
mixture for 30 minutes. Cool the mixture to room temperature.
The reaction flask used to prepare the phenyl magnesium bromide is cooled in an ice
bath. The ice bath is then removed and 9 mL of methyl benzoate in 30 mL anhydrous
ether is slowly added dropwise at such a rate to maintain a gentle reflux. Keep the ice
bath near just in case you need to cool the reaction. Stir the reaction efficiently
throughout the addition of methyl benzoate. After the addition is over reflux the
mixture for 30 minutes with a warm water bath. Prepare a 500 mL Erlenmeyer and
add to it 100 mL 10% sulphuric acid and 50 gr ice. Pour your reaction mixture into
the Erlenmeyer with the chilled ice. Rinse the reaction flask with a small amount of
ether (not anhydrous) and 10% sulphuric acid. Stir the Erlenmeyer mixture to assure
complete hydrolysis. The triphenyl carbinol should be in the organic phase. Add, if
needed, more ether (not anhydrous) to completely dissolve the carbinol. Remove all,
if any, unreacted magnesium from the mixture. Pour the mixture into a separatory
funnel. Wash the organic layer with an additional portion of 10% sulphuric acid and
then with brine. Dry the organic phase with MgSO4, filter and evaporate.
Recrystallize your compound from 1:1 petroleum ether/diethyl ether. Record the
melting point and yield. Prepare samples for with DCM as solvent and for NMR with
CDCl3.
1 ניסוי
10 מתוך6 עמוד
Track E (')מסלול ה: Triphenyl carbinol from bromobenzene and benzophenone
From Vogel 3rd p 756.
Into a dry 3-neck 250 mL RB-flask with stirring magnet, reflux condenser with CaCl2
trap and a dropping funnel place 4 gr of dry magnesium turnings, 1 crystal of iodine
and 5-10 mL dry ether. Into the dropping funnel add 18 mL of bromobenzene and
80 mL dry ether. Add ca. 10 drops from the funnel. Warm gently until the magnesium
starts to react (disappearance of iodine color and cloudiness). Add the bromobenzene
solution dropwise over a period of 30 minutes, maintaining a gentle reflux. Reflux the
mixture for 30 minutes Cool the mixture to room temperature.
The reaction flask used to prepare the phenyl magnesium bromide is cooled in an ice
bath. The ice bath is then removed and 13 gr benzophenone in 30 mL anhydrous
ether is slowly added dropwise at such a rate to maintain a gentle reflux. Keep the ice
bath near just in case you need to cool the reaction. Stir the reaction efficiently
throughout the addition of benzophenone. After the addition is over reflux the
mixture for 30 minutes with a warm water bath. Prepare a 500 mL Erlenmeyer and
add to it 100 mL 10% sulphuric acid and 50 gr ice. Pour your reaction mixture into
the Erlenmeyer with the chilled ice. Rinse the reaction flask with a small amount of
ether (not anhydrous) and 10% sulphuric acid. Stir the Erlenmeyer mixture to assure
complete hydrolysis. The triphenyl carbinol should be in the organic phase. Add, if
needed, more ether (not anhydrous) to completely dissolve the carbinol. Remove all,
if any, unreacted magnesium from the mixture. Pour the mixture into a separatory
funnel. Wash the organic layer with an additional portion of 10% sulphuric acid and
then with brine. Dry the organic phase with MgSO4, filter and evaporate.
Recrystallize your compound from 1:1 petroleum ether/diethyl ether. Record the
melting point and yield. Prepare samples for GCMS with DCM as solvent and for
NMR with CDCl3.
1 ניסוי
10 מתוך7 עמוד
Track F (')מסלול ו: 2-methylpentan-2ol from bromobutane and acetone
From Vogel 3rd, p257.
Into a dry 3-neck 100 mL RB-flask with stirring magnet, reflux condenser with CaCl2
trap and a dropping funnel place 1.5 gr of dry magnesium turnings, 1 crystal of iodine
and 5-10 mL dry ether. Into the dropping funnel add 6.7 mL of n-propyl bromide and
20 mL dry ether. Add ca. 10 drops from the funnel. Warm gently until the magnesium
starts to react (disappearance of iodine color and cloudiness). Add the bromide
solution dropwise over a period of 30 minutes, maintaining a gentle reflux. Reflux the
mixture for 30 minutes. Cool the mixture to room temperature.
Add 4.8 mL of dry acetone in 10 mL anhydrous ether dropwise, while cooling the
flask. Decompose the remaining magnesium with 50 mL of 10% sulphuric acid.
Transfer the mixture to a separatory funnel, separate the two phases. Extract the
aqueous phase twice with ether. Wash the combined organic phases with NaHCO3
solution, dry with potassium carbonate and filter the solution. Remove the ether by
evaporation and distill the product. Record the yield and B.P. Prepare samples for
with DCM as solvent and for NMR with CDCl3.
1 ניסוי
10 מתוך8 עמוד
Nucleophilic aromatic substitution
Track A + E (' ה+ )מסלול א: N-phenyl-2,4-dinitroaniline from 2,4dinitrochlorobenzene and aniline
Track B + F (' ו+ )מסלול ב: N-(p-methoxyphenyl)-2,4-dinitroaniline from 2,4dinitrochlorobenzene and p-anisidine
2, 4-Dinitrochlorobenzene (1.5 gr, 7.5 mmol) is dissolved in 20 mL of ethanol and
warmed on a water bath. To this solution 0.015 mole of the desired amine is added
(calculate the needed amount), and the mixture is then heated on the water bath for 15
minutes It is thoroughly chilled in ice and the product is isolated by Büchner
filtration. These compounds show a tendency to form super-saturated solutions, and
scratching with a glass rod is usually necessary. Recrystallize from ethanol and record
M.P and yield. Prepare samples for GCMS with DCM as solvent and for NMR with
CDCl3.
1 ניסוי
10 מתוך9 עמוד
Track C (')מסלול ג: 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine from 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene
and hydrazine hydrate
From Organic Synthesis, Coll. Vol.2, p.228; Vol. 13, p. 36.
In a 100 mL flask with a stirrer and reflux condenser, add 5.00 gr (0.25 mol) of
2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene is dissolved in 25 mL of ethanol. Add 0.25 mol of hydrazine
hydrate (98%) solution (calculate the needed amount) and reflux with stirring for one
hour. Most of the product separates during the first ten minutes. Cooled the flask
well, filter the solid on Büchner funnel and wash, once with 50 mL of warm ethanol
(60°C) to remove unchanged halide and then with 50 mL of hot water. It is pure
enough for most purposes. Record the M.P, yield. Prepare samples for GCMS with
DCM as solvent and for NMR with CDCl3.
1 ניסוי
10 מתוך10 עמוד
Track D (')מסלול ד: 2,4-dintroiodobenzene from 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene and
sodium iodide
From Organic Synthesis, Coll. Vol.5, p.478; Vol. 40, p. 34.
In a 100 mL flask with a stirrer and reflux condenser, add 4.0 gr of
2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene and 15.0 gr. of sodium iodide. Dissolve in 20 mL of
redistilled technical grade dimethylformamide. The red-brown mixture is refluxed for
15 minutes. Pour the hot reaction mixture to a beaker with about 75 gr. of crushed ice.
The beaker is filled with water, and the mixture is stirred to dissolve inorganic salts.
The insoluble red-brown solid is collected on a Büchner filter. Transfer this crude
product, even while damp, to a 250 mL round-bottomed flask and add a mixture of 40
mL of petroleum ether (60-80) and 15 mL of toluene is added. Reflux for 15 minutes.
Transfer the resulting solution into a second 250 mL flask, leaving in the first flask
some liquid and a red-brown solid residue. Add 0.7 gr. of powdered activated carbon.
Reflux for 5 more minutes. Filter the hot mixture (hot filtration) through a fluted filter
into an Erlenmeyer flask. Slowly cool the solution until crystallization of the product.
Collect the product on a Büchner funnel. Recrystallize from petroleum ether (60-80)
with addition of activated carbon (and hot filtration) if needed. Record M.P and yield.
Prepare samples for GCMS with DCM as solvent and for NMR with CDCl3.
1 ניסוי