Exp01 Electronics (AC)
advertisement

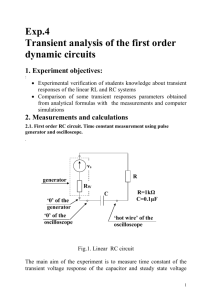
ELTRY251 Please Print Name: Lab 01 Electronics (AC) Introduction In this experiment, you will learn the basic concept of Alternating Current (AC) and the operation of a Function Generator and Oscilloscope. You will also learn how to measure the frequency of a sinusoidal waveform with an oscilloscope. Function Generator is basically an AC voltage source which is capable of producing Sine, Square, and Triangle waveforms. The output magnitude and frequency is adjustable. Oscilloscope is a device that shows a representation of voltage vs. time. With an oscilloscope you can visually inspect the waveform and measure the voltage, period and frequency. Equipment 1. 2. 3. 4. Function Generator Digital Multi-meter (Fluke 87) Oscilloscope Alligator – alligator wires Procedure 1. Turn on the Oscilloscope and wait few seconds for the display 2. Set the scope controls as following. Note: Following setting might be different for different brand of scope. This setting is to make sure you will see a straight line in the middle of the display. If after power up you see the straight line, skip this setting. Scope Controls Trigger Source Trigger Slope Trigger Coupling Time/Cm Volt/Cm AC/DC Vertical Mode Intensity Focus Vertical Position Horizontal Position Setting Channel 1 + AC 0.5 ms (Calibrated) 1 V (Calibrated, Pushed in) AC Channel 1 Mid-position Mid-position Mid-position Mid-position (Pushed in) C:\PCC\Eltry251\Labs\ Page 1 of 4 ELTRY251 Please Print Lab 01 Name: Electronics (AC) 3. Connect the Function Generator to the DMM and scope as shown below. Scope Function Generator O O O O O O + V GND O O O Ch2 Ch1 Sin Sqr O Tri GND Out 8 8 8 8 O O O O O O - Volt Meter 4. Set the voltmeter to measure AC Voltage. 5. Turn on the function generator and set it as following. Note the frequency setting is approximate and voltage reading is via DMM and is RMS. Fun. Gen. Controls Setting Output Sine Wave Magnitude 5 V (RMS) Frequency 5000 Hz 6. Adjust the scope to observe a stable sine wave. 7. Read the frequency form the function generator and the voltage (RMS) from the DMM and record it in the following table. Function Generator DMM Frequency (Hz) RMS (V) C:\PCC\Eltry251\Labs\ Page 2 of 4 ELTRY251 Please Print Lab 01 Name: Electronics (AC) 8. Read the scope and record it in the following table. Oscilloscope Measurement # Horz. Time / # Vert. Volts / div. Div. Div Div Period (Sec) Freq (Hz) Calculation VPP VP (V) (V) VRMS (V) 9. Calculate the Period, Frequency, VPP, VP, and VRMS and record it in the above table. Period (T) = (# Horizontal Divisions) * (Time / Div) Freq = 1 / T VPP = (# Vertical Divisions) * (Volts / Div) VP = VPP / 2 VRMS = 0.707 * VP 10. Draw an exact representation of what you see on the scope. 11. Change the output of the function generator to square wave. 12. Change the output of the function generator to triangle wave. C:\PCC\Eltry251\Labs\ Page 3 of 4 ELTRY251 Please Print Lab 01 Name: Electronics (AC) 13. Describe your observation. 14. Change the output of the function generator back to sine wave. 15. Adjust the frequency and magnitude of the function generator according to the following table. 16. Adjust the scope for best visual inspection for each setting and complete the following table. Func. Gen DMM Freq (Hz) RMS (V) 10 KHz 15 KHz 25 KHz 50 KHz Measured Oscilloscope # Horiz Div Time / Div. # Vert Div Volts / Div Calculated T (Sec) Freq (Hz) VPP (V) VP (V) 1V 2V 2.5 V 3V Conclusion C:\PCC\Eltry251\Labs\ Page 4 of 4 VRMS (V)