Oscilloscopes - ResearchGate
advertisement

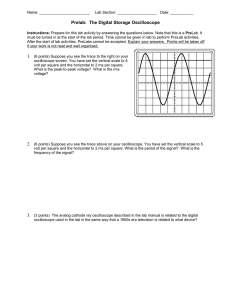
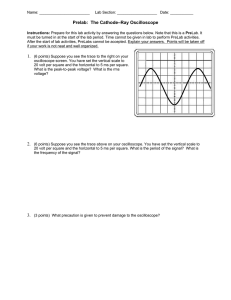
Introduction • What is an oscilloscope? 1 Introduction A graph-displaying device of electrical signal X axis: Time Y axis: Voltage Z axis: Intensity or brightness 2 Introduction Information given by oscilloscopes Time and voltage Frequency and phase DC and AC components Spectral analysis Rise and fall time Mathematical analysis 3 Control panel of an oscilloscope Vertical Section Horizontal Section Trigger Section 4 Basic setting Vertical system Horizontal system attenuation or amplification of signal (volts/div) The Time base (sec/div) Trigger system To stabilize a repeating signal and to trigger on a single event 5 Analog oscilloscope Real-time display of signals Block diagram Sweep generator and vertical amplifier Earthquake recorder 6 Digital oscilloscope Capture and view events Digital storage oscilloscope (DSO) 7 Digital oscilloscope (contd.) Sampling Interpolation 8 Advantage of Digital Scope Trend towards digital. Easy to use. One-shot measurement Recoding Triggering Data reuse Connectivity 9 Probes Components 10 Probes High quality connector High impedance (10M) 50 for high frequency measurement 11 Passive probe 10 attenuation Good for low circuit loading Suitable to high frequency signal Difficult to measure less than 10mV signals 1 attenuation Good for small signals Introducing more interference 12 Active probe Signal conditioning ⇒ oscilloscope Require power source Good for high speed digital signals over 100MHz clock frequency 13