PHY122
advertisement

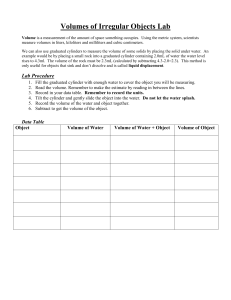
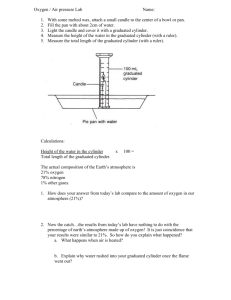
PHY122 Lab # 1 Making Calculations NAME ____________________ Lab Partners: Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to practice manipulating data using the proper rules of mathematics, as well as to practice using various measuring instruments. Apparatus triple beam balance vernier caliper 1 graduated cylinder (100 ml or 250 ml) 1 overflow tank with capture bucket 3 different size cylinders Procedure for Part A 1) Obtain the materials listed in the apparatus section of this lab. 2) Measure the diameter of the first object and record it in the data table provided. 3) Calculate and record the surface area of the base of the first cylinder. 4) Measure and record the height of the first cylinder. 5) Repeat steps 2 to 4 using the second and third cylinders. Note: all measurements are to be made using the most precise measuring instrument capable of making that measurement and are to be recorded to show the full precision. DATA TABLE Object Number Diameter of Base Area Of Base Height Of Cylinder First Cylinder Second Cylinder Third Cylinder (Make sure to indicate the units used in the measurements.) Procedure for Part B 1) Measure and record the mass of the graduated cylinder. The mass of the graduated cylinder is __________________. 2) Fill with water to the 10 ml level. Measure and record the mass of the graduated cylinder and water. The combined mass of the graduated cylinder and water is ________________. 3) Calculate the mass of the water in the graduated cylinder. The mass of 10 ml of water is _________________. 4) Fill with water to the 50 ml level. Measure and record the mass of the graduated cylinder and water. The combined mass of the graduated cylinder and water is ________________. Total Volume 5) Calculate the mass of the water in the graduated cylinder. The mass of 50 ml of water is _________________. 6) Fill with water to the 100 ml level. Measure and record the mass of the graduated cylinder and water. The combined mass of the graduated cylinder and water is ________________. 7) Calculate the mass of the water in the graduated cylinder. The mass of 100 ml of water is _________________. Based upon your measurements for the mass of 100 ml of water, what would you say that the mass of 1ml of water is __________________? Procedure Part C 1) Place the capture bucket next to the overflow tank so that any water that comes out of the tube on the side of the overflow tank will fall into the capture bucket. Note: there should be a small space between the overflow tank and the capture bucket so that the bucket can be removed without disturbing the overflow tank. 2) Using the graduated cylinder to “top it off”, fill the overflow tank up until the water starts coming out of the overflow tube. Wait for it to stop coming out of the tube. Note: You must be careful to make sure that the table is not disturbed. The waves would cause more water to leave the tank than it should. 3) Pour the water inside the capture bucket out and then measure and record the mass of the “empty” capture bucket at this point. (Note: any water inside the capture bucket at this point will not really matter. The mass of the “empty” capture bucket is ___________________. 4) Slowly submerge the largest size cylinder used in part A into the overflow tank while capturing all of the water in the capture bucket. (Lower the cylinder to the bottom of the tank with a piece of string and let it rest on the bottom of the tank. You tend to get motion and “ripples” on the surface if you try to hold the cylinder off the bottom of the tank, but below the surface of the water.) 5) Measure the mass of the capture bucket again. Record the mass below. (Note: This will give you the mass of the capture bucket plus the mass of the water inside it.) The new mass of the capture bucket and water is ___________________. 6) Using the change in mass of the capture bucket, determine the volume of the object lowered in to the tank. The apparent volume based upon part C is _________________. The volume that was calculated in part A was _________________. 7) How close are these two volumes obtained for this large cylinder? (Remember… any time I ask you how “close” two numbers are, you need to calculate the relative difference.) Questions for Lab # 1 Making Calculations Using the method for “comparison” discussed in class, which pair of numbers is closer. First compare Then compare 870 to 850 94 to 89 Using the proper rules of mathematics, what should you say that you get when you perform the following calculations: 2) Add a length of 1.73 cm to 19.2 cm. 3) Subtract 7.2 mm from 9.1 cm. 4) Multiply 25.8 cm by 2.3 cm.