Quick Guide to Literacy & the Work Sample
advertisement

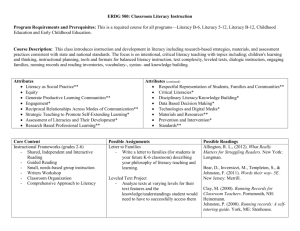
Quick Guide to Literacy & the Work Sample OAR 584-017-0185 requires the work sample give “purposeful attention to literacy instruction based upon content requirements, appropriate authorization level and student needs in at least one subject.” Literacy includes acts of listening, speaking, reading, and writing; listed here are only strategies for some reading and writing events. (See Oregon Standards and the Common Core State Standards for additional descriptions & guidance). Reading: Before Reading: Set purposes for reading Activate prior knowledge Develop questions Make predictions During Reading: Sample text Visualize Hypothesize Confirm/alter predictions Determine what’s important Use five senses Ask questions Monitor comprehension Possible Strategies to Use: Quick Guide to Literacy in the Work Sample D.K. Phillips, M.L. Larson & F. Ross 8.22.11 Front load vocabulary Think Aloud Brainstorming KWL Anticipation Guide Dramatic Role Play Watch a video clip Guided Reading Shared Reading Storytelling Post-it Notes Coding Text Bookmark Double-Entry Journal Sketching/Diagramming/Mapping/Clustering It says/I say/And so Say Something (partner reading w/designated stops & questions) QAR Quickwrite/sketch Text Guide Sheet Grand Conversations Reciprocal Teaching/Reciprocal Questioning Reading Response Logs Sketch-to-Stretch Quickwrite/Quickdraw Learning Log SQ4R List/Group/Label Key Vocabulary Word Sort Word Wall Directed Reading-Thinking Activity Venn Diagram/Character Comparison Word Meaning Graphic Organizer Vocabulary Tree List/Group/Label Key Vocabulary Alphaboxes Word Walls Character Web Character Trait and Analysis Character Grid Character Comparison Cubing 1 After Reading: Recall/Retell Evaluate Discuss Reread Apply Read More Retelling Dramatic Role Play/Reader’s Theater Script Sketching/Diagramming/mapping (clustering) Text It says/I say/And so Say Something (partner reading w/designated stops & questions) Exit slips KWL Dialogue Journals Learning Logs SQ3R Venn Diagram Quickwrite/draw Word Meaning Graphic Organizer Vocabulary Tree List/Group/Label Key Vocabulary Comprehension Constructor with Connections Guide Proficient Readers Use: Comprehension strategies to make sense of text: Synthesize Predict Infer Activate schema (make text-to-life connections; text-to-text connections; text-to-world connections) Visualize Determine what’s important Ask questions as they read Analyze Evaluate Quick Guide to Literacy in the Work Sample D.K. Phillips, M.L. Larson & F. Ross 8.22.11 Text Guide Sheet Reading Response Logs Highlight & Revisit Cubing Data Charts Directed ReadingThinking Activity Word Sorts/Word Walls Alphaboxes Found Poetry Make Your Own Test Open Mind Portrait Character Web Character Trait and Analysis Character Grid Character Comparison R.A.F.T. Possible Strategies to Use: Model one strategy at a time. Then allow students to practice using the strategy during interactive read aloud, shared reading, guided reading, or a reading conference. 2 Fix-up strategies to make sense of unknown words in text: Use pictures clues Skip a word, read on, go back and check Look at the first letter Chunk the word Model one fix-up strategy at a time during a read aloud. Then allow students to practice using the strategy during shared reading, partner reading, guided reading, independent reading or a reading conference. Fluency to make sense of text: Rate Pace Flow Reader’s Theater Choral Reading Shared Reading (Poetry, Big Books, Raps, Songs) Plays Literary Elements to make sense of literary texts: Characters Plot o Exposition o Rising Action o Climax o Falling Action o Resolution Setting Theme Point of View Perspective Style and language Illustrations Design Style Quick Guide to Literacy in the Work Sample D.K. Phillips, M.L. Larson & F. Ross 8.22.11 Use a read aloud text to highlight an element. Then allow students to practice finding the elements during shared reading, partner reading, guided reading, independent reading or reading conferences. Use graphic organizers for characters, plot and setting. 3 Literary Devices to make sense of literary texts: Alliteration Allusion Ambiguity Analogy Aphorism Atmosphere Caricature Dialect Exaggeration Flashback Flash-Forward Foreshadowing Hyperbole Imagery Inference Internal Rhyme Irony Metaphor Onomatopoeia Paradox Parallel Story Parody Personification Poetic Justice Point-of-view Rhyme Rhyme Scheme Satire Simile Stereotype/Reverse Stereotype Symbol Theme Tone Understatement Use a read aloud text to highlight a literary device. Then allow students to practice finding literary devices during shared reading, partner reading, guided reading, independent reading or reading conferences. Use post-it notes to mark passages with a literary device. Use a read aloud or shared reading to highlight text structures. Use graphic organizers before, during, and after reading to scaffold the structure of informational text. Allow students to use graphic organizers during guided reading, partner reading, independent reading and reading conferences to organize information from their text. Text Structures to make sense of informational text: Cause and effect Timeline/Temporal /Chronological Sequences Compare/Contrast Problem and Solution Description/Web Quick Guide to Literacy in the Work Sample D.K. Phillips, M.L. Larson & F. Ross 8.22.11 4 Quick Guide to Literacy in the Work Sample D.K. Phillips, M.L. Larson & F. Ross 8.22.11 5 Text Features to make sense of informational text: Print Features Font Bold & Colored print Bullets Titles Headings & Subheadings Italics Labels Captions Illustrations Photographs Drawings Graphic Aids Diagrams Sketches Graphs Figures Maps Charts Tables Overlays Organizational Aids Table of Contents Index Glossary Pronunciation Guide Appendix Stages of Writing Drafting: Collaborative text writing 1st Draft: Quick writing for self (not an audience) Get the ideas down quickly Content Revisions & Continued Drafting: Revise the piece for content Infuse with additional resources, quotes, references, citations (non-fiction) Infuse with narrative structures & techniques Conference with others (peers & teacher) to determine effectiveness of writing Organize according to desired format/structure Work with word choice Quick Guide to Literacy in the Work Sample D.K. Phillips, M.L. Larson & F. Ross 8.22.11 Point out text features during read aloud and shared reading. Think aloud how a reader might use these text features to make sense of text. Allow students time to practice with a partner, in groups, and independently identifying and using text features. Possible Strategies to Use: Provide environment for draft writing Make sure proper writing tools are available for varying abilities Encourage “skip a line” Leads Sequence flashbacks Dialogue Alliterations Endings References & citations Descriptions Finding quality sources (internet & hard Word choice references) Sentence structure Organizational Character development structures Point of view Reasons for writing Literary opposites Active verbs Voice Setting Irony Symbolism 6 Stages of Writing Prewriting: Discover a meaningful purpose Activate interests Find possibilities Editing for Conventions Correct for grade appropriate spelling, punctuation, and grammar Conference with others (peers & teacher) All work made public must be correct. Publishing Publish work for an audience greater than the teacher Celebrate work Quick Guide to Literacy in the Work Sample D.K. Phillips, M.L. Larson & F. Ross 8.22.11 Possible Strategies to Use: Think Aloud Brainstorming Quick Writes Draw/Sketch Cluster/Web Mini-Lessons Storyboards Photos/Pictures Find ideas for writing in reading activities Read multiple genres of text Provide mini-lessons on such topics as: Difficult spelling words How to use a word wall Sentence structure Uses of punctuation Verb agreement Homonyms, antonyms How to use: thesaurus, instant spellers, dictionaries & on-line resources (including checking word processors & spelling) Address why correctness matters Individualized conventions lists & goals Provide varied opportunities for meaningful publishing (class magazines, school literary magazine, school yearbook & newspaper, magazine, posters, classroom bulletin board, displays at public events, petitions, local newspaper, etc) Explore electronic options 7 Literacy and English Language Learners Possible Strategies Quick Guide to Literacy in the Work Sample D.K. Phillips, M.L. Larson & F. Ross 8.22.11 Collaborative text writing Dialogue journals Frontload vocabulary, grammatical structures through songs, chants & poems Graphic organizers Guided reading Jigsaw and paired reading Language experience approach Learning logs Mimic writing Shared reading Story-telling and retelling Using bilingual text Word study Guided writing Write labels, captions, lists Mimic writing Write stories based on photographs and videos 8 References Atwell, N. (1998). In the middle: New understandings about writing, reading, and learning (2nd ed.). Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Billmeyer, R. & Barton, M.L. (2002). Teaching reading in the content areas: If not me, then who? (2nd ed.). Aurora, CO: Mid-continent Regional Educational Laboratory. Bromley, K., Irwin-De Vitis, L. & Modlo, M. (1995). Graphic organizers: Visual strategies for active learning. New York: Scholastic. Burke, J. (2003). The English teacher’s companion: A complete guide to classroom, curriculum, and the profession. (2nd ed.). Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann Cloud, N., Genesee, F. & Hamayan, E. (2009). Literacy instruction for English language learners. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Daniels, H., & Zemelman, S. (2004). Subjects matter: Every teacher's guide to content-area reading. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Fountas, I. C., & Pinnell, G.S. (2001). Guiding readers and writers grades 3-6: Teaching comprehension, genre, and content literacy. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Hall, S. (1994). Using picture storybooks to teach literary devices: Recommended books for children and young adults Vol. II. Phoenix, AZ: Oryx Press. Keene, E. O., & Zimmermann, S. (1997). Mosaic of thought: Teaching comprehension in a reader's workshop. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Portalupi, J. & Fletcher, R. (2001). Nonfiction craft lessons: Teaching information writing K-8. Portland, ME: Stenhouse. Routman, R. (2003). Reading essentials: The specifics you need to teach reading well. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Routman, R. (2005). Writing essentials: Raising expectations and results while simplifying teaching. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Tompkins, G. E. (1998). 50 literacy strategies: Step by step. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill. Tovani, C. (2004). Do I really have to teach reading? Content, comprehension, grades 6 - 12.Portland, Maine: Stenhouse. Additional Literacy References Allen, J. (2004). Tools for teaching content literacy. Portland, ME: Stenhouse. Altieri, J. (2011). Content counts! Developing disciplinary literacy skills, K-6. Newark, DE: International Reading Association. Quick Guide to Literacy in the Work Sample D.K. Phillips, M.L. Larson & F. Ross 8.22.11 9 Atwell, N. (2002). Lessons that change writers. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Fletcher, R. & Portalupi, J. (1998). Craft lessons: Teaching writing K-8. Portland ME: Stenhouse. Fountas, I. C., & Pinnell, G.S. (2006). Teaching for comprehending and fluency: Thinking, talking, and writing about reading, K-8. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Grant, M. & Fisher, D. (2010). Reading and writing in science: Tools to develop disciplinary literacy. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin. Heard, G. (2002). The revision toolbox: Teaching techniques that work. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Hoyt, L. (1999). Revisit, reflect, retell: Strategies for improving reading comprehension. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Hoyt, L. (2000). Snapshots: Literacy minilessons up close. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Kovacs, E. (1994). Writing across cultures: A handbook on writing poetry and lyrical prose. Hillsboro, OR: Blue Heron. Manzo, Manzo, & Thomas, (2004). Content area literacy (4th ed.). San Francisco: Wiley/Jossey-Bass. McCarrier, A., Pinnell, G. S., & Fountas, I. C. (2000). Interactive writing: How language & literacy come together, k-12. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Portland State University. (2005). A guide to Oregon’s new reading standards, grades 6-CIM. Portland, OR: Portland State University. Portland State University. (2005). A guide to Oregon’s new reading standards, grades K-6. Portland, OR: Portland State University Routman, R. (2001). Conversations: Strategies for teaching, learning, and evaluating. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Ruddell, M.R. (2005). Teaching content reading and writing (4th ed.). Hoboken, NH: Wiley. Strong, W. (2006). Write for insight: Empowering content area learning grades 6-12. Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon. Tama, C. & McClain, A.. (2001). Guiding reading and writing in the content areas: Practical strategies (2nd ed.). Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt Publishers. Urquhart & McIver. (2005). Teaching writing in the content areas. Aurora, CO: ASCD Vacca, R. & Vacca, J. (2005). Content area reading (8th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon. Zemelman, S., & Harvey, D. (1988). A community of writers: Teaching writing in the junior and senior high school. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann. Quick Guide to Literacy in the Work Sample D.K. Phillips, M.L. Larson & F. Ross 8.22.11 10