CM3004 Peptides
advertisement
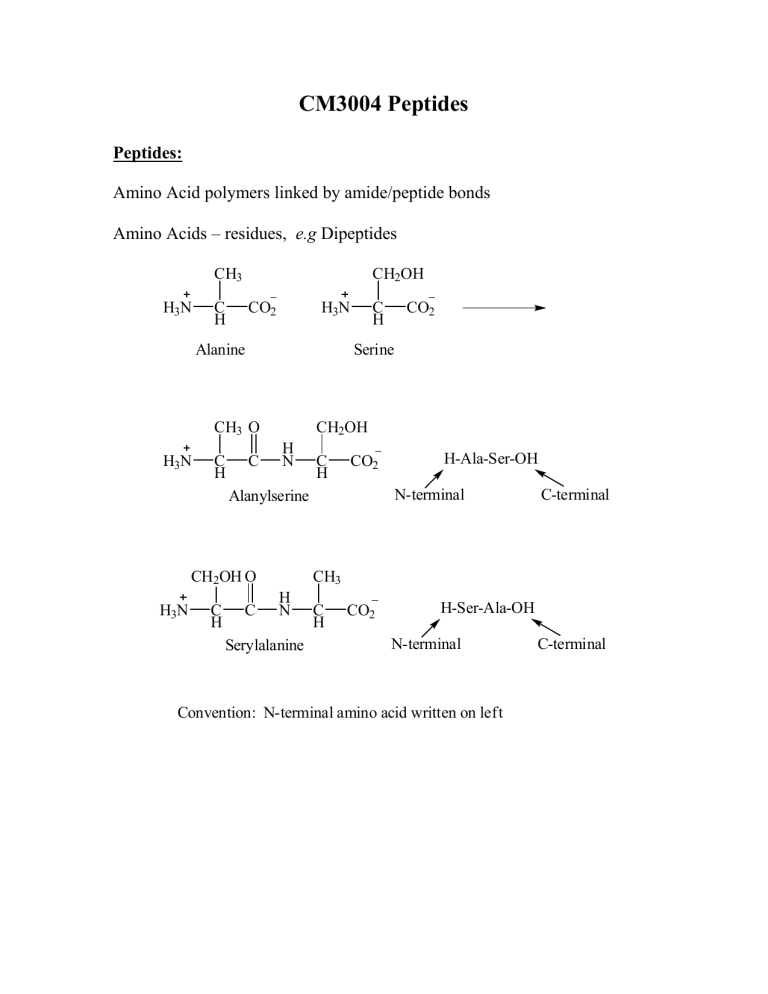
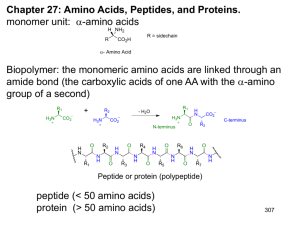
CM3004 Peptides Peptides: Amino Acid polymers linked by amide/peptide bonds Amino Acids – residues, e.g Dipeptides CH3 H3N CH2OH C H CO2 H3N Alanine C H C CH2OH H N C H CO2 CH2OH O C H C H-Ala-Ser-OH N-terminal Alanylserine H3N CO2 Serine CH3 O H3N C H C-terminal CH3 H N Serylalanine C H CO2 H-Ser-Ala-OH N-terminal Convention: N-terminal amino acid written on left C-terminal Strategy for Polypeptide Synthesis R2 R1 P P H N H N C H CO2H + H2N R1 O R2 C H C H N C H CO2P selective deprotection C H CO2P P H N R1 O C H C R2 H N C H CO2H R3 H2N P H N R1 O C H C H N R2 O C H C C H CO2P R3 H N C H CO2P selective deprotection P H N R1 O C H C H N R2 O C H C R3 H N C H CO2H Sequence of protection, coupling, selective deprotection, coupling etc. is very tedious! Synthesis of Peptides Selective Coupling Ph O O PhH2C O C H N C H + CO2H H2N Cbz-L-Val-OH C H C OtBu H-L-Phe-OtBu N-Terminal Protected C-Terminal Protected Protecting groups must be: (1) stable to amide formation conditions (2) removable without cleaving amide bond Coupling agent used: Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) N C N DCC Ph O PhH2C O C O H N C H C + O H N C H N Dicyclohexylurea H N C H CO2tBu Ph O PhH2C O O H N C C H C H N C H CO2H C H HBr CO2tBu AcOH Ph O H2N C H Br H N C H-Val-Phe-OH Mechanism: R R N C R1CO + N N 2H C N R R H O O H R1 R N C N H R O R2 O R H2N 1 C H CO2tBu O-Acyl isourea activated intermediate R2 O R1 C H N C H O CO2tBu + R H N C H N R Peptide bond- normal amide bond. There is restricted rotation due to a certain degree of double bond character due to resonance delocalization. Restricted rotation H N H N CO2 H3N H3N O O Also N less basic/nucleophilic than in free amine Peptide Backbone Reactions - Reactions of polyamide chain e.g. Racemisation – Azlactone formation Peptide side chain reactions e.g. CO2H, NH2 – usual reactivity When peptides contains cystine residues C HC O H2 C SH HS O H2 C NH C Mild oxidation CH NH Reduction (Reversible) Thiols C HC O H2 C S S NH O H2 C C CH NH Disulfide Cystine Disulf ide CO2 Can link 2 peptide chains or form a loop in a chain: SH HS S S Important in Protein Structure Peptide Analysis (i) Need to know which amino acid is present, how much of each and the sequence Amino Acid analysis: Hydrolyse the peptide – gives an amino acid mixture which can be passed through an ion exchange column. Use pH controlled buffers as the eluent. Each amino acid has a fixed elution rate. Abs Thr Ala Asp Glu Pro Identifies AA present t Very sensitive - Detects down to 10-9 mol A.A. Proline - Different adduct, yellow - V. weak and broad peak Proline is a 2o amino acid and reacts with only one molecule of ninhydrin to f orm the f ollowing products: O O N O Yellow N CH O Very weak broad band CH Detection - Reaction with Ninhydrin O O OH O OH O O R Exists as hydrate H2N OH O O R CH + CO2 + N O Only N remains f rom AA Get same product f rom all AA except Proline Mixture Ion-exchange column AA - UV/vis detector Ninhydrin - O Purple C H CO2H Mechanism O O OH O OH O O R H2N CO2H C H O O R N N C R O C C O H H O O H+ + CO2 O O NH2 Imine hydrolysis N + RCHO CHR H O O O OH O O O N N - H O Purple colour O O Exists mainly as enol due to extended conjugation (ii) Sanger Method - Identifies N-terminal amino acid of a polypeptide NO2 O2N 2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene - susceptible to nucleophilic substitution with strong nucleophiles e.g amines F R1 H2N C H NO2 H N O 2N R1 O C H C H N R2 O C H C H N R3 O C H C Substitution at N-terminal only NO2 Hydrolysis O 2N H N R1 O C H C OH + Amino acid mixture Only the N terminal amino acid is labelled with dinitrophenyl group (DNP) - Identitf y labelled AA by HPLC or other techniques (ii) Edman Degradation Again from N-terminal but more usef ul as it can be repeated sequentially - peptide sequence from N-terminal Uses phenyl isothiocyanate PhN=C=S S H+ H N C H2N N Rest of peptide O Ph O O NH PhHN Ph N H O O S N S N H N H Ph NH S S PhHN N H Phenylthiohydantoin Identify by chromatography N H + Shorter Peptide Sequence Repeat Edman Sequence – 2nd AA etc. This way we can sequence the peptide from N-terminal (iv) Analysis from C-terminal - Enzyme carboxypeptidase cleaves from C-terminal P H N R1 O C H C H N R2 O C H C R3 H N C H CO2H Enzyme cleaves here P H N R1 O C H C H N R2 O C H C R3 H3N OH C H CO2 Enzyme cleaves here next Measure the rate of appearance of amino acid in solution - information on peptide sequence (v) Proteases - Specific cleavage at certain residues E.g. Serine Proteases - Breaks peptides into smaller fragments (vi) Selective cleavage at methionine using cyanogen bromide BrCN O H N Methionine residue H C C H N R2 O C H C H N BrCN O O SCH3 + CH3SCN + HN R2 O C H C Homoserine lactone