Name
advertisement

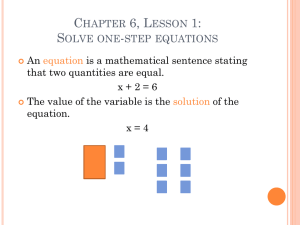
Name: __________________________________________ ENV SCI Date: _______ Ecosystems & Biogeochemical Systems Review Packet Part 1 – Match each of the following _____ 1. Ammonification A. One organism feeds on and usually lives on or in another, usually larger, organism _____ 2. Coevolution B. When two species use the same resource _____ 3. Combustion C. Carbon dioxide is a by-product of this biological reaction _____ 4. Commensalism D. Defensive chemicals used by plants _____ 5. Competition E. A relationship between two species in which both species benefit _____ 6. Denitrification F. One organism feeding on another _____ 7. Erosion G. This process releases carbon from fossil fuels _____ 8. Mutualism H. Two or more species living together in a close, longterm relationship _____ 9. Parasitism I. Carbon becomes available to other organisms through this process acting on limestone _____ 10. Predation J. Back and forth evolutionary changes between members of an ecosystem _____ 11. Respiration K. This process returns nitrogen gas to the atmosphere _____ 12. Secondary Compounds L. This process converts nitrogen into a useable form for organisms _____ 13. Symbiosis M. A relationship in which one species benefits and the other neither benefits nor is harmed Part 2 – Choose the best possible answer _____ 14. This occurs when water evaporates from the leaves of plants. A. Evaporation B. Condensation C. Precipitation D. Transpiration _____ 15. What is it called when water seeps into the soil and stays underground? A. Precipitation B. Surface Water C. Ground Water D. Body of Water _____ 16. A cycle, such as the carbon cycle, that contains biological, geological, and chemical aspects of an ecosystem is known as which of the following? A. Biogeochemical B. Ecological C. Biology D. Chemistry _____ 17. What is the study of interactions of living organisms with one another and with their physical environment? A. Biology B. Chemistry C. Ecology D. Environmental Science _____ 18. Which two organisms exist in a predator-prey relationship? A. Bear & Fish B. Tree & Grass C. Male & Female Penguins D. Mosquito & Ladybug _____ 19. What is the exclusion of one species by another due to competition? A. Fundamental Niche B. Competitive Exclusion C. Biological Connectedness D. Realized Niche _____ 20. If it has been proven that a barnacle can live in shallow and deep water, but is restricted to shallow water when in competition with a barnacle that can only survive in deep water, the shallow water is the barnacle’s niche. A. Fundamental Niche B. Competitive Exclusion C. Biological Connectedness D. Realized Niche _____ 21. Where is most of Earth’s surface water contained? A. Lake Ecosystems B. River Ecosystems C. Reservoir Ecosystems D. Oceanic Ecosystems _____ 22. Which of the following demonstrates a parasitic relationship? A. Tick on a human B. Sea anemone and clownfish C. Ants and aphids D. Lion eating a zebra _____ 23. Which of the following demonstrates a mutualistic relationship? A. Tick on a human B. Sea anemone and clownfish C. Ants and aphids D. Lion eating a zebra _____ 24. Which of the following demonstrates a commensal relationship? A. Tick on a human B. Sea anemone and clownfish C. Ants and aphids D. Lion eating a zebra _____ 25. Which of the following demonstrates a predator-prey relationship? A. Tick on a human B. Sea anemone and clownfish C. Ants and aphids D. Lion eating a zebra Part 3 – Diagrams Use your book to help you complete the following diagrams, which can be found in Chapter 16 and Chapter 17 26. Label the trophic levels of the following food chain and also label the type of producers and consumers. 27. Label the following parts of the water cycle: Transpiration, Precipitation, Runoff, Percolation, Ground Water, Water Vapor, Evaporation (x2) 28. Label the following parts of the carbon cycle: Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide, Death & Decomposition, Cellular Respiration, Fossil Fuels, Combustion, Photosynthesis, Limestone 29. Label the following parts of the nitrogen cycle: Atmospheric Nitrogen, Denitrification, Assimilation, Nitrification, Ammonification, Nitrogen Fixation (x2) Part 4 – Short answer Explain why scientists believe that most animals would become extinct if all plants died. Compare how succession would occur after a forest fire versus how it would occur if a glacier receded for the first time. Why can nutrients cycle but energy cannot? Is the relationship between a plant and its pollinator mutualistic? Why or why not? A scientist finds no evidence that species in a community are competing and concludes that competition never played a role in the development of this community. Is this conclusion valid? Why or why not?