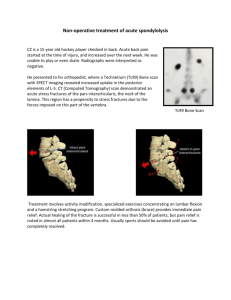
EBM Guidelines 2473
advertisement

EBM Guidelines 2473 Preface: What is new in EBM Guidelines 1/2004 Preface: What is Evidence-Based Medicine Guidelines 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. Dermatology 79 Gastroenterology 82 Haematology 42 Infectious diseases 148 Info 5 Internal medicine 349 Microbiology 11 Neoplastic diseases 44 Nephrology 27 Neurology 125 Obstetrics 22 Ophthalmology 45 Otorhinolaryngology 97 Paediatrics 142 Pharmacology 49 Pulmonary diseases 68 Rheumatology 59 Surgery 212 Traumatology 66 Bacteriology 3 Virology 3 Anaesthesiology 18 Cardiology 91 Clinical physiology 14 Endocrinology 79 Geriatrics 22 Nutritional medicine 18 Radiology 21 Thoracic surgery 8 Genetics 12 Occupational medicine 12 Orthopaedics 57 Physical medicine 53 Plastic surgery 14 Urology 37 Vascular surgery 11 Allergology 33 Occupational health service 20 Psychiatry 78 Dental medicine 20 Maxillofacial surgery 8 Environmental health service 5 Clinical chemistry 4 Gynaecology 47 Sports medicine 15 Alcohol-related diseases 8 Administration 5 Radiation therapy 1 Neurosurgery 17 Clinical neurophysiology 7 Forensic medicine 5 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. Paediatric psychiatry 29 Paediatric surgery 1 Phoniatrics 3 School health service 2 Adolescent psychiatry 5 Paediatric neurology 2 Forensic Psychiatry 1 Audiology 3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Malocclusion and headache Complications following tooth extraction and oral surgery Dermoid cyst Amyloidosis Measles Balanitis in a child Redness or swelling of a child-s face or eyelids - cellulitis Dermatology 79 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. Erysipeloid Lyme borreliosis (LB) Herpes zoster Schistosomal dermatitis Guidelines for antimicrobial therapy Conservative treatment of leg ulcers Pinch grafting of the skin Sarcoidosis Cheilitis Burning mouth and glossalgia Skin diseases and the mouth Pruritus ani Balanitis, balanoposthitis, and paraphimosis in the adult Syphilis One-glance diagnosis of dermatoses Itch Hair loss Diagnostic tests in dermatology Indications for and techniques of skin biopsy Hand dermatitis Inguinal dermatitis Leg dermatitis Allergic dermatitis Toxic eczema Seborrhoeic dermatitis Nummular eczema Herpesvirus skin infections Erysipelas Necrotising fasciitis and gas gangrene Impetigo and other pyoderma Skin abscess and folliculitis 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. Warts (verruca vulgaris) Molluscum contagiosum Scabies Head lice and pubic lice Insect bites and stings Dermatomycoses Pityriasis versicolor Acne Rosacea Perioral dermatitis Chronic bullous diseases (dermatitis herpetiformis, pemphigoid) Psoriasis Pityriasis rosea Lichen planus Hives (urticaria) Erythema nodosum Solar keratosis Skin cancer Keloid Ingrowing toenail: avulsion of the nail edge and phenolization Protecting the skin from freezing, sun, and drying Drugs and light sensitivity Prevention and treatment of pressure sores Investigation of atopy Hypersensitivity to drugs Food additives and hypersensitivity Latex allergy Food hypersensitivity and allergy Cow's milk allergy Allergen-specific immunotherapy Palliative treatment of cancer Psoriatic arthropathy Scleroderma Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) Pharmacological glucocorticoid treatment APECED (autoimmune polyendocrinopathy -candidiasis -ectodermal dystrophy) Allergic diseases in the child health clinic Fever and rash in a child Chickenpox Rubella Exanthema subitum Nappy rash Itch in a child Atopic dermatitis in children: clinical picture and diagnosis Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children Henoch-Schönlein purpura Otitis externa External tumours of the nose Gastroenterology 82 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. Yersiniosis Echinococcosis Tapeworm disease Ascariasis Pinworm (enterobiasis) Giardiasis Cryptosporidiosis Amoebiasis Prevention and treatment of infections in splenectomized patients Guidelines for antimicrobial therapy Prevention and first aid treatment of traveller's diarrhoea Involuntary weight loss Nausea and vomiting Dysphagia Haematemesis Faecal incontinence Obstipation in the adult Abdominal pain and swelling-the irritable bowel Acute abdomen in the adult Syndroma pelvis spastica Organizing endoscopy in primary care Gastroscopy Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy Heartburn; reflux oesophagitis Dyspepsia Treatment of dyspepsia, peptic ulcer and helicobacter infection Safe use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Orientation on diarrhoea in adult patients Clinical features and treatment of diarrhoea in adults according to aetiology Antibiotic diarrhoea Food poisoning Prolonged diarrhoea in the adult Examining a patient with rectal bleeding Diseases causing rectal bleeding Melena Anal pain Pruritus ani Haemorrhoids Anal fissure Anal abscess Colorectal cancer Prevention and screening of colorectal cancer Postoperative follow-up of colorectal cancer Long-term follow-up of patients at risk of colorectal cancer Chronic inflammatory bowel disease Intestinal obstruction, paralytic ileus, and pseudo-obstruction Diverticulitis and diverticulosis Lactose intolerance Coeliac disease Hernias Postoperative gastric problems The icteric patient Gilbert's syndrome Assessing a patient with an abnormal liver function test result 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) Viral hepatitis Chronic hepatitis Cirrhosis of the liver Primary biliary cirrhosis Cholelithiasis Sclerosing cholangitis Acute pancreatitis Recurrent or chronic pancreatitis Pancreatic insufficiency Carcinoma of the pancreas Cow's milk allergy Hereditary angioedema (HAE) and ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema Palliative treatment of cancer Groin pain Reactive arthritis and rheumatic fever Acute porphyria Lower abdominal pain of gynaecological origin Investigating a child with abdominal symptoms Acute abdominal symptoms in children Recurrent abdominal pain in children Diarrhoea and vomiting in children Foreign body in the gastrointestinal tract of a child Henoch-Schönlein purpura Enteroarthritis, borrelia and other acute forms of arthritis in children Intra-abdominal injuries and bleeding in children Recurring psychogenic stomach-aches and headaches among children Relief from constipation-instructions for the patient Haematology 42 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Prevention and treatment of infections in splenectomized patients Deep venous thrombosis Thrombophilia (inherited) Oral anticoagulation therapy Bone marrow examination Blood films Elevated ESR (hypersedimentation) Leucocytosis Leucocytopenia Eosinophilia Erythrocytosis Macrocytosis (increased MCV) Thrombocytosis Thrombocytopenia Assessment of anaemia in adults Iron deficiency anaemia Anaemia of pregnancy Secondary anaemia Megaloblastic anaemia Haemolytic anaemia Easy bruising, petechiae and ecchymoses 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. Assessment and treatment of a patient with bleeding diathesis Haemophilia and von Willebrand's disease Tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: general guidelines Chronic myelogenous leukaemia (CML) Polycythaemia vera (PV) Myelofibrosis (MF) Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) Lymphomas Acute leukaemia in adults Multiple myeloma (MM) Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia (WM) Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) Essential thrombocythaemia (ET) Indications for and techniques of red cell transfusion Transfusion reactions Anaemia in athletes Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) Haemochromatosis Fever and rash in a child Anaemia in children Bruises and purpura in children: ITP and its differential diagnosis Infectious diseases 148 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. Prolonged fever in the adult Yersiniosis Tularaemia Erysipeloid Listeriosis Tetanus Diphtheria Gas gangrene Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Lyme borreliosis (LB) Influenza Herpes zoster Mononucleosis Nephropathia epidemica (NE) Pogosta disease HIV infection Suspicion of rabies Schistosomal dermatitis Echinococcosis Tapeworm disease Trichinosis Ascariasis Pinworm (enterobiasis) Giardiasis Cryptosporidiosis Toxoplasmosis Amoebiasis Septicaemia Infections in immunosuppressed and cancer patients 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. Prevention and treatment of infections in splenectomized patients Ecology of the use of antimicrobial drugs Guidelines for antimicrobial therapy Streptococcal epidemics Traveller's infection prophylaxis Diagnosis and prevention of malaria in travellers Prevention and first aid treatment of traveller's diarrhoea Fever in returning traveller Bacterial diseases in warm climates Viral diseases in warm climates Parasitic diseases of warm climate: protozoa and worms SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) Vaccinations Prevention of bacterial endocarditis Acute bronchitis Pneumonia Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections Exposure to tuberculous infection Diagnosing tuberculosis Antituberculous medication in ambulatory care Atypical mycobacterial infections Viral infections of the oral mucosa Oral fungal infections Orientation on diarrhoea in adult patients Clinical features and treatment of diarrhoea in adults according to aetiology Antibiotic diarrhoea Food poisoning Prolonged diarrhoea in the adult Anal abscess Viral hepatitis Treatment of urinary tract infection Acute prostatitis Chronic prostatitis Balanitis, balanoposthitis, and paraphimosis in the adult Chlamydial urethritis and cervicitis Gonorrhoea Syphilis Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection (Condyloma) Genital herpes Rare venereal diseases: chancres Erysipelas Necrotising fasciitis and gas gangrene Impetigo and other pyoderma Skin abscess and folliculitis Warts (verruca vulgaris) Molluscum contagiosum Scabies Head lice and pubic lice Dermatomycoses Erythema nodosum Elevated ESR (hypersedimentation) Leucocytopenia Bite wounds Bursitis (patella and elbow) 85. Early recognition of complications after joint replacement 86. Disease-specific symptoms and signs in patients with inflammatory 87. joint diseases 88. Reactive arthritis and rheumatic fever 89. Delirium in the elderly 90. Infections in old age 91. Mastitis 92. Vaginitis 93. Bartholinitis; Bartholin's duct abscess and cyst 94. Diagnosis and treatment of acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) 95. Antibiotics and pregnancy 96. Recurrent infections and immunodeficiencies 97. Febrile convulsions 98. Child with fever but no localizing symptoms 99. Treatment of fever in children 100. Fever and rash in a child 101. Tonsillitis and pharyngitis in children 102. Sinusitis in children 103. Wheezing in children 104. Treatment of obstructive bronchitis and acute asthma in children 105. Laryngitis in children 106. Epiglottitis in children and adults 107. Prolonged cough in children 108. Whooping cough 109. When should a child with a cough be treated with antibiotics? 110. Treatment of pneumonia in children 111. Indications for and interpretation of chest x-ray in a child with 112. symptoms of an infection 113. Oral candidiasis in children 114. Stomatitis in children 115. Prevention of otitis media in children 116. Otitis media in children: definition, epidemiology and diagnosis 117. Chickenpox 118. Rubella 119. Erythema infectiosum 120. Exanthema subitum 121. Meningitis in children 122. Encephalitis in children 123. Infections in immunocompromized children 124. Mumps 125. Discharging BCG scars in infants 126. Enlarged lymph nodes and other neck lumps in children 127. Itch in a child 128. Enteroarthritis, borrelia and other acute forms of arthritis in children 129. Kawasaki disease 130. Infection and central nervous system manifestation 131. Meningitis 132. Encephalitis 133. Brain abscess 134. Slow viral infections of the central nervous system 135. Poliomyelitis and post-polio syndrome 136. Upper respiratory tract infections in adults 137. Hoarseness, laryngitis and dysphonia 138. Sore throat and tonsillitis 139. Throat bacterial swab 140. 141. 142. 143. 144. 145. 146. 147. 148. 149. 150. 151. Drainage of a peritonsillar abscess Acute maxillary sinusitis Acute frontal sinusitis Chronic sinusitis Acute otitis media in adults Chronic otitis media Acute mastoiditis Health care for refugees arriving to Northern Europe Occupational exposure to viral agents Epidemics due to contaminated drinking water Acute bronchitis (instructions for the patient) Treatment of influenza-instructions for the patient Internal medicine 349 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. Prolonged fever in the adult Yersiniosis Tularaemia Erysipeloid Listeriosis Tetanus Diphtheria Gas gangrene Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Lyme borreliosis (LB) Influenza Herpes zoster Mononucleosis Nephropathia epidemica (NE) Pogosta disease HIV infection Suspicion of rabies Schistosomal dermatitis Echinococcosis Tapeworm disease Trichinosis Ascariasis Pinworm (enterobiasis) Giardiasis Cryptosporidiosis Toxoplasmosis Septicaemia Infections in immunosuppressed and cancer patients Prevention and treatment of infections in splenectomized patients Ecology of the use of antimicrobial drugs Guidelines for antimicrobial therapy Streptococcal epidemics Traveller's infection prophylaxis Diagnosis and prevention of malaria in travellers Prevention and first aid treatment of traveller's diarrhoea Bacterial diseases in warm climates Viral diseases in warm climates 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. Vaccinations Interpretation of adult ECG Ventricular hypertrophies (RVH, LVH) in ECG Bundle branch blocks in the ECG Ambulatory ECG monitoring Computerised ECG interpretation Echocardiography The most common acquired adult valvular heart diseases and associated murmurs Heart valve replacement: patient follow-up Hypertension: definition, prevalence and classification Risk factors for hypertension Diagnosis of and initial investigations for hypertension Thresholds for starting therapy and targets for treatment of hypertension Non-pharmacological therapy for hypertension Pharmacotherapy of hypertension Antihypertensive drug choice for different patient groups Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) in hypertensive patients Secondary hypertension Symptoms of arrhythmia and examination of an arrhythmia patient Syncope: causes and investigations Supraventricular ectopic beats Sinus tachycardia Supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) Ventricular ectopic beats Ventricular tachycardia Differential diagnosis of broad complex tachycardia Bradycardia Atrial fibrillation: drug treatment and electric cardioversion Indications and contraindications for anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation Sick sinus syndrome Cardiac pacemakers: follow-up of patients and surveillance of pacemaker function Differential diagnosis of chest pain Unstable angina pectoris Nitrate infusion in angina pectoris and myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction Thrombolytic therapy and PTCA in acute ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) Right ventricle infarction Coronary heart disease (CHD): symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Coronary angiography and indications for CABG or angioplasty Follow-up of a revascularized patient Acute pulmonary oedema CPAP treatment in pulmonary oedema Chronic heart failure Prevention of bacterial endocarditis Myocarditis Dilated cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Primary pulmonary hypertension Leg oedema Calf pain Doppler stethoscopy in diagnostics 93. Deep venous thrombosis 94. Thrombophilia (inherited) 95. Prevention of venous thrombosis 96. Pulmonary embolism (PE) 97. Oral anticoagulation therapy 98. Conservative treatment of leg ulcers 99. Intermittent compression for leg swelling 100. Ischaemic disease of the lower limb 101. Cholesterol embolization 102. Vibration syndrome (vibration-induced white fingers) 103. Aortic aneurysm and dissection 104. Prolonged cough in adults 105. Dyspnoea 106. Hyperventilation 107. Acute respiratory failure 108. Acute bronchitis 109. Pneumonia 110. Diagnosing tuberculosis 111. Antituberculous medication in ambulatory care 112. Atypical mycobacterial infections 113. Pulmonary fibrosis 114. Sarcoidosis 115. Pleural effusions -Thoracentesis 116. Bad breath 117. Involuntary weight loss 118. Nausea and vomiting 119. Motion sickness 120. Haematemesis 121. Faecal incontinence 122. Obstipation in the adult 123. Abdominal pain and swelling-the irritable bowel 124. Organizing endoscopy in primary care 125. Gastroscopy 126. Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy 127. Heartburn; reflux oesophagitis 128. Dyspepsia 129. Treatment of dyspepsia, peptic ulcer and helicobacter infection 130. Safe use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) 131. Orientation on diarrhoea in adult patients 132. Clinical features and treatment of diarrhoea in adults according to 133. aetiology 134. Antibiotic diarrhoea 135. Food poisoning 136. Prolonged diarrhoea in the adult 137. Examining a patient with rectal bleeding 138. Diseases causing rectal bleeding 139. Chronic inflammatory bowel disease 140. Lactose intolerance 141. Coeliac disease 142. The icteric patient 143. Gilbert's syndrome 144. Assessing a patient with an abnormal liver function test result 145. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) 146. Chronic hepatitis 147. Cirrhosis of the liver 148. 149. 150. 151. 152. 153. 154. 155. 156. 157. 158. 159. 160. 161. 162. 163. 164. 165. 166. 167. 168. 169. 170. 171. 172. 173. 174. 175. 176. 177. 178. 179. 180. 181. 182. 183. 184. 185. 186. 187. 188. 189. 190. 191. 192. 193. 194. 195. 196. 197. 198. 199. 200. 201. 202. Primary biliary cirrhosis Sclerosing cholangitis Acute pancreatitis Recurrent or chronic pancreatitis Pancreatic insufficiency Polyuria Elevated serum creatinine Proteinuria Sampling and investigating urine Treatment of urinary tract infection Acute renal failure Treatment of chronic renal failure Kidney transplantation Nephrotic syndrome Glomerulonephritis IgA nephropathy Renal cysts Rhabdomyolysis Haematuria Impotence Hypogonadism in the aging male Syphilis Itch Erysipelas Necrotising fasciitis and gas gangrene Erythema nodosum Prevention and treatment of pressure sores Anaphylaxis Hereditary angioedema (HAE) and ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema Bone marrow examination Blood films Elevated ESR (hypersedimentation) Leucocytosis Leucocytopenia Eosinophilia Erythrocytosis Macrocytosis (increased MCV) Thrombocytosis Thrombocytopenia Assessment of anaemia in adults Iron deficiency anaemia Anaemia of pregnancy Secondary anaemia Megaloblastic anaemia Haemolytic anaemia Easy bruising, petechiae and ecchymoses Assessment and treatment of a patient with bleeding diathesis Haemophilia and von Willebrand's disease Chronic myelogenous leukaemia (CML) Polycythaemia vera (PV) Myelofibrosis (MF) Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) Lymphomas Acute leukaemia in adults Multiple myeloma (MM) 203. 204. 205. 206. 207. 208. 209. 210. 211. 212. 213. 214. 215. 216. 217. 218. 219. 220. 221. 222. 223. 224. 225. 226. 227. 228. 229. 230. 231. 232. 233. 234. 235. 236. 237. 238. 239. 240. 241. 242. 243. 244. 245. 246. 247. 248. 249. 250. 251. 252. 253. 254. 255. 256. 257. Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia (WM) Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) Essential thrombocythaemia (ET) Indications for and techniques of red cell transfusion Transfusion reactions Palliative treatment of cancer Resuscitation Endotracheal intubation Prehospital emergency care Pulse oximetry Treatment of poisoning Drug poisoning Poisonings caused by inebriating substances (alcohols, drugs) Carbon monoxide poisoning Hypothermia Acute heat illnesses Physical activity in the prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of diseases Contraindications to physical exercise ECG in athletes Anaemia in athletes Groin pain Baker's cyst Bursitis (patella and elbow) Fibromyalgia Clinical examination of patients with joint inflammation in primary health care Diagnosis of joint inflammation in the adult Disease-specific symptoms and signs in patients with inflammatory joint diseases Raynaud's phenomenon and acrocyanosis Local corticosteroid injections in soft tissues and joints Investigation of synovial fluid Drug treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Follow-up of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatic surgery Psoriatic arthropathy Reactive arthritis and rheumatic fever Ankylosing spondylitis Scleroderma Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) Sjögren's syndrome The vasculitides Polymyalgia rheumatica Giant cell arteritis Gout Dietary treatment of gout Chondrocalcinosis (pseudogout) Aurothiomalate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Auranophin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Sulfasalazine in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Antimalarials in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Azathioprine in the treatment of rheumatic diseases 258. 259. 260. 261. 262. 263. 264. 265. 266. 267. 268. 269. 270. 271. 272. 273. 274. 275. 276. 277. 278. 279. 280. 281. 282. 283. 284. 285. 286. 287. 288. 289. 290. 291. 292. 293. 294. 295. 296. 297. 298. 299. 300. 301. 302. 303. 304. 305. 306. 307. 308. 309. 310. 311. 312. Cyclosporin in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Podophyllotoxin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Falls of the elderly Delirium in the elderly Urinary incontinence in the elderly Infections in old age Reviewing an elderly patient's medications Diabetes: definition, differential diagnosis and classification Hypoglycaemia in a diabetic patient Diabetic ketoacidosis Non-ketotic, hyperglycaemic, hyperosmolaric coma Primary and follow-up examinations in diabetes Insulin treatment of type 1 diabetes Type 1 diabetes: dietary treatment and exercise Newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes Treatment and follow-up in type 2 diabetes Treatment and follow-up in type 2 diabetes Lifestyle education in type 2 diabetes Oral antidiabetic drugs in the treatment of type 2 diabetes Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes Metabolic syndrome (MBS) Diabetic eye disease, with special reference to diabetic retinopathy The diagnosis and treatment of diabetic nephropathy Diabetic neuropathy Diabetic macroangiopathy Treatment of the diabetic foot Assessment of an obese patient Treatment of obesity Hypokalaemia Hyperkalaemia Hyponatraemia Hypernatraemia Magnesium deficiency Hypocalcaemia, hypoparathyroidism and vitamin D deficiency Hypercalcaemia and hyperparathyroidism Osteoporosis: diagnostics and pharmacotherapy Laboratory testing of thyroid function Enlarged or nodular thyroid gland Subacute thyroiditis Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Cushing's syndrome Primary aldosteronism (Conn's syndrome) Hypocortisolism Classification of hyperlipidaemias Investigations in patients with hyperlipidaemia Strategies and priorities in screening for hyperlipidaemia Lipid measurements and their sources of error: LDL cholesterol Treatment of hyperlipidaemia: aims and selection Diet therapy for high serum cholesterol levels Drug treatment for hyperlipidaemias Excessive hair growth (hirsutism) Male hypogonadism and hormone replacement Gynaecomastia 313. 314. 315. 316. 317. 318. 319. 320. 321. 322. 323. 324. 325. 326. 327. 328. 329. 330. 331. 332. 333. 334. 335. 336. 337. 338. 339. 340. 341. 342. 343. 344. 345. 346. 347. 348. 349. 350. 351. 352. 353. 354. 355. 356. 357. 358. Clinical use of vitamins Haemochromatosis Acute porphyria Pituitary tumours Rare endocrine tumours (pheochromocytoma and insulinoma) Amenorrhoea and oligomenorrhoea Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Galactorrhoea and other discharge from the nipple Vulvodynia Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy Pregnancy and blood pressure Systemic diseases in pregnancy Antibiotics and pregnancy Causes of infertility Contraception in patients with systemic diseases Whooping cough Rubella Mumps Adder (Vipera berus) bite A patient with psychosomatic symptoms Depression, drugs and somatic diseases Differential diagnostics of paroxysmal loss of consciousness An unconscious patient Fatigued or tired patient Treatable causes of dementia and memory disorder Infection and central nervous system manifestation Meningitis Brain abscess Slow viral infections of the central nervous system Headache Polyneuropathies Pain in and around the eye Quinine amblyopia A lump on the neck Sore throat and tonsillitis Treatment of alcohol withdrawal Steroid doping Smoking cessation The most common health risks of smoking Opacity in chest x-ray Urography and pyelography Health care for refugees arriving to Northern Europe Occupational exposure to viral agents Epidemics due to contaminated drinking water Treatment of hypertension without medicines-instructions for the patient Microbiology 11 1. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) 2. Amoebiasis 3. Traveller's infection prophylaxis 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Prevention and first aid treatment of traveller's diarrhoea Vaccinations Pneumonia Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections Viral hepatitis Sampling and investigating urine Throat bacterial swab Occupational exposure to viral agents Neoplastic diseases 44 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. Infections in immunosuppressed and cancer patients Lung cancer Palliative treatment of a patient with lung cancer Asbestos-related diseases Pleural effusions -Thoracentesis Cancer and oral health Colorectal cancer Prevention and screening of colorectal cancer Postoperative follow-up of colorectal cancer Long-term follow-up of patients at risk of colorectal cancer Carcinoma of the pancreas Prostate cancer Cancers of the urinary system and testes Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection (Condyloma) Solar keratosis Skin cancer Leucocytopenia Tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: general guidelines Lymphomas Adverse effects of radiotherapy Adverse effects of antineoplastic drugs Pharmacological treatment of cancer pain Palliative treatment of cancer Public health policy on screening for cancer Problems of long-term survivors of childhood cancer Indications for plastic surgery Lymphoedema Breast reconstruction Bone tumours Sarcomas Pap (cervical) smear and endometrial biopsy Physical examination of the breast; diagnosing a lump and pain in the breasts Breast cancer Gynaecological tumours Systemic diseases in pregnancy Infections in immunocompromized children Enlarged lymph nodes and other neck lumps in children Hoarseness, laryngitis and dysphonia A lump on the neck Tumours of the ear canal 42. 43. 44. 45. External tumours of the nose Tumours of the nasal and paranasal cavities Smoking cessation The most common health risks of smoking Nephrology 27 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. Nephropathia epidemica (NE) Guidelines for antimicrobial therapy Secondary hypertension Safe use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Polyuria Elevated serum creatinine Proteinuria Sampling and investigating urine Treatment of urinary tract infection Acute renal failure Treatment of chronic renal failure Kidney transplantation Nephrotic syndrome Glomerulonephritis IgA nephropathy Renal cysts Rhabdomyolysis Haematuria The vasculitides Cyclosporin in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Urinary incontinence in the elderly The diagnosis and treatment of diabetic nephropathy Systemic diseases in pregnancy Urinary tract infection in a child Urine aspiration sampling in children Henoch-Schönlein purpura Urography and pyelography Neurology 125 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Listeriosis Tetanus Lyme borreliosis (LB) Suspicion of rabies Symptoms of arrhythmia and examination of an arrhythmia patient Syncope: causes and investigations Hyperventilation Sleep apnoea Disturbances of taste Nausea and vomiting Syphilis 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. Chronic pain Skull and brain injury Brain concussion (commotio cerebri) Brain contusion Intracranial haematomas Spinal cord injuries Acute heat illnesses Winged scapula (Scapula alata) Ulnar tunnel syndrome Meralgia paraesthetica Restless legs, akathisia and muscle cramps The vasculitides Polymyalgia rheumatica Giant cell arteritis Complex regional pain syndrome (Reflex sympathetic dystrophy) Falls of the elderly Delirium in the elderly Assessment of physical and mental functioning Diabetic neuropathy Pharmacological glucocorticoid treatment Acute porphyria Pituitary tumours Systemic diseases in pregnancy Speech and language development Headache in children Treatment of acute seizures and status epilepticus in children Febrile convulsions Epilepsy in children Sleep disorders in children Detection of neurological disorders in children Hydrocephalus and complications of cranial shunts ADHD and MBD syndromes Encountering the family of a child with a neurological disability Treating psychological problems of the intellectually disabled in primary health care Meningitis in children Encephalitis in children Guidelines regarding sudden unexpected death in infancy Recurring psychogenic stomach-aches and headaches among children Learning disorders Mental disorders due to organic disease Treatment of insomnia Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) Depression, drugs and somatic diseases Evaluation of a neurological patient Paralysis-muscle weakness Gait disturbances Differential diagnostics of paroxysmal loss of consciousness An unconscious patient Involuntary movements Size difference between pupils Double vision (diplopia) Sleep disorders Fatigued or tired patient Clinical use of neuroradiological imaging 67. Clinical use of neurophysiological tests 68. Lumbar puncture, examination of cerebrospinal fluid and findings 69. Memory disorders and dementia 70. Examination of patients with memory disorders and dementia 71. Treatable causes of dementia and memory disorder 72. Vascular dementia 73. Alzheimer's disease 74. Other conditions leading to dementia 75. Treatment of dementia 76. Neuropsychological disorders 77. Transient ischaemic attack (TIA) 78. Cerebral infarction 79. Subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) 80. Intracerebral haemorrhage 81. Rehabilitation of the stroke patient 82. Aphasia and dysphasia 83. Examination of patients with epileptic symptoms 84. Treatment of status epilepticus 85. Treatment of epilepsy in adults 86. Epileptic patients in traffic and at work 87. Alcohol and epilepsy 88. Infection and central nervous system manifestation 89. Meningitis 90. Encephalitis 91. Brain abscess 92. Slow viral infections of the central nervous system 93. Poliomyelitis and post-polio syndrome 94. Headache 95. Tension-type headache 96. Migraine 97. Cluster Headache (Horton's syndrome) 98. Tremor 99. Essential tremor 100. Parkinson's disease 101. Neurological complications of alcoholism 102. Multiple sclerosis (MS) 103. Rehabilitation in spinal cord injuries 104. Diseases of the spinal cord 105. Treatment of spasticity 106. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) 107. Myopathies 108. Myasthenia gravis and myasthenic syndrome 109. Peripheral neuropathies: examination of the patient 110. Nerve entrapment and compression disorders 111. Quick diagnostics of peripheral nerve disorders 112. Polyneuropathies 113. Radiculopathies 114. Guillain-Barré syndrome (polyradiculitis) 115. Facial paralysis 116. Trigeminal neuralgia 117. Hiccup 118. Increased intracranial pressure 119. Sequelae of traumatic brain injury 120. Brain tumours 121. Ptosis 122. 123. 124. 125. 126. Tinnitus Disturbances of the sense of smell Vertigo Méniere's disease Benign positional vertigo Obstetrics 22 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. Listeriosis Toxoplasmosis Anaemia of pregnancy Mastitis Antenatal clinics and specialist care: consultations, referrals, treatment guidelines Antenatal clinics: care and examinations Ultrasound scanning during pregnancy Screening for foetal chromosomal abnormalities Counselling and problems of breastfeeding Ectopic pregnancy Bleeding during pregnancy (first and second trimesters, under 28 weeks) Recurrent miscarriage Threatening premature labour Pregnancy and blood pressure Systemic diseases in pregnancy Bleeding in late pregnancy Antibiotics and pregnancy Substance abuse in pregnancy Management of delivery (outside hospital) Intrauterine device Erythema infectiosum Postpartum psychosis and other postpartum mental disorders Ophthalmology 45 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Tularaemia Toxoplasmosis Sarcoidosis Blow-out fractures Sjögren's syndrome Diabetic eye disease, with special reference to diabetic retinopathy Examination of the eyes and vision as a part of paediatric health care Lacrimal duct stenosis in an infant Size difference between pupils Double vision (diplopia) Assessment of vision Assessment of visual impairment and disability Refractive errors 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. Work with visual display terminals (VDTs) and health Impaired vision Red, wet, or sore eye Pain in and around the eye Entropion and ectropion Ptosis Lagophthalmos Chalazion and hordeolum Blepharitis Preseptal cellulitis and eyelid wounds Orbital cellulitis Subconjunctival haemorrhage (suggillation) Conjunctivitis Pterygium Corneal ulcers and erosions Marginal ulcer of the cornea A foreign body on the cornea Ocular injuries Photophthalmia Eye problems in contact lens users Dry eye syndrome Episcleritis Iridocyclitis (iritis) Cataract Glaucoma Occlusion of the central retinal artery Retinal venous thrombosis Vitreous haemorrhage (VH) Detached retina Age-related macular degeneration (ARMD) Retinoblastoma Quinine amblyopia Otorhinolaryngology 97 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Tularaemia Diphtheria Mononucleosis Guidelines for antimicrobial therapy Streptococcal epidemics Foreign body in the respiratory passages Sleep apnoea Dryness of the mouth Bad breath Swelling of the salivary glands Burning mouth and glossalgia Oral mucosal ulcers Viral infections of the oral mucosa Oral fungal infections Skin diseases and the mouth Benign lesions of the tongue Cancer and oral health 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. Cleft palate Nausea and vomiting Motion sickness Dysphagia Skin cancer Investigation of atopy Food additives and hypersensitivity Allergen-specific immunotherapy Facial injuries Le Fort fractures (I-III) Lateral fractures of the face Fractures of the mandible Subacute thyroiditis Pituitary tumours Speech and language development Screening for secretory otitis media at the child health clinic Structural anomalies in children (extremities, trunk, genitals, frenulum of the tongue) Allergic diseases in the child health clinic Tonsillitis and pharyngitis in children Sinusitis in children Laryngitis in children Epiglottitis in children and adults Whooping cough Oral candidiasis in children Stomatitis in children Prevention of otitis media in children Otitis media in children: definition, epidemiology and diagnosis Treatment and follow-up of acute otitis media in children Acoustic impedance testing Treating low middle ear pressure with nasal insufflation Otorrhoea in children with tympanostomy tubes Enlarged lymph nodes and other neck lumps in children Foreign body in the gastrointestinal tract of a child Ingestion of a caustic substance in a child Differential diagnostics of paroxysmal loss of consciousness Facial paralysis Pain in and around the eye Upper respiratory tract infections in adults Hoarseness, laryngitis and dysphonia Ear pain in an adult Tinnitus Ear wax Disturbances of the sense of smell A lump on the neck Globus syndrome (sensation of a lump in the throat) Interpretation of an audiogram: impaired hearing Technical rehabilitation of hearing impairment Otosclerosis Sore throat and tonsillitis Throat bacterial swab Drainage of a peritonsillar abscess Post-tonsillectomy haemorrhage Chronic pharyngitis Diagnosis of sinusitis 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. 98. Acute maxillary sinusitis Acute frontal sinusitis Chronic sinusitis Acute otitis media in adults Chronic otitis media Otitis externa Acute mastoiditis Injuries of the auricle Barotitis and barotrauma Noise-induced hearing loss Fracture of the nose Foreign body in the ear canal Foreign body in the nose Epistaxis Allergic rhinitis Examination of a nasal smear Occupational rhinitis Nasal polyposis Nasal obstruction Atrophic rhinitis and ozaena Tumours of the ear canal External tumours of the nose Tumours of the nasal and paranasal cavities Vertigo Méniere's disease Benign positional vertigo Paediatrics 142 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. Mononucleosis Vaccinations Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections Impetigo and other pyoderma Food hypersensitivity and allergy Cow's milk allergy How to investigate symptoms associated with foods? Problems of long-term survivors of childhood cancer Baker's cyst APECED (autoimmune polyendocrinopathy -candidiasis -ectodermal dystrophy) Clinical use of vitamins Counselling and problems of breastfeeding Medical examinations at Child Health Clinics Heart auscultation and blood pressure recording in children Cardiac murmur in a child Examination of the eyes and vision as a part of paediatric health care Speech and language development Congenital dislocation of the hip Screening for secretory otitis media at the child health clinic Lacrimal duct stenosis in an infant Structural anomalies in children (extremities, trunk, genitals, frenulum of the tongue) 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. Undescended testicle Enuresis in a child Recurrent infections and immunodeficiencies Allergic diseases in the child health clinic Heart auscultation: audio samples and phonocardiograms The premature infant Growth disturbances in children Pubertal development and disturbances Doctor's check-ups in school health care Occupational guidance in school health care Headache in children Treatment of acute seizures and status epilepticus in children Febrile convulsions Epilepsy in children Sleep disorders in children Detection of neurological disorders in children Hydrocephalus and complications of cranial shunts ADHD and MBD syndromes Encountering the family of a child with a neurological disability Foetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) Down's syndrome Child with fever but no localizing symptoms Treatment of fever in children Fever and rash in a child Tonsillitis and pharyngitis in children Sinusitis in children Wheezing in children Treatment of obstructive bronchitis and acute asthma in children Diagnosis and treatment of childhood asthma Laryngitis in children Epiglottitis in children and adults Prolonged cough in children Whooping cough When should a child with a cough be treated with antibiotics? Treatment of pneumonia in children Indications for and interpretation of chest x-ray in a child with symptoms of an infection Cystic fibrosis (CF) Oral candidiasis in children Stomatitis in children Prevention of otitis media in children Otitis media in children: definition, epidemiology and diagnosis Treatment and follow-up of acute otitis media in children Acoustic impedance testing Treating low middle ear pressure with nasal insufflation Otorrhoea in children with tympanostomy tubes Chickenpox Rubella Erythema infectiosum Exanthema subitum Urinary tract infection in a child Urine aspiration sampling in children Meningitis in children Encephalitis in children Infections in immunocompromized children 79. Mumps 80. Discharging BCG scars in infants 81. Anaemia in children 82. Bruises and purpura in children: ITP and its differential diagnosis 83. Enlarged lymph nodes and other neck lumps in children 84. Interpretation of ECG in children 85. Hypertension in children 86. Investigating a child with abdominal symptoms 87. Acute abdominal symptoms in children 88. Recurrent abdominal pain in children 89. Diarrhoea and vomiting in children 90. Ingestion of a caustic substance in a child 91. Adder (Vipera berus) bite 92. Nappy rash 93. Itch in a child 94. Atopic dermatitis in children: clinical picture and diagnosis 95. Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children 96. Clinical examination of a child with arthritic symptoms 97. Diagnosis and epidemiology of arthritis in children 98. Urticaria and arthritis (serum sickness) 99. Henoch-Schönlein purpura 100. Transient synovitis of the hip 101. Enteroarthritis, borrelia and other acute forms of arthritis in children 102. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis 103. Kawasaki disease 104. A child with a limp or refusing to walk 105. Epiphysiolysis of the femoral head 106. Perthes' disease (Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease, pseudocoxalgia) 107. Osgood-Schlatter disease 108. Back problems in children and adolescents 109. Innocent leg aches in children 110. Injuries in children: lacerations and incisions 111. Excoriations and bite injuries in children 112. Fractures in children 113. Joint and ligament injuries in children 114. Central nervous system injuries in children 115. Intra-abdominal injuries and bleeding in children 116. Suturing a wound 117. Incidental glucosuria in children 118. Rickets 119. Diagnosis and treatment of childhood hypercholesterolaemia 120. Guidelines regarding sudden unexpected death in infancy 121. Recurring psychogenic stomach-aches and headaches among children 122. Childhood depression 123. Adjustment disorders in childhood 124. Childhood panic disorder 125. Learning disorders 126. A child psychiatrist's view of enuresis 127. Encopresis 128. Tic disorders in childhood 129. Selective mutism 130. Autism 131. Suicidal behaviour in childhood and adolescence 132. Psychopharmacotherapy of children and adolescents 133. Psychotherapeutic forms of treatment for children and adolescents 134. 135. 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. 141. 142. 143. 144. 145. Bullying at school Violence and abuse towards children and adolescents Recognition and treatment of sexual abuse of a child Eating disorders among children and adolescents Depression of adolescents Risk of suicide in adolescence Adolescent psychosis The adolescent and long-term illness Marginalization of adolescents Psychiatric evaluation and referral to treatment of adolescents Hoarseness, laryngitis and dysphonia Sore throat and tonsillitis Pharmacology 49 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. Ecology of the use of antimicrobial drugs Guidelines for antimicrobial therapy Pharmacotherapy of hypertension Antihypertensive drug choice for different patient groups Indications and contraindications for anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation Nitrate infusion in angina pectoris and myocardial infarction Chronic heart failure Oral anticoagulation therapy Antituberculous medication in ambulatory care Safe use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Drugs and light sensitivity Hypersensitivity to drugs Adverse effects of antineoplastic drugs Pharmacological treatment of cancer pain Treatment of poisoning Drug poisoning Poisonings caused by inebriating substances (alcohols, drugs) Drug treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Aurothiomalate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Auranophin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Sulfasalazine in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Antimalarials in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Azathioprine in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Cyclosporin in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Podophyllotoxin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Reviewing an elderly patient's medications Oral antidiabetic drugs in the treatment of type 2 diabetes Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes Osteoporosis: diagnostics and pharmacotherapy Pharmacological glucocorticoid treatment Drug treatment for hyperlipidaemias Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy Antibiotics and pregnancy Treatment of fever in children Urticaria and arthritis (serum sickness) Psychopharmacotherapy of children and adolescents 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. Treatment of insomnia Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) Panic disorder Drugs used in psychiatric emergencies Antidepressants from the General Practitioner's viewpoint Clozapine therapy Drug treatment of anxiety and related disorders Treatment of status epilepticus Treatment of epilepsy in adults Quinine amblyopia Encountering a drug addict in ambulatory care Treatment of drug addicts Pulmonary diseases 68 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. Tularaemia Influenza Echinococcosis Guidelines for antimicrobial therapy Air travel and illness SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) Acute pulmonary oedema CPAP treatment in pulmonary oedema Haemoptysis Prolonged cough in adults Dyspnoea Hyperventilation Acute respiratory failure Pulmonary function tests Acute bronchitis Pneumonia Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections Exposure to tuberculous infection Diagnosing tuberculosis Antituberculous medication in ambulatory care Atypical mycobacterial infections Bronchiectasias Asthma: symptoms and diagnosis Treatment of acute exacerbation of asthma Occupational asthma Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Pulmonary fibrosis Allergic alveolitis (farmer's lung, etc.) Eosinophilic pneumonia Sarcoidosis Acute pulmonary reactions to irritant gases Lung cancer Palliative treatment of a patient with lung cancer Asbestos-related diseases Silicosis Foreign body in the respiratory passages Pneumothorax 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. Pneumomediastinum Sleep apnoea In-line nebulizers and positive pressure ventilators Pleural effusions -Thoracentesis Bad breath Safe use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Anaphylaxis Investigation of atopy Food additives and hypersensitivity Allergen-specific immunotherapy Blood gas analysis and acid-base balance Pulse oximetry Preoperative assessment Pharmacological glucocorticoid treatment Allergic diseases in the child health clinic Wheezing in children Treatment of obstructive bronchitis and acute asthma in children Diagnosis and treatment of childhood asthma Prolonged cough in children Whooping cough When should a child with a cough be treated with antibiotics? Treatment of pneumonia in children Indications for and interpretation of chest x-ray in a child with symptoms of an infection Cystic fibrosis (CF) Smoking cessation The most common health risks of smoking Opacity in chest x-ray Adverse health effects of ambient air pollution Exposure to microbes in water-damaged buildings Acute bronchitis (instructions for the patient) Rheumatology 59 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Prolonged fever in the adult Yersiniosis Lyme borreliosis (LB) Pogosta disease Cholesterol embolization Pulmonary fibrosis Pleural effusions -Thoracentesis Elevated ESR (hypersedimentation) Ganglion Groin pain Buttock and hip pain Painful knee Baker's cyst Bursitis (patella and elbow) Painful conditions of the ankle and foot in children and adults Heel pain Fibromyalgia Clinical examination of patients with joint inflammation in primary 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. health care Diagnosis of joint inflammation in the adult Disease-specific symptoms and signs in patients with inflammatory joint diseases Raynaud's phenomenon and acrocyanosis Local corticosteroid injections in soft tissues and joints Investigation of synovial fluid Drug treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Follow-up of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatic surgery Psoriatic arthropathy Reactive arthritis and rheumatic fever Ankylosing spondylitis Scleroderma Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) Sjögren's syndrome The vasculitides Polymyalgia rheumatica Giant cell arteritis Gout Dietary treatment of gout Chondrocalcinosis (pseudogout) Aurothiomalate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Auranophin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Sulfasalazine in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Antimalarials in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Azathioprine in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Cyclosporin in the treatment of rheumatic diseases Podophyllotoxin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis Pharmacological glucocorticoid treatment Systemic diseases in pregnancy Clinical examination of a child with arthritic symptoms Diagnosis and epidemiology of arthritis in children Urticaria and arthritis (serum sickness) Henoch-Schönlein purpura Transient synovitis of the hip Enteroarthritis, borrelia and other acute forms of arthritis in children Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis Kawasaki disease A child with a limp or refusing to walk Dry eye syndrome Surgery 212 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Tetanus Gas gangrene Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Prevention and treatment of infections in splenectomized patients The most common acquired adult valvular heart diseases and associated murmurs 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. Heart valve replacement: patient follow-up Coronary angiography and indications for CABG or angioplasty Calf pain Doppler stethoscopy in diagnostics Varicose veins and venous insufficiency of the lower limbs Superficial venous thrombosis Deep venous thrombosis Prevention of venous thrombosis Conservative treatment of leg ulcers Surgical treatment of leg ulcers Pinch grafting of the skin Intermittent compression for leg swelling Ischaemic disease of the lower limb Cholesterol embolization Aortic aneurysm and dissection Lung cancer Pneumothorax Pneumomediastinum Malocclusions Cleft palate Dental traumas Involuntary weight loss Nausea and vomiting Dysphagia Haematemesis Faecal incontinence Obstipation in the adult Abdominal pain and swelling-the irritable bowel Acute abdomen in the adult Syndroma pelvis spastica Organizing endoscopy in primary care Gastroscopy Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy Heartburn; reflux oesophagitis Dyspepsia Treatment of dyspepsia, peptic ulcer and helicobacter infection Safe use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Prolonged diarrhoea in the adult Examining a patient with rectal bleeding Diseases causing rectal bleeding Melena Anal pain Pruritus ani Haemorrhoids Anal fissure Anal abscess Colorectal cancer Prevention and screening of colorectal cancer Postoperative follow-up of colorectal cancer Long-term follow-up of patients at risk of colorectal cancer Chronic inflammatory bowel disease Intestinal obstruction, paralytic ileus, and pseudo-obstruction Diverticulitis and diverticulosis Hernias Postoperative gastric problems 62. The icteric patient 63. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) 64. Chronic hepatitis 65. Primary biliary cirrhosis 66. Cholelithiasis 67. Sclerosing cholangitis 68. Acute pancreatitis 69. Recurrent or chronic pancreatitis 70. Carcinoma of the pancreas 71. Treatment of urinary tract infection 72. Kidney transplantation 73. Renal cysts 74. Rhabdomyolysis 75. Poor urine flow 76. Urinary retention 77. Urinary incontinence in women 78. Haematuria 79. Urinary bladder tamponade (blood clots in the bladder) 80. Haematospermia 81. Acute prostatitis 82. Chronic prostatitis 83. Benign prostatic hyperplasia 84. Prostate cancer 85. Balanitis, balanoposthitis, and paraphimosis in the adult 86. Peyronie's disease (Induratio penis plastica) 87. Testis pain 88. Enlarged scrotum or palpable mass in scrotum 89. Choosing a method for bladder emptying 90. Catheterization of the urinary bladder 91. Suprapubic cystostomy 92. Urinary calculi 93. Cancers of the urinary system and testes 94. Skin cancer 95. Keloid 96. Ingrowing toenail: avulsion of the nail edge and phenolization 97. Prevention and treatment of pressure sores 98. Latex allergy 99. Palliative treatment of cancer 100. Endotracheal intubation 101. Preoperative assessment 102. Facial injuries 103. Skull and brain injury 104. Brain concussion (commotio cerebri) 105. Brain contusion 106. Intracranial haematomas 107. Dislocation of the temporomandibular joint 108. Le Fort fractures (I-III) 109. Blow-out fractures 110. Lateral fractures of the face 111. Fractures of the spine 112. Spinal cord injuries 113. Fractures of the ribs and pelvis 114. Fractures of the mandible 115. Fractures of clavicula and scapula 116. Dislocation of the shoulder 117. 118. 119. 120. 121. 122. 123. 124. 125. 126. 127. 128. 129. 130. 131. 132. 133. 134. 135. 136. 137. 138. 139. 140. 141. 142. 143. 144. 145. 146. 147. 148. 149. 150. 151. 152. 153. 154. 155. 156. 157. 158. 159. 160. 161. 162. 163. 164. 165. 166. 167. 168. 169. 170. 171. Dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint Treatment of humeral and forearm fractures Dislocation of the elbow joint Treatment of wrist and metacarpal fractures Dislocation of the interphalangeal (IP) joint and injury of the first metacarpophalangeal (MCP) collateral ligament Femoral fractures Knee fractures Dislocation of the patella Knee injuries Fractures of the leg Casts in the treatment of lower extremity fractures Ankle fractures Sprain of the ankle Treatment of the fractures of the foot Post-operative treatment of osteosynthesis and indications for the removal of the osteosynthetic material Burn injuries Electrical trauma Frostbite injuries Indications for plastic surgery Injuries requiring plastic surgery Lymphoedema Replantation of the extremity or part of the body Breast reconstruction Subunguinal haematoma Muscle injuries Bite wounds Stress fracture Examination of the shoulder joint Disorders of the rotator cuff of the shoulder Biceps muscle tendinitis and rupture Winged scapula (Scapula alata) Tennis elbow Radial styloid tendovaginitis (De Quervain's disease) Ganglion Lunatomalacia (Kienböck's disease) Dupuytren's contracture Low back pain Lumbar spinal stenosis Groin pain Buttock and hip pain Painful knee Examination of knee instability Patellar chondromalacia Jumper's knee Meniscus tears Baker's cyst Osteochondritis dissecans in the knee Painful conditions of the ankle and foot in children and adults Heel pain Achilles tendon peritendinitis and tendon rupture Hallux valgus Thoracic outlet syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) 172. 173. 174. 175. 176. 177. 178. 179. 180. 181. 182. 183. 184. 185. 186. 187. 188. 189. 190. 191. 192. 193. 194. 195. 196. 197. 198. 199. 200. 201. 202. 203. 204. 205. 206. 207. 208. 209. 210. 211. 212. 213. 214. 215. 216. 217. 218. Ulnar tunnel syndrome Treatment of osteoarthritis Early recognition of complications after joint replacement Muscle compartment syndromes Bone tumours Sarcomas Treatment of an amputated inferior limb Clinical examination of patients with joint inflammation in primary health care Rheumatic surgery Complex regional pain syndrome (Reflex sympathetic dystrophy) Falls of the elderly Urinary incontinence in the elderly Treatment of the diabetic foot Physical examination of the breast; diagnosing a lump and pain in the breasts Breast cancer Lower abdominal pain of gynaecological origin Gynaecological hernias Ectopic pregnancy Congenital dislocation of the hip Structural anomalies in children (extremities, trunk, genitals, frenulum of the tongue) Investigating a child with abdominal symptoms Acute abdominal symptoms in children Recurrent abdominal pain in children Foreign body in the gastrointestinal tract of a child Epiphysiolysis of the femoral head Perthes' disease (Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease, pseudocoxalgia) Osgood-Schlatter disease Back problems in children and adolescents Injuries in children: lacerations and incisions Excoriations and bite injuries in children Fractures in children Joint and ligament injuries in children Central nervous system injuries in children Intra-abdominal injuries and bleeding in children Suturing a wound Rehabilitation in spinal cord injuries Nerve entrapment and compression disorders Radiculopathies Facial paralysis Sequelae of traumatic brain injury A lump on the neck Injuries of the auricle Fracture of the nose Urography and pyelography Traumatology 66 1. Tetanus 2. Gas gangrene 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. Prevention and treatment of infections in splenectomized patients Foreign body in the respiratory passages Dental traumas Rhabdomyolysis Indications for and techniques of red cell transfusion Facial injuries Skull and brain injury Brain concussion (commotio cerebri) Brain contusion Intracranial haematomas Dislocation of the temporomandibular joint Le Fort fractures (I-III) Blow-out fractures Lateral fractures of the face Fractures of the spine Spinal cord injuries Fractures of the ribs and pelvis Fractures of the mandible Fractures of clavicula and scapula Dislocation of the shoulder Dislocation of the acromioclavicular joint Treatment of humeral and forearm fractures Dislocation of the elbow joint Treatment of wrist and metacarpal fractures Dislocation of the interphalangeal (IP) joint and injury of the first metacarpophalangeal (MCP) collateral ligament Femoral fractures Knee fractures Dislocation of the patella Knee injuries Fractures of the leg Casts in the treatment of lower extremity fractures Ankle fractures Sprain of the ankle Treatment of the fractures of the foot Post-operative treatment of osteosynthesis and indications for the removal of the osteosynthetic material Burn injuries Electrical trauma Frostbite injuries Hypothermia Indications for plastic surgery Injuries requiring plastic surgery Replantation of the extremity or part of the body Subunguinal haematoma Muscle injuries Bite wounds Acute heat illnesses Stress fracture Groin pain Examination of knee instability Meniscus tears Complex regional pain syndrome (Reflex sympathetic dystrophy) Falls of the elderly Injuries in children: lacerations and incisions 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. Excoriations and bite injuries in children Fractures in children Joint and ligament injuries in children Central nervous system injuries in children Suturing a wound Rehabilitation in spinal cord injuries Sequelae of traumatic brain injury A foreign body on the cornea Ocular injuries Injuries of the auricle Fracture of the nose Bacteriology 3 1. Traveller's infection prophylaxis 2. Prevention and first aid treatment of traveller's diarrhoea 3. Vaccinations Virology 3 1. Traveller's infection prophylaxis 2. Vaccinations 3. Herpesvirus skin infections Anaesthesiology 18 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. CPAP treatment in pulmonary oedema Acute respiratory failure Treatment of acute exacerbation of asthma Foreign body in the respiratory passages Indications for and techniques of red cell transfusion Transfusion reactions Resuscitation Endotracheal intubation Prehospital emergency care Blood gas analysis and acid-base balance Pulse oximetry Carbon monoxide poisoning Preoperative assessment Chronic pain Hypothermia Acute heat illnesses Hyponatraemia Adder (Vipera berus) bite Cardiology 91 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. Interpretation of adult ECG Ventricular hypertrophies (RVH, LVH) in ECG Bundle branch blocks in the ECG Ambulatory ECG monitoring Computerised ECG interpretation Long QT syndrome (LQT) Echocardiography Innocent heart murmurs in adults The most common acquired adult valvular heart diseases and associated murmurs Heart valve replacement: patient follow-up Hypertension: definition, prevalence and classification Risk factors for hypertension Diagnosis of and initial investigations for hypertension Thresholds for starting therapy and targets for treatment of hypertension Non-pharmacological therapy for hypertension Pharmacotherapy of hypertension Antihypertensive drug choice for different patient groups Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) in hypertensive patients Secondary hypertension Symptoms of arrhythmia and examination of an arrhythmia patient Syncope: causes and investigations Supraventricular ectopic beats Sinus tachycardia Supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) Ventricular ectopic beats Ventricular tachycardia Differential diagnosis of broad complex tachycardia Bradycardia Atrial fibrillation: drug treatment and electric cardioversion Indications and contraindications for anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation Sick sinus syndrome Cardiac pacemakers: follow-up of patients and surveillance of pacemaker function Differential diagnosis of chest pain Unstable angina pectoris Nitrate infusion in angina pectoris and myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction Thrombolytic therapy and PTCA in acute ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) Right ventricle infarction Coronary heart disease (CHD): symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Coronary angiography and indications for CABG or angioplasty Follow-up of a revascularized patient Acute pulmonary oedema CPAP treatment in pulmonary oedema Chronic heart failure Infectious endocarditis Prevention of bacterial endocarditis Myocarditis 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. 82. 83. 84. 85. 86. 87. 88. 89. 90. 91. 92. 93. 94. 95. 96. 97. Dilated cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Primary pulmonary hypertension Leg oedema Calf pain Doppler stethoscopy in diagnostics Pulmonary embolism (PE) Oral anticoagulation therapy Intermittent compression for leg swelling Ischaemic disease of the lower limb Cholesterol embolization Aortic aneurysm and dissection Prolonged cough in adults Dyspnoea Hyperventilation Acute respiratory failure Safe use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Pulse oximetry Preoperative assessment Physical activity in the prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of diseases Contraindications to physical exercise ECG in athletes The vasculitides Diabetic macroangiopathy Primary aldosteronism (Conn's syndrome) Classification of hyperlipidaemias Investigations in patients with hyperlipidaemia Strategies and priorities in screening for hyperlipidaemia Lipid measurements and their sources of error: LDL cholesterol Treatment of hyperlipidaemia: aims and selection Diet therapy for high serum cholesterol levels Drug treatment for hyperlipidaemias Pregnancy and blood pressure Systemic diseases in pregnancy Heart auscultation and blood pressure recording in children Cardiac murmur in a child Heart auscultation: audio samples and phonocardiograms Interpretation of ECG in children Hypertension in children Differential diagnostics of paroxysmal loss of consciousness Quinine amblyopia The most common health risks of smoking Opacity in chest x-ray Treatment of hypertension without medicines-instructions for the patient Clinical physiology 14 1. Interpretation of adult ECG 2. Ventricular hypertrophies (RVH, LVH) in ECG 3. Bundle branch blocks in the ECG 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Ambulatory ECG monitoring Computerised ECG interpretation Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) in hypertensive patients Ventricular tachycardia Differential diagnosis of broad complex tachycardia Acute respiratory failure Pulmonary function tests Asthma: symptoms and diagnosis Sleep apnoea Blood gas analysis and acid-base balance Clinical use of neurophysiological tests Endocrinology 79 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. Secondary hypertension Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) Polyuria Treatment of chronic renal failure Impotence Hypogonadism in the aging male Blood gas analysis and acid-base balance Physical activity in the prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of diseases Doping in sports Diabetes: definition, differential diagnosis and classification Hypoglycaemia in a diabetic patient Diabetic ketoacidosis Non-ketotic, hyperglycaemic, hyperosmolaric coma Primary and follow-up examinations in diabetes Insulin treatment of type 1 diabetes Type 1 diabetes: dietary treatment and exercise Newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes Treatment and follow-up in type 2 diabetes Treatment and follow-up in type 2 diabetes Lifestyle education in type 2 diabetes Oral antidiabetic drugs in the treatment of type 2 diabetes Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes Metabolic syndrome (MBS) Diabetic eye disease, with special reference to diabetic retinopathy The diagnosis and treatment of diabetic nephropathy Diabetic neuropathy Diabetic macroangiopathy Treatment of the diabetic foot Assessment of an obese patient Treatment of obesity Hypokalaemia Hyperkalaemia Hyponatraemia Hypernatraemia Magnesium deficiency Hypocalcaemia, hypoparathyroidism and vitamin D deficiency Hypercalcaemia and hyperparathyroidism 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. Osteoporosis: diagnostics and pharmacotherapy Laboratory testing of thyroid function Enlarged or nodular thyroid gland Subacute thyroiditis Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis Hypothyroidism Hyperthyroidism Cushing's syndrome Primary aldosteronism (Conn's syndrome) Hypocortisolism Pharmacological glucocorticoid treatment Classification of hyperlipidaemias Investigations in patients with hyperlipidaemia Strategies and priorities in screening for hyperlipidaemia Lipid measurements and their sources of error: LDL cholesterol Treatment of hyperlipidaemia: aims and selection Diet therapy for high serum cholesterol levels Drug treatment for hyperlipidaemias Excessive hair growth (hirsutism) Male hypogonadism and hormone replacement Gynaecomastia APECED (autoimmune polyendocrinopathy -candidiasis -ectodermal dystrophy) Haemochromatosis Pituitary tumours Rare endocrine tumours (pheochromocytoma and insulinoma) Abnormal menstrual bleeding Amenorrhoea and oligomenorrhoea Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Galactorrhoea and other discharge from the nipple Menopausal complaints Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy Systemic diseases in pregnancy Causes of infertility How to investigate and treat infertility Undescended testicle Growth disturbances in children Pubertal development and disturbances Incidental glucosuria in children Rickets Diagnosis and treatment of childhood hypercholesterolaemia A lump on the neck Steroid doping Geriatrics 22 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Thresholds for starting therapy and targets for treatment of hypertension Benign prostatic hyperplasia Prevention and treatment of pressure sores Falls of the elderly Delirium in the elderly 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. Delusional symptoms in the elderly Depression in old age Nutritional disorders in the elderly Urinary incontinence in the elderly Infections in old age Reviewing an elderly patient's medications Hypertension in elderly patients Health check for the elderly Assessment of physical and mental functioning Organisation of elder care-Intermediate services Assessment of the need for institutionalization Day hospital care of the elderly Treatable causes of dementia and memory disorder Vascular dementia Alzheimer's disease Treatment of dementia Relief from constipation-instructions for the patient Nutritional medicine 18 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Non-pharmacological therapy for hypertension Lactose intolerance Coeliac disease Pancreatic insufficiency Food hypersensitivity and allergy Cow's milk allergy How to investigate symptoms associated with foods? Dietary treatment of gout Nutritional disorders in the elderly Type 1 diabetes: dietary treatment and exercise Assessment of an obese patient Treatment of obesity Diet therapy for high serum cholesterol levels Clinical use of vitamins The premature infant Diagnosis and treatment of childhood hypercholesterolaemia Eating disorders among children and adolescents Treatment of hypertension without medicines-instructions for the patient Radiology 21 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Echocardiography Coronary angiography and indications for CABG or angioplasty Asbestos-related diseases Pneumomediastinum Stress fracture Painful conditions of the ankle and foot in children and adults Early recognition of complications after joint replacement 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. Osteoporosis: diagnostics and pharmacotherapy Gynaecological ultrasound examination Ultrasound scanning during pregnancy Sinusitis in children Indications for and interpretation of chest x-ray in a child with symptoms of an infection Epiphysiolysis of the femoral head Clinical use of neuroradiological imaging Headache Diagnosis of sinusitis Acute maxillary sinusitis Opacity in chest x-ray Urography and pyelography Ultrasonographic examinations: indications and preparation of the patient Determining the volume of residual urine by ultrasonography Thoracic surgery 8 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. The most common acquired adult valvular heart diseases and associated murmurs Heart valve replacement: patient follow-up Coronary angiography and indications for CABG or angioplasty Follow-up of a revascularized patient Aortic aneurysm and dissection Lung cancer Pneumothorax Pneumomediastinum Genetics 12 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Thrombophilia (inherited) Colorectal cancer Hereditary angioedema (HAE) and ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema APECED (autoimmune polyendocrinopathy -candidiasis -ectodermal dystrophy) Acute porphyria Screening for foetal chromosomal abnormalities Down's syndrome Treating psychological problems of the intellectually disabled in primary health care Tic disorders in childhood Myopathies Polyneuropathies Retinoblastoma Occupational medicine 12 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Vibration syndrome (vibration-induced white fingers) Acute pulmonary reactions to irritant gases Asbestos-related diseases Silicosis Viral hepatitis Allergic dermatitis Toxic eczema Latex allergy Noise-induced hearing loss Occupational rhinitis Physical hazards at work Chemical hazards at work Orthopaedics 57 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. Calf pain Dislocation of the shoulder Sprain of the ankle Stress fracture Neck and shoulder pain Examination of the shoulder joint Disorders of the rotator cuff of the shoulder Biceps muscle tendinitis and rupture Winged scapula (Scapula alata) Tennis elbow Radial styloid tendovaginitis (De Quervain's disease) Ganglion Lunatomalacia (Kienböck's disease) Dupuytren's contracture Low back pain Lumbar spinal stenosis Groin pain Buttock and hip pain Painful knee Examination of knee instability Patellar chondromalacia Jumper's knee Meniscus tears Baker's cyst Bursitis (patella and elbow) Osteochondritis dissecans in the knee Painful conditions of the ankle and foot in children and adults Heel pain Achilles tendon peritendinitis and tendon rupture Hallux valgus Thoracic outlet syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) Ulnar tunnel syndrome Meralgia paraesthetica Treatment of osteoarthritis 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. Early recognition of complications after joint replacement Muscle compartment syndromes Bone tumours Tietze's syndrome Treatment of an amputated inferior limb Clinical examination of patients with joint inflammation in primary health care Disease-specific symptoms and signs in patients with inflammatory joint diseases Follow-up of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatic surgery Complex regional pain syndrome (Reflex sympathetic dystrophy) Treatment of the diabetic foot Osteoporosis: diagnostics and pharmacotherapy Congenital dislocation of the hip Structural anomalies in children (extremities, trunk, genitals, frenulum of the tongue) A child with a limp or refusing to walk Epiphysiolysis of the femoral head Perthes' disease (Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease, pseudocoxalgia) Osgood-Schlatter disease Back problems in children and adolescents Diseases of the spinal cord Nerve entrapment and compression disorders Radiculopathies Physical medicine 53 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. Calf pain Syndroma pelvis spastica Chronic pain Spinal cord injuries Muscle injuries Stress fracture Physical activity in the prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of diseases Neck and shoulder pain Examination of the shoulder joint Disorders of the rotator cuff of the shoulder Biceps muscle tendinitis and rupture Winged scapula (Scapula alata) Tennis elbow Radial styloid tendovaginitis (De Quervain's disease) Ganglion Lunatomalacia (Kienböck's disease) Dupuytren's contracture Low back pain Lumbar spinal stenosis Groin pain Buttock and hip pain Trochanteric bursitis Patellar chondromalacia 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. Jumper's knee Baker's cyst Bursitis (patella and elbow) Painful conditions of the ankle and foot in children and adults Heel pain Achilles tendon peritendinitis and tendon rupture Thoracic outlet syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) Ulnar tunnel syndrome Meralgia paraesthetica Acupuncture Treatment of osteoarthritis Restless legs, akathisia and muscle cramps Muscle compartment syndromes Fibromyalgia Tietze's syndrome Treatment of an amputated inferior limb Clinical examination of patients with joint inflammation in primary health care Diagnosis of joint inflammation in the adult Local corticosteroid injections in soft tissues and joints Follow-up of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis Ankylosing spondylitis Treatment of the diabetic foot Back problems in children and adolescents Innocent leg aches in children Rehabilitation of the stroke patient Tension-type headache Rehabilitation in spinal cord injuries Treatment of spasticity Pain in and around the eye Plastic surgery 14 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Surgical treatment of leg ulcers Pinch grafting of the skin Cleft palate Acne Skin cancer Prevention and treatment of pressure sores Burn injuries Frostbite injuries Indications for plastic surgery Injuries requiring plastic surgery Lymphoedema Replantation of the extremity or part of the body Breast reconstruction Facial paralysis Urology 37 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. Doppler stethoscopy in diagnostics Treatment of urinary tract infection Kidney transplantation Renal cysts Poor urine flow Urinary retention Urinary incontinence in women Haematuria Urinary bladder tamponade (blood clots in the bladder) Haematospermia Acute prostatitis Chronic prostatitis Benign prostatic hyperplasia Prostate cancer Balanitis, balanoposthitis, and paraphimosis in the adult Peyronie's disease (Induratio penis plastica) Testis pain Enlarged scrotum or palpable mass in scrotum Choosing a method for bladder emptying Catheterization of the urinary bladder Suprapubic cystostomy Impotence Urinary calculi Cancers of the urinary system and testes Hypogonadism in the aging male Syphilis Rare venereal diseases: chancres Reactive arthritis and rheumatic fever Urinary incontinence in the elderly Gynaecological hernias How to investigate and treat infertility Undescended testicle Enuresis in a child Urinary tract infection in a child Urine aspiration sampling in children Urography and pyelography Determining the volume of residual urine by ultrasonography Vascular surgery 11 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Calf pain Doppler stethoscopy in diagnostics Varicose veins and venous insufficiency of the lower limbs Superficial venous thrombosis Deep venous thrombosis Prevention of venous thrombosis Surgical treatment of leg ulcers Intermittent compression for leg swelling Ischaemic disease of the lower limb Cholesterol embolization Thoracic outlet syndrome Allergology 33 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. Asthma: symptoms and diagnosis Treatment of acute exacerbation of asthma Occupational asthma Allergic alveolitis (farmer's lung, etc.) Eosinophilic pneumonia Diagnostic tests in dermatology Hand dermatitis Allergic dermatitis Hives (urticaria) Anaphylaxis Investigation of atopy Hypersensitivity to drugs Food additives and hypersensitivity Latex allergy Food hypersensitivity and allergy Cow's milk allergy How to investigate symptoms associated with foods? Allergen-specific immunotherapy Hereditary angioedema (HAE) and ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema Allergic diseases in the child health clinic Diagnosis and treatment of childhood asthma Prolonged cough in children Itch in a child Atopic dermatitis in children: clinical picture and diagnosis Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children Urticaria and arthritis (serum sickness) Conjunctivitis Eye problems in contact lens users Allergic rhinitis Examination of a nasal smear Nasal obstruction Indoor air pollution Exposure to microbes in water-damaged buildings Occupational health service 20 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Occupational asthma Acute pulmonary reactions to irritant gases Asbestos-related diseases Silicosis Viral hepatitis Allergic dermatitis Toxic eczema Latex allergy Assessment of vision Work with visual display terminals (VDTs) and health 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Noise-induced hearing loss Occupational rhinitis Brief interventions for heavy use of alcohol Physical hazards at work Chemical hazards at work Occupational exposure to viral agents Burnout Adverse health effects of ambient air pollution Epidemics due to contaminated drinking water Indoor air pollution Psychiatry 78 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. Dyspnoea Hyperventilation Involuntary weight loss Chronic prostatitis Fibromyalgia Delirium in the elderly Delusional symptoms in the elderly Depression in old age Care of a rape victim Systemic diseases in pregnancy Infertility crisis Medical examinations at Child Health Clinics Enuresis in a child ADHD and MBD syndromes Treating psychological problems of the intellectually disabled in primary health care Childhood depression Adjustment disorders in childhood Childhood panic disorder Obsessive-compulsive disorder in children A child psychiatrist's view of enuresis Encopresis Tic disorders in childhood Selective mutism Autism Suicidal behaviour in childhood and adolescence Psychiatric illness of a parent with respect to the child Psychopharmacotherapy of children and adolescents Psychotherapeutic forms of treatment for children and adolescents Bullying at school Violence and abuse towards children and adolescents Recognition and treatment of sexual abuse of a child Eating disorders among children and adolescents Depression of adolescents Risk of suicide in adolescence Adolescent psychosis Marginalization of adolescents Psychiatric evaluation and referral to treatment of adolescents Mental disorders due to organic disease 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. A patient with psychosomatic symptoms Treatment of insomnia A violent patient A suicidal patient Schizophrenia Delusional disorder Postpartum psychosis and other postpartum mental disorders Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) Recognition and diagnostics of depression Major depressive disorder Bipolar disorder (manic-depressive disorder) Chronic depression (dysthymia) Depression and other psychiatric disorders Depression, drugs and somatic diseases Panic disorder Anxiety disorder Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) Antisocial personality disorder Adjustment disorders Acute stress reaction and post-traumatic stress disorder Drugs used in psychiatric emergencies Antidepressants from the General Practitioner's viewpoint Clozapine therapy Drug treatment of anxiety and related disorders Psychotherapy in general practice Psychotherapies for adults Transsexualism Differential diagnostics of paroxysmal loss of consciousness Involuntary movements Fatigued or tired patient Memory disorders and dementia Examination of patients with memory disorders and dementia Vascular dementia Treatment of dementia Infection and central nervous system manifestation Globus syndrome (sensation of a lump in the throat) Brief interventions for heavy use of alcohol Encountering a drug addict in ambulatory care Treatment of drug addicts Burnout Dental medicine 20 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Dryness of the mouth Cheilitis Disturbances of taste Bad breath Swelling of the salivary glands Burning mouth and glossalgia Malocclusions Oral mucosal ulcers Viral infections of the oral mucosa 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Oral fungal infections Skin diseases and the mouth Cancer and oral health Developmental defects in teeth Dental caries and other diseases of the hard tissues of the teeth and dental pulp Periodontal diseases (gingival inflammation and dental calculus) Dental traumas First aid for severe dental pain Emergency treatment of a gingival abscess Dislocation of the temporomandibular joint Pain in and around the eye Maxillofacial surgery 8 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Malocclusions Dental traumas Facial injuries Dislocation of the temporomandibular joint Le Fort fractures (I-III) Blow-out fractures Lateral fractures of the face Fractures of the mandible Environmental health service 5 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Food poisoning Adverse health effects of ambient air pollution Epidemics due to contaminated drinking water Indoor air pollution Exposure to microbes in water-damaged buildings Clinical chemistry 4 1. Sampling and investigating urine 2. Blood gas analysis and acid-base balance 3. Investigation of synovial fluid 4. Laboratory testing of thyroid function Gynaecology 47 1. Urinary incontinence in women 2. Chlamydial urethritis and cervicitis 3. Gonorrhoea 4. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection (Condyloma) 5. Genital herpes 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. Latex allergy Urinary incontinence in the elderly Excessive hair growth (hirsutism) Pituitary tumours Pap (cervical) smear and endometrial biopsy Gynaecological ultrasound examination Dysmenorrhoea Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) Altering the time of menstruation Abnormal menstrual bleeding Amenorrhoea and oligomenorrhoea Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Physical examination of the breast; diagnosing a lump and pain in the breasts Galactorrhoea and other discharge from the nipple Mastitis Breast cancer Vaginitis Bartholinitis; Bartholin's duct abscess and cyst Vulvodynia Lower abdominal pain of gynaecological origin Diagnosis and treatment of acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) Endometriosis Gynaecological hernias Gynaecological tumours Menopausal complaints Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy Care of a rape victim Ectopic pregnancy Bleeding during pregnancy (first and second trimesters, under 28 weeks) Recurrent miscarriage Systemic diseases in pregnancy Bleeding in late pregnancy Causes of infertility How to investigate and treat infertility Infertility crisis Contraception: first examination and follow-up Choice of contraception method Hormonal contraception (combined oral contraceptives, progestogenonly pills, skin patch and vaginal ring, hormone-releasing intrauterine device) Intrauterine device Barrier methods for contraception Postcoital contraception Contraception in patients with systemic diseases Sports medicine 15 1. Protecting the skin from freezing, sun, and drying 2. Muscle injuries 3. Acute heat illnesses 4. Physical activity in the prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. diseases Contraindications to physical exercise Diving medicine and hyperbaric oxygen therapy ECG in athletes Doping in sports Anaemia in athletes Jumper's knee Meniscus tears Achilles tendon peritendinitis and tendon rupture Muscle compartment syndromes Type 1 diabetes: dietary treatment and exercise Steroid doping Alcohol-related diseases 8 1. Macrocytosis (increased MCV) 2. Alcohol and epilepsy 3. Neurological complications of alcoholism 4. Recognition of alcohol and drug abuse 5. Providing care for an alcohol or drug abuser 6. Brief interventions for heavy use of alcohol 7. Treatment of alcohol withdrawal 8. Drugs used in alcohol dependence Administration 5 1. Public health policy on screening for cancer 2. Diving medicine and hyperbaric oxygen therapy 3. Organisation of elder care-Intermediate services 4. Providing care for an alcohol or drug abuser 5. Health care for refugees arriving to Northern Europe Radiation therapy 1 1. Adverse effects of radiotherapy Neurosurgery 17 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Skull and brain injury Brain concussion (commotio cerebri) Brain contusion Intracranial haematomas Spinal cord injuries Pituitary tumours Hydrocephalus and complications of cranial shunts Central nervous system injuries in children 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Transient ischaemic attack (TIA) Subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) Intracerebral haemorrhage Parkinson's disease Rehabilitation in spinal cord injuries Diseases of the spinal cord Increased intracranial pressure Sequelae of traumatic brain injury Brain tumours Clinical neurophysiology 7 1. Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) 2. Sleep disorders 3. Clinical use of neurophysiological tests 4. Examination of patients with epileptic symptoms 5. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) 6. Peripheral neuropathies: examination of the patient 7. Nerve entrapment and compression disorders Forensic medicine 5 1. Care of a rape victim 2. Guidelines regarding sudden unexpected death in infancy 3. Recognition and treatment of sexual abuse of a child 4. Determining the time of death 5. Examining a victim of sexual assault or incest Paediatric psychiatry 29 1. Medical examinations at Child Health Clinics 2. Treating psychological problems of the intellectually disabled in primary 3. health care 4. Babies with a tendency to cry - from the point of view of a child 5. psychiatrist 6. Recurring psychogenic stomach-aches and headaches among children 7. Childhood depression 8. Adjustment disorders in childhood 9. Childhood panic disorder 10. Obsessive-compulsive disorder in children 11. Learning disorders 12. Conduct disorders of children and adolescents 13. A child psychiatrist's view of enuresis 14. Encopresis 15. Tic disorders in childhood 16. Selective mutism 17. Autism 18. Suicidal behaviour in childhood and adolescence 19. Psychiatric illness of a parent with respect to the child 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. Psychopharmacotherapy of children and adolescents Psychotherapeutic forms of treatment for children and adolescents Bullying at school Violence and abuse towards children and adolescents Recognition and treatment of sexual abuse of a child Eating disorders among children and adolescents Depression of adolescents Risk of suicide in adolescence Adolescent psychosis The adolescent and long-term illness Marginalization of adolescents Psychiatric evaluation and referral to treatment of adolescents Paediatric surgery 1 1. Undescended testicle Phoniatrics 3 1. Speech and language development 2. Aphasia and dysphasia 3. Hoarseness, laryngitis and dysphonia School health service 2 1. Doctor's check-ups in school health care 2. Occupational guidance in school health care Adolescent psychiatry 5 1. Treating psychological problems of the intellectually disabled in primary 2. health care 3. Conduct disorders of children and adolescents 4. Risk of suicide in adolescence 5. The adolescent and long-term illness 6. Substance abuse of adolescents Paediatric neurology 2 1. Encountering the family of a child with a neurological disability 2. Foetal alcohol syndrome (FAS Forensic Psychiatry 1 2. Transsexualism Audiology 3 1. Tinnitus 2. Interpretation of an audiogram: impaired hearing 3. Technical rehabilitation of hearing impairment D:\Arhiv\Smernice\EBM Guidelines 2473 kazalo 14.2.05.doc 9 Ustvarjeno: 14.2.2005 9:17