Biological Plant Science Unit 5 Review – Plant Genetics and
advertisement

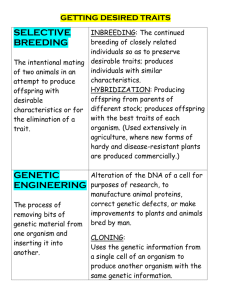
Biological Plant Science Unit 5 Review – Plant Genetics and Heritability 5.1 Define Terms Match the following terms with their BEST definition listed below: A. F1 hybrid B. genotype C. heritability D. heteroyzygous E. homozygous F. hybrid vigor (heterosis) G. phenotype H. Punnett Square I. selective breeding _____ 1. The portion of the difference in animals that is transmitted from parent to offspring. _____2. Having identical alleles at one or more loci and therefore producing identical gametes. _____3. A common method of predicting the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring using a matrix. _____4. The genetic makeup. _____5. Choosing plants for breeding based on their desired qualities or fitness. _____6. Having different alleles for a single trait and therefore producing identical gametes. _____7. An offspring of two parents in which the offspring is sterile. _____8. The physical appearance of an organism. _____9. The act of the offspring outperforming the parents due to gene combination. Match the following terms with the BEST definition listed below: A. Allele B. chromosome C. deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) D. dominant gene E. gene F. hormone G. incomplete dominance H. mutation I. recessive gene _____10. That part of a cell that contains information about genetic makeup and transmits that information to offspring. _____11. A chemical messenger substance produced in one location of an organism and carried to another where it has a specific effect(s). _____12. An accident of heredity in which an offspring has different characteristics than the genetic code intended. _____13. Causes a certain characteristic to be expressed; present in offspring. _____14. The specific determiner of heredity. _____15. A genetic protein-like nucleic acid in plant and animal genes and chromosomes that controls inheritance. _____16. When either gene is dominant, both genes are expressed (example: red and white cattle produced a roan colored calf) _____17. The character will be masked if either parent has a dominant gene; will only be expressed if the alleles from both parents are the same (and not dominant). _____18. Matching genes on homologous chromosomes. 5.2 Discuss the role and importance of genetics and heritability in the biological plant sciences 19. Briefly explain the principle of dominance: 20. Briefly explain how the purpose of the Punnett Square: For each of the following crosses, use a Punnett Square to predict the possible outcomes: 21. Tall heterozygous plant (Tt) with a Tall heterozygous plant (Tt): 22. Tall homozygous plant (TT) with a Tall heterozygous plant (Tt): 23. Tall heterozygous plant (Tt) with a Short plant (tt): 5.3 Illustrate the importance of the various plant breeding schemes 24. Briefly explain the purpose of selective breeding: 25. Briefly explain the purpose of cross-pollination: 26. Briefly explain the purpose of hand pollination: 5.4 Explain how genetic principles are used to improve agricultural production 27. Briefly explain how grafting is beneficial in preserving genetic material: 28. Briefly explain why hybrid varieties are typically preferred over purebred varieties: