Ch 14 Vocabulary - Plain Local Schools
advertisement

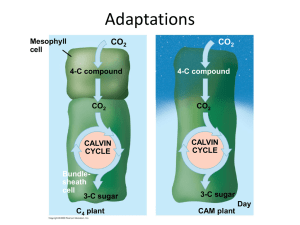
Ch 14 Vocabulary Name:__________________ 1. Evolution- generation-to-generation change in the proportion of different inherited genes in a population that account for all of the changes that have transformed life over an immense time 2. Adaptation- inherited characteristic that improves an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment 3. Decent with Modification- process by which descendants of ancestral organisms spread into various habitats and accumulate adaptations to diverse ways of life 4. Natural Selection- process by which individuals with inherited characteristics well-suited to the environment leave more offspring than do other individuals 5. Fossil- preserved remains or marking left by an organism that lived in the past 6. Fossil Record- chronological collection of life's remains in sedimentary rock layers 7. Extinct- no longer existing as a living species on Earth 8. Homologous Structure- similar structure found in more than one species that share a common ancestor 9. Vestigial Structure- remnant of a structure that may have had an important function in a species' ancestors, but has no clear function in the modern species 10. Population- group of individuals of the same species living in a particular area at the same time 11. Variation- difference among members of a species 12. Artificial Selection- selective breeding of domesticated plants and animals to produce offspring with desired genetic traits 13. Gene Pool- all of the alleles in all the individuals that make up a population 14. Microevolution- evolution on the smallest scale—a generation-to-generation change in the frequencies of alleles within a population 15. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium- condition that occurs when the frequency of alleles in a particular gene pool remain constant over time 16. Genetic Drift- change in the gene pool of a population due to chance 17. Gene Flow- exchange of genes between populations 18. Darwinian Fitness- contribution that an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation compared to the contributions of other individuals 19. Antibiotic- medicine that kills or slows the growth of bacteria ANSWERS - Chapter 14: Evolution: A History and a Process Concept Check 14.1 1. How did the work of Lyell and Malthus influence Darwin as he developed his theory of evolution? - Lyell’s work caused Darwin to think about gradual change over very long times. Malthus’s idea on overproduction of offspring was applied to all offspring 2. What characteristics of the Galápagos Islands were particularly important for Darwin? - Each island had organisms that were different from but related to those of the mainland and other islands 3. What is natural selection? - Explanation for how species change over time. Natural selection results when some organisms in a population have heritable traits that give them an advantage. Advantages allow survival and reproductive success over other individuals. 4. Which of the following is an adaptation: the sharp teeth of a house cat, or a scar on the cat's ear? Explain. - Tooth shape because it’s controlled by DNA. Wound of a scar does not change a cat’s DNA. Concept Check 14.2 1. Why are older fossils generally in deeper rock layers than younger fossils? - Sedimentary rocks form on top of one another over time 2. How can evolutionary theory explain why Australia is home to relatively few native placental mammals? - Many marsupial species evolved from ancestors after Australia became separate from other continents where more placental mammals evolved. 3. What are homologous structures? - Similar structures that evolve from a common ancestor, but may serve different functions in different related species. 4. What can you infer about species that differ significantly in their DNA sequences? - They are less closely related than species with similar DNA. Concept Check 14.3 1. In Darwin's view, what conditions lead to a struggle for existence among individuals in a population? - Excessive numbers of offspring; limited number of resource 2. What is the goal of artificial selection? - Produce changes in plants or animals for traits that human’s value 3. Why does a specific pesticide become less effective over time? - Insects that are resistant survive and produce in greater numbers. Concept Check 14.4 1. What is a gene pool? - All the alleles in all the individuals that make up a population 2. How has genetic drift affected the world's populations of cheetahs? - Decreases in genetic variety from bottlenecking events leaves the population with less variation. This decrease in variety leaves them prone to environmental changes and diseases. 3. Describe what is meant by a "biologically fit" organism. - Helps the population’s gene pool by producing offspring 4. Describe the Grants' hypothesis about how environmental conditions led to microevolution among the finches of Daphne Major. - Changes in rainfall cycles affected seed types available for food. Average beak size varies in corresponding patterns. 5. What are the two main forces of evolutionary change in gene pools? - Genetic drift and natural selection Concept Check 14.5 1. Under what conditions is the sickle cell allele beneficial to a heterozygous individual? - Individual lives where malaria is common 2. Identify a possible risk of overuse of antibiotics. -Resistance to antibiotics increases in a population. Drugs are useless to fight bacteria