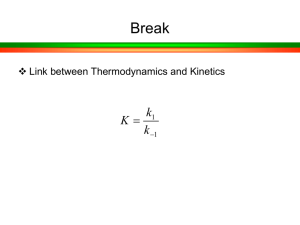
Catalysts at work
advertisement
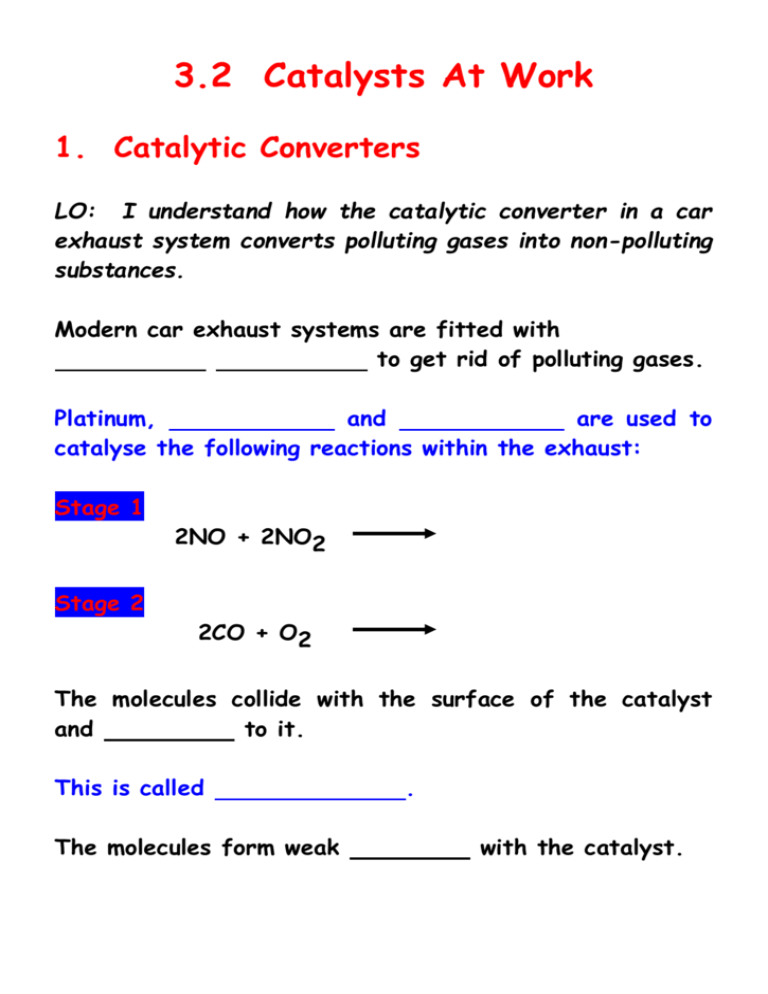
3.2 Catalysts At Work 1. Catalytic Converters LO: I understand how the catalytic converter in a car exhaust system converts polluting gases into non-polluting substances. Modern car exhaust systems are fitted with to get rid of polluting gases. Platinum, and are used to catalyse the following reactions within the exhaust: Stage 1 2NO + 2NO2 Stage 2 2CO + O2 The molecules collide with the surface of the catalyst and to it. This is called The molecules form weak . with the catalyst. This in turn the bonds between the atoms in the molecule so that they are more able to react with each other. After the reaction, the bonds between the catalyst and the new molecules break, leaving the surface of the catalyst ready to more polluting molecules. petrol must be used with catalytic converters. Lead atoms in leaded petrol to the surface of the catalyst stopping the molecules of polluting gas from adsorbing. This is known as the catalyst. 2. Heterogeneous Catalysis LO: I know some examples of heterogeneous catalysis. In heterogeneous catalysis the catalyst is in a different state from the reactants. In some reactions the catalyst can become with by-products. . If the catalyst is expensive then it must be removed and (renewed). 3. Homogeneous Catalysis LO: I know some examples of homogeneous catalysis. In homogeneous catalysis the catalyst is in the same state as the reactants. Enzymes are catalysts. They are complex protein molecules which speed up specific chemical changes by homogeneous catalysis.