ionic bonding
advertisement
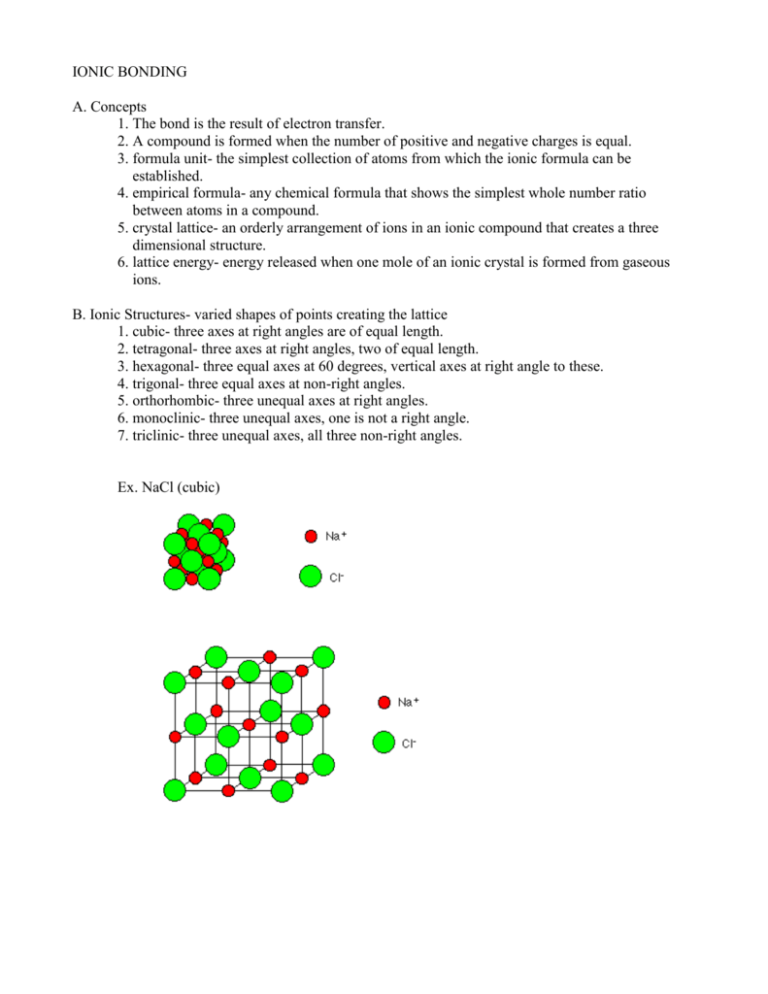
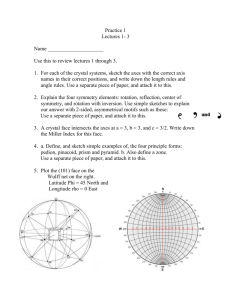
IONIC BONDING A. Concepts 1. The bond is the result of electron transfer. 2. A compound is formed when the number of positive and negative charges is equal. 3. formula unit- the simplest collection of atoms from which the ionic formula can be established. 4. empirical formula- any chemical formula that shows the simplest whole number ratio between atoms in a compound. 5. crystal lattice- an orderly arrangement of ions in an ionic compound that creates a three dimensional structure. 6. lattice energy- energy released when one mole of an ionic crystal is formed from gaseous ions. B. Ionic Structures- varied shapes of points creating the lattice 1. cubic- three axes at right angles are of equal length. 2. tetragonal- three axes at right angles, two of equal length. 3. hexagonal- three equal axes at 60 degrees, vertical axes at right angle to these. 4. trigonal- three equal axes at non-right angles. 5. orthorhombic- three unequal axes at right angles. 6. monoclinic- three unequal axes, one is not a right angle. 7. triclinic- three unequal axes, all three non-right angles. Ex. NaCl (cubic)