File
advertisement
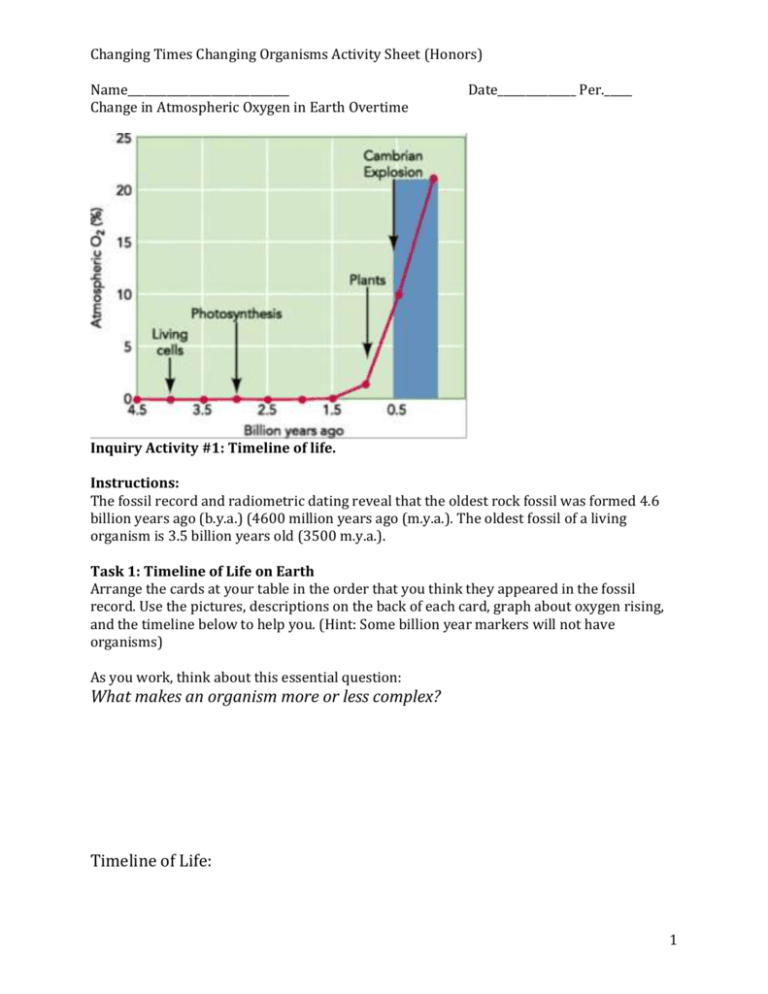
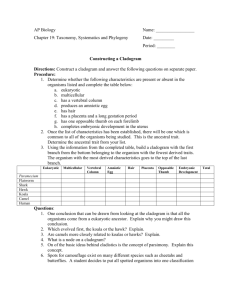
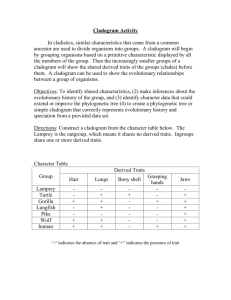
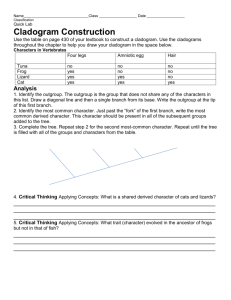
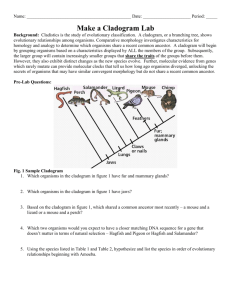
Changing Times Changing Organisms Activity Sheet (Honors) Name_____________________________ Change in Atmospheric Oxygen in Earth Overtime Date______________ Per._____ Inquiry Activity #1: Timeline of life. Instructions: The fossil record and radiometric dating reveal that the oldest rock fossil was formed 4.6 billion years ago (b.y.a.) (4600 million years ago (m.y.a.). The oldest fossil of a living organism is 3.5 billion years old (3500 m.y.a.). Task 1: Timeline of Life on Earth Arrange the cards at your table in the order that you think they appeared in the fossil record. Use the pictures, descriptions on the back of each card, graph about oxygen rising, and the timeline below to help you. (Hint: Some billion year markers will not have organisms) As you work, think about this essential question: What makes an organism more or less complex? Timeline of Life: 1 Changing Times Changing Organisms Activity Sheet (Honors) Name_____________________________ Date______________ Per._____ 1. Generate a theory on what makes organisms less complex and more complex. (In your own words and a complete sentence) Share theories as a class. Task 2: Classifying Life on Earth Words to know as you go: Mammary gland- gland to produce milk to feed infants Ectothermic (Cold-blooded)- blood must be warmed by environment Endothermic (warm-blooded)- Blood is warmed by body heat Live birth- newborn grows inside the mother and is born alive Vertebrate- Animal has a backbone and spinal cord Photosynthetic- conducts photosynthesis Eukaryotic- cell with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles prokaryotic- cell without a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles Now that we organized organisms in a timeline of life based on their complexity, let’s plot them in a way that shows how organisms are related and change overtime. In evolutionary biology we use a phylogenetic tree or cladogram. To make a cladogram, begin by collecting data on the organisms. Use the chart below to collect data on the organisms you arranged in your timeline. Mark an ‘X’ for ‘yes’ traits and (--) for ‘no traits’. If an organism has two similar characteristics, (ex. amphibians have hair or fur) mark an ‘X’ for both traits. 2 Changing Times Changing Organisms Activity Sheet (Honors) Name_____________________________ Traits: Genetic Prokar Eukar Character yote yote Trait Photosynt X X hetic Nucleus X Membrane X -bound organelles Unicellular Multicellular Vertebrate (backbone ) Lays eggs Live birth Gills Lungs Four legs Mammary glands Skin: Scales Skin: Feathers Skin: Fur Total “yes” Date______________ Per._____ 1st Multicelled X Fish X X X X Amph ibian Reptil e Bird Mam mal Total “yes” 3 X X X X X X X X 7 7 Understanding Cladograms Words to know as you go: Cladogram- Diagrams used to show phylogenies Phylogenetic tree- another word for a cladogram Phylogeny hypothesized evolutionary history between species based on physical traits, biochemical traits and fossil records. Divergence- When a common ancestor evolves into tow or more distinct species Node- area on cladogram where two or more species share a common ancestor 3 Changing Times Changing Organisms Activity Sheet (Honors) Name_____________________________ Date______________ Per._____ Outgroup- species that is most closely related to the common ancestor (most primitive organisms in a cladogram) Branch- extension of a cladogram devoted to a specific species Derived trait- trait that is favored by evolution, leads to a diverse species, and trait not found in the outgroup Shared derived trait- trait that is shared between two or more species that was favored by evolution, leads to diverse species, and distinct from the outgroup Mammary glands- glands that produce milk for infant offspring Speciation- When a new species is formed due to evolution Interpreting a Cladogram First, let’s practice interpreting some cladograms. Looking at the image and answer the questions below. 1. Which species is the outgroup? a. lizard b. mouse c. hagfish d. chimp 4 Changing Times Changing Organisms Activity Sheet (Honors) Name_____________________________ Date______________ Per._____ 2. After which animals did mammary glands develop? a. hagfish b. mouse c. pigeon d. salamander 3. What animal does not have jaws? a. perch b. hagfish c. monkey d. pigeon 4. Which animals have lungs? a. salamander b. pigeons c. hagfish d. Both a. and b. 5. What character trait separates salamanders and lizards? a. feathers b. mammary glands c. lungs d. claws or nails 6. List at least one shared derived character and explain who it is shared by. 7. List at least one derived character and explain why. 8. Based on the cladogram, which shared a common ancestor most recently? a. a mouse and a lizard b. a mouse and a perch c. a mouse and a hagfish 9. What evolutionary event occurs when a species branches off from the main line? a. speciation (new species evolves) b. extinction (species dies) c. endangered species status (species in danger of dying out) 5 Changing Times Changing Organisms Activity Sheet (Honors) Name_____________________________ Date______________ Per._____ Practice Timeline Cladogram Connect the timeline organisms from least to most complex on the cladogram provided: Most ancient Most recent Label: a) names of organisms, b) character traits that lead to a divergence (see example cladogram above for help). Practice: Use this evidence diagram of embryos to make a cladogram showing the relationship between fish, salamander, tortoise, chicken pig, cow, rabbit, and human. Include: a) names of organisms b) 8 nodes branching from a common ancestor (see example cladogram above). 6 Changing Times Changing Organisms Activity Sheet (Honors) Name_____________________________ Date______________ Per._____ 7