18 Wk - Images
advertisement

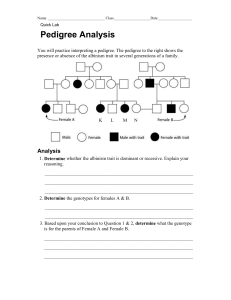
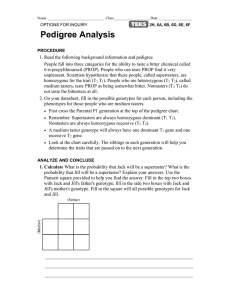
12 Wk. Benchmark Study Guide Questions (Use the 6 wk BM SG Notes, the 12 wk BM SG Notes, and your workbooks to help you answer these questions) 1. Name the order of classification groups from largest to smallest: 2. What is the science of naming called? 3. What is the 2-word system of naming called? 4. Who developed the system in #3? 5. What uses paired statements to identify an unknown organism? 6. What type of diagram shows evolutionary relationships? 7. Explain what each letter of the HOGRECR characteristics of life means and give an example of each. 8. List the 3 parts of the cell theory: a. b. c. 9. Which kingdom contains eukaryotic heterotrophs that are decomposers? 10. Which kingdom contains organisms with prokaryotic cells? 11. Which kingdom contains eukaryotic autotrophs? 12. Which kingdom contains eukaryotic heterotrophs that can move to find food? 13. Which kingdom contains mostly one-celled eukaryotes? 14. What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? 15. What is a pedigree? What do each of the symbols in a pedigree stand for? 16. How do you know if a person is a carrier on a pedigree? 17. What is incomplete dominance? Give an example: 18. What is codominance? Give an example: 19. What is multiple allele inheritance? Give an example: 20. What is the difference between a haploid cell and a diploid cell? 21. Give an example of a heterozygous genotype, a homozygous dominant genotype, and a homozygous recessive genotype. 22. Which process involving sister chromatids provides genetic variability in organisms? 23. A plant that is homozygous for purple flowers is crossed with a plant that is homozygous for white flowers. (Remember that purple is dominant). What is the genotypic ratio? What is the phenotypic ratio? 24. A heterozygous black-haired guinea pig is mated with another heterozygous black-haired guinea pig. (Black is dominant). What is the chance (percentage) of there being any brown offspring? 25. A man that is homozygous for Blood Type A marries a woman with Blood Type O. What is the chance that their first child will have blood type O? __________________________________________________________________________________ 26. List the 4 Macromolecules and the monomers (building blocks) for each: a. aa. b. bb. c. cc. d. dd. 27. List the job/function of each macromolecule in the order you listed them above: a. b. c. d. 28. What is a specialized protein that controls the rate of reactions in living things? 29. Name the three things that can affect the activity of the protein in #3: a. b. c. 30. What is the term to describe the protein if it becomes damaged? 31. How do you know the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? 32. List 10 of the cell structures/organelles and the job of each: a. aa. b. bb. c. cc. d. dd. e. ee. f. ff. g. gg. h. hh. i. ii. j. jj. 33. What are the two main structures that make up the cell membrane? a. b. 34. What is the property of the cell membrane that allows it to decide what enters and leaves the cell? 35. What is the difference between active transport and passive transport? 36. Name and describe the three types of passive transport we discussed in class: a. b. c. 37. Name and describe the three types of active transport we discussed in class: a. b. c. 38. What is the difference between facilitated diffusion and protein pumps? 39. What is the main organelle involved in photosynthesis in plants? 40. What is the main organelle involved in cellular respiration? 41. What is the equation for photosynthesis? 42. What is the equation for cellular respiration? 43. Name the three main differences between plant cells and animal cells. a. b. c. 44. What are the two processes involved in photosynthesis? Define each. a. b. 45. What are the three processes involved in cellular respiration? Define each. a. b. c.