Supplementary Data (doc 50K)
advertisement

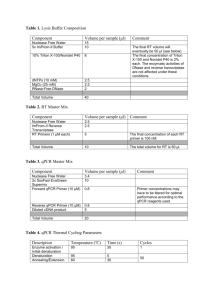
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Osteogenic BMPs promote tumor growth of human osteosarcomas that harbor differentiation defects Xiaoji Luo,1,2* Jin Chen,1,2* Wen-Xin Song,2 Ni Tang,1,2 Jinyong Luo,1,2 Zhong-Liang Deng,1,2 Katie A. Sharff,2 Gary He,2,3 Yang Bi,1,2 Bai-Cheng He,1,2 Erwin Bennett,2 Jiayi Huang,1,2 Quan Kang,1,2 Wei Jiang,2 Hong Yin,2 Jeffrey S. Souris,4 Michael A. Simon,2 Terrance D. Peabody,2 Anthony G. Montag,2,3 Rex C. Haydon,2 Hue H. Luu,2, # and Tong-Chuan He,1,2,# Materials and methods Cell culture and chemicals. Human OS lines MG63, TE85, U2OS, SaOS2, and 143B were purchased from ATCC. Human osteoblast line hFOB1.19 was kindly provided by Dr. Thomas C. Spelsberg. Tumorderived cells were isolated from resected OS specimens according to the approved by the Institutional Review Board. The above cell lines were maintained in complete MEME supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS; HyClone). HEK293 and C3H10T1/2 lines were obtained from ATCC, and maintained in complete DMEM and Basal Medium Eagle, respectively. Unless otherwise indicated, all chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich or Fisher. Establishment of OS lines stably expressing luciferase. OS lines MG63 and 143B were infected with a packaged retroviral vector expressing firefly luciferase under a human EF1 promoter. Pools of stable cells, designated as MG63-Luc and 143B-Luc, were obtained by selecting with blasticidin. Luciferase activity of the pooled stable cells was assessed by using Promega’s Luciferase Assay system. Establishment of Id-expressing stable lines. Mouse Id1, Id2, and Id3 coding regions were amplified and cloned into a retroviral vector that conferred resistance to hygromycin. The retroviral vectors (empty vector as a control) were packaged and retrovirus supernatants were used to infect MG63-Luc cells under hygromycin selection (62). The resultant stable pools were designated as MG63-Id1, MG63-Id2, MG-Id3, and control MG63-RV. Overexpression of Id genes was verified by quantitative real-time PCR. RNA isolation and quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) analysis. Total RNA was isolated using TRIZOL Reagents (Invitrogen). qPCR was carried out as described (28, 29, 61). qPCR primers (Suppl. Table 1) were 18-mers, designed by using the Primer3 program to amplify the gene of interest (approximately 120bp). SYBR Green-based qPCR analysis was carried out using Opticon DNA Engine (M J Research). The pUC19 was used as a standard. Duplicate reactions were carried out. All samples were normalized by the expression level of GAPDH. Subcutaneous implantation of MSCs and OS cells. The use and care of animals was approved by the IACUC. C3H10T1/2 and MG63 cells were infected with AdBMP2, AdBMP9, or AdGFP for 16h, and collected for subcutaneous injection (5x106 cells/injection, 4 injections/group) into the flanks of athymic nude (nu/nu) mice (4-6wk old, Harlan Sprague Dawley). At 6wk, animals were sacrificed and the implantation sites were retrieved for histologic evaluation. Intratibial tumor injection. Athymic nude (nu/nu) mice (4-6wk old male) were used. MG63-Luc and 143B-Luc cells were infected with adenoviruses (BMPs, GFP, and/or Runx2). Cells were harvested, and resuspended in PBS to a final density of 2x107 cells/ml. 1x106 cells in 20μl of PBS were injected into the proximal tibiae as described (41). Animals were subjected to Xenogen imaging at the indicated time points. Animals injected with MG63-Luc were sacrificed after 10wk, while 143B-Luc injected animals were sacrificed after 6 wk due to large tumor burdens. Xenogen bioluminescence imaging. Animal imaging was carried out at the institution’s Optical Imaging Core Facility. Briefly, animals were first anesthetized with 2.0-4.0% isoflurane delivered in 100% oxygen and attached to a nose-cone mask within Xenogen IVIS 200 imaging system. For bioluminescence imaging, animals were injected (i.p.) with the luciferase substrate DLuciferin sodium salt (Gold BioTechnology) at 100mg/kg in 0.1 ml sterile saline for 10 minutes prior to imaging. The images shown are pseudoimages of the emitted light in photons/second/cm2/steradian, superimposed over the gray-scale photographs of the animal. Quantitative analysis of the acquired images was conducted using Xenogen’s Living Image V2.50.1 software. Cell cycle analysis Cells were plated in 24-well plates and infected with GFP or BMP9 adenovirus. At indicated time points, cells were collected by using trypsin and fixed with ethanol at -20oC for 2hrs, followed by a treatment with 0.25% Triton-X100/PBS. The cells were then incubated with the Propidium Iodide (PI)/RNase Staining Buffer (BD Biosciences Pharmingen) at room temperature for 20 min and subjected to flow cytometry assay (585 nm) using a FACScan flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson). The data were analyzed using FlowJo 7.1.0 software (Tree Star, Ashland, OR). At least 20,000 cells were counted for each measurement. Supplemental Table 1. List of primers used for qPCR analysis. Supplemental Figure 1. (a), Osteogenic BMPs fail to induce bone formation in OS cells. OS lines 143B and MNNG/HOS were first infected with AdBMP2 or AdBMP9 and injected subcutaneously in athymic nude mice as described in Figure 5a. Animals were sacrificed at 4 to 6 weeks after injection, and retrieved masses were subjected to H & E staining. Magnification, 200x. (b), Verification of exogenous Id expression in the Id stable lines. Total RNA was isolated from the pooled stable Id lines and vector control line, and subjected to RT-PCR reactions, and qPCR analysis using mouse Id gene-specific primers as described in Methods and Figure 1. Supplemental Figure 2. Cell proliferative activity of xenograft tumors as assessed by Ki-67 immunohistochemical staining. Immunohistochemstry was carried out as described (12, 63). Briefly, the paraffin-embedded sections were deparaffinized and then rehydrated in a graduated fashion. After antigen retrieval and fixation, slides were blocked, and then incubated with a rabbit anti-Ki67 antibody (Lab Vision, Fremont, CA) at room temperature. The slides were incubated with EnVision+ System-HRP and visualized using DAB substrate (DakoCytomation). Ki-67 positively stained cells are indicated by arrows. A negative control using rabbit IgG accompanied each specimen was run with each series of specimens. Magnification, 100x.