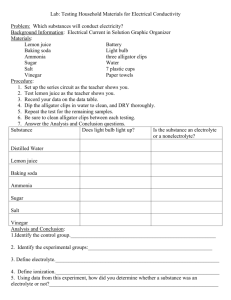
Answer Key - Parkway C-2

Some questions to ponder…(AND DO!) Name: _________________
1.
A strong acid is very concentrated / exists primarily as ions. (circle)
2.
A weak base is a nonelectrolyte / weak electrolyte / strong electrolyte.
3.
A strong base is a nonelectrolyte / weak electrolyte / strong electrolyte.
4.
At the same concentration (Molarity) a strong acid will have a higher / lower / the same pH as a weak acid.
5.
As concentration of a weak acid increases, the pH increases / decreases / remains constant.
6.
As concentration of a weak base increases, the pH increases / decreases / remains constant.
7.
As the concentration of a weak acid increases, the number of ions increases / decreases / remains
constant.
8.
As the concentration of a weak acid increases, conductivity increases / decreases / remains constant.
9.
As the strength of a weak acid increases, the proportion of ions to molecules increases / decreases.
10.
As the strength of a weak acid increases, the conductivity increases / decreases / remains constant.
11.
In your own words, define reversible reactions.
12.
How do the amounts of reactants and products change after a reaction has reached chemical equilibrium?
The amount of products and reactants remains the same over time at equilibrium.
13.
What is the “equal” part of equilibrium?
The rate of transfer. The amount of products and reactants over time.
14.
Would you consider strong acids and bases to be involved in reversible reactions? Why?
NO! Because strong acids and bases ionizes completely.
15.
Arrange these solutions in order of decreasing acidity. (Thinking about pH might help!)
0.1
M NaOH, 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M HC
2
H
3
O
2
, 0.1 M NH
4
OH
HCl, HC
2
H
3
O
2
, NH
4
OH, NaOH
More
16.
How does NH
4
Cl break apart in water? (Write as a reaction)
NH
4
Cl NH
4
+ + Cl -
17.
NH
4
+ + H
2
O ↔ H
3
O + + NH
3
Acid Base C. Acid C. Base
18.
Is NH
4
Cl an acidic or basic salt? How do you know?
When NH
4
Cl breaks apart, the NH
4
+ acts as an acid (shown in #17)
19.
How does NaC
2
H
3
O
2
break apart in water? (Write as a reaction)
NaC
2
H
3
O
2
Na + + C
2
H
3
O
2
-1
20.
C
2
H
3
O
2
+ H
2
O ↔ HC
2
H
3
O
2
+ OH -1
Base Acid C. Acid C. Base
21.
Is NaC
2
H
3
O
2
an acidic or basic salt? How do you know?
When NaC
2
H
3
O
2
breaks apart, the C
2
H
3
O 2 acts as a base (shown in #20)