Transaction Processing Systems
advertisement

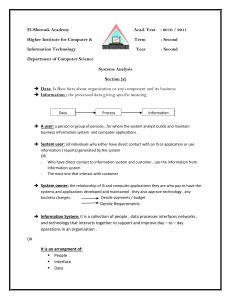
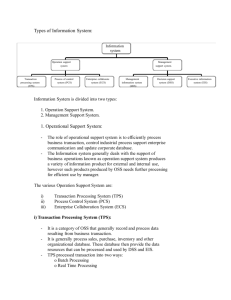
Transaction Processing Systems Definition (collect, store, modify and retrieve the transactions) Two types o Batch processing o Real time processing Concurrency Atomicity Transaction processing Monitor Characteristics of transaction processing systems Rapid Response Reliability Inflexibility Controlled processing Data Validation Transaction initiation Field checking o Range check o List check o Type check o Check digit Historical Significance of TPS UNIVAC o John Presper Eckert and John William Mauchly Manual Transaction Systems POS o 11 steps Examples of Transaction processing Systems Components of a TPS Users Participants People Examples of Real Time Transaction Processing Reservation systems POS terminals Library Loan Systems Examples of Batch Transaction processing Cheque clearance Bill generation Credit card sales transactions Storing and Retrieving Databases and Files Definition of a database 3 main types of databases o hierarchical databases o network databases o relational databases good database design necessary to find correct information o good data placement o short transactions o real time backup o high normalization o archiving of historical data o good hardware configuration 5 basic types of files o A master file o Transaction file o Report file o Work file o Program file Data Warehousing Different data sources Collected real time Provides data that is: o Consolidated o Subject oriented o Historical o Read only Backup Procedures Minimize disruptions Regular Can rebuild system Should be stored offsite or separate location. Recovery Process o Periodic backup o Journals o Checkpoint o Recovery manager o 2 types of recovery backward recovery forward recovery magnetic tape still most commonly used Grandfather-father-son Partial backups Updating in a Batch 2 stages o collecting and storage of transaction data o Processing of the Data Involves sequential access (often stored on tape) Updating in Real Time Involves large numbers of users Direct access (random access) Other Information Processes Collecting Hardware o MICR (magnetic ink character recognition) o ATM (automatic teller machine) o Barcode reader Forms o Paper forms o E-forms (on screen forms (web forms, database forms) Analysing Data Decision Support Systems (DSS) o Data Mining o Data warehousing Management Information Systems (MIS) o Common examples of MIS output include: reports on sales, stock inventory, payroll, orders and budgets o Types of reports include 1. Scheduled reports (printed on regular basis) 2. Forecasting reports (to make business forecasts) 3. On-demand reports (generated on request) 4. Exception reports (to alert people to special events) Issues Related To TPS Nature of Work Automation of jobs o Job losses o Need for training to keep up with changes People as participants o Cash transactions at ATMs o Internet purchase o Web forms Non Computer Procedures Still used during breakdowns Some times easier not to use TPS Bias Data must be bias free Not skewed o Charts must use appropriate scale o Tables must contain relevant details Ethical issue when data is knowingly misrepresented Importance of Data Data Security o Encryption during transmission o Firewalls to authenticate access o Passwords o Biometric devices Data Accuracy o Data should be free from errors o Use data validation techniques to reduce data entry errors range checks, list checks, type checks, check digits o Use data verification techniques to ensure data is up to date o Opportunities need to exist to change and update data if it is wrong. Data Integrity (describes reliability) o ACID test Atomicity Consistency Isolation Durability Control in Transaction Processing Needed to safeguard accuracy To safeguard against corruption and fraud The organisation should not be dictated by TPS