Drug addiction and the brain reward system
advertisement

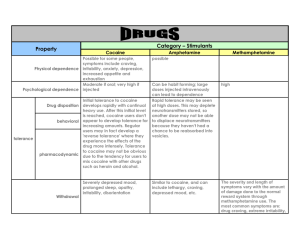
組員:Sam Wang王煜豪 Pony Lien連顥庭 Reward-- positive value of an internal physical state Incentive motivation (Brain’s dopamine system) Affect (Incentive salience) (Want) (Like) Incentive salience Psychological reward Anatomy Modulation by drugs modification of behavior sensory properties of rewards. more effective than punishment in enforcing positive behavior Ex:altruism Dopamine mesolimbic pathway mesocortical pathway Region near the base of the brain Inputs of the reward system Releasing Dopamine mesolimbic pathway Inhibitory neuron Dopamine releasing VTA neuron Cerebral neuron of reward pathway stimulate (D1 Receptor) inhibit (D2 Receptor) increase the dopamine release Arises psychological drug tolerance , sensitization. Psychological drug tolerance CREB protein delta FosB activating genes causes sensitization. intense cravings (associated with drug addiction) extend the peripheral cues of drug use Impulsive, destructive behavior medication Can’t help taking medicine 3 major reasons to lead to drug addiction 1.Hyperactive incentive system 2.Uncomfortable withdrawal symptoms 3.Permanent change in incentive system Most of drugs can lead to hyperactive incentive system. They act on Brain’s dopamine system directly , so they can make mesolimbic pathway more vigor Tolerance:need more medicaine to reach the general level of joy. Withdrawal: the unpleasant effects of getting used to not taking a drug that they have become dependent on Neural sensitization: dopamine nerve cells were activated easily by drugs. obtained from the leaves of the coca plant stimulant of the central nervous system, an appetite suppressant, and a topical anesthetic The decreased dopaminergic signaling after chronic cocaine use may contribute to depressive mood disorders and sensitize this important brain reward circuit to the reinforcing effects of cocaine •psychostimulant drug •increased wakefulness and focus •decreased fatigue and appetite •vesicular level •dopamine transporter DAT •reverse tolerance •sensitization to psychological locomotor-stimulating effects •benzodiazepines •Barbiturates Cocaine binds directly to the DAT transporter, inhibiting reuptake with more efficacy than amphetamines which phosphorylate it causing internalization; instead primarily releasing DAT (which cocaine does not do) and only inhibiting its reuptake as a secondary, and much more minor, mode of action than cocaine and in another manner: from the opposite conformation/orientation to DAT. Diamorphine from morphine deacetylated 3-monoacetylmorphine 6monoacetylmorphine μ-opioid agonists morphine 6-MAM a strong analgesic name from the Greek god of dreams Morpheus is a potent opiate analgesic medication Can be used as an analgesic to relieve can be taken orally, rectally, subcutaneously, intravenously, intrathecally or epidurally