THE REACTION OF MAGNESIUM AND HYDROCHLORIC
advertisement

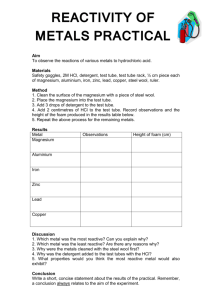
THE REACTION OF MAGNESIUM AND HYDROCHLORIC ACID Purpose: To study the relationship between the mass of magnesium used and the volume of hydrogen gas produced in the following chemical reaction: magnesium + hydrochloric acid magnesium chloride + hydrogen gas (solution) Materials: 10 mL graduated cylinder thermometer gas measuring tube one-hole stopper 250 mL beaker clamp retort stand 1000 mL graduated cylinder hydrochloric acid magnesium thread (15 cm) ruler Method: 1) Obtain a piece of magnesium ribbon from your teacher. Using your ruler, measure the length of the magnesium, in cm, to two decimal places. 2) Roll the magnesium ribbon into a coil and tie one end of a piece of thread to it. 3) Using a 10 mL graduated cylinder, put 10 mL of hydrochloric acid into the gas measuring tube. Using the 250 mL beaker, slowly fill the remainder of the tube to the brim with water. 4) Holding the thread, lower the magnesium approx. 5 cm. into the water. (You will have to shake the magnesium back and forth to break through the surface tension of the water.) Place the stopper into the mouth of the gas measuring tube so that the thread is caught between the stopper and the side of the tube. 5) Put approx. 150 mL of water in the 250 mL beaker and put the beaker on the base of the retort stand. Then, cover the hole in the stopper with your finger, invert the tube and place it in the 250 mL beaker. Clamp the tube in place so that the end of it is approx. 2 cm above the bottom of the beaker. 6) After the reaction has finished, try to dislodge any bubbles clinging to the side of the tube by tapping the tube. Then, wait for 5 minutes to allow the gas to come to room temperature. While you are waiting, hold the thermometer up in the air and ,when the temperature reading is constant, write down the room temperature in the observations table. You can also work on parts 1, 2 and 3 of the conclusions section. 7) Cover the hole in the stopper with your finger and transfer the inverted tube to a 1000 mL graduated cylinder filled with water. Remove your finger and position the gas measuring tube so that the liquid level inside it is the same as the water level outside in the 1000 mL graduated cylinder. Hold the gas measuring tube in that position while you read the volume of the gas to one decimal place. Also, write down the atmospheric pressure and the water vapour pressure (see the table on page 507 in your text). Observations: length of magnesium ribbon mass of 100 cm of magnesium __________________ cm 1.9985 g room temperature __________________ C volume of hydrogen gas (actual yield) __________________ mL atmospheric pressure __________________ kPa water vapour pressure __________________ kPa Conclusions: 1) Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction based on the word equation at the top of this page. 2) Calculate the mass of the piece of magnesium that was used to start the reaction. (Show your work.) 3) Calculate the volume of dry hydrogen gas that should be collected over water i.e. the theoretical yield. (Show your work.) 4) Calculate the % yield. (Show your work.) 5) State two possible reasons involving the equipment and/or the method which could explain the difference between your actual yield and the theoretical yield. Be specific! (Even if your results were perfect, you should still state two possible reasons to explain the difference that one might get between the actual yield and the theoretical yield in this experiment.)