template
advertisement

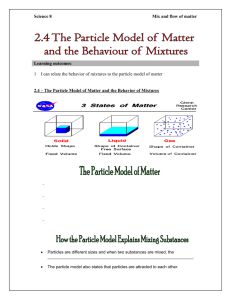
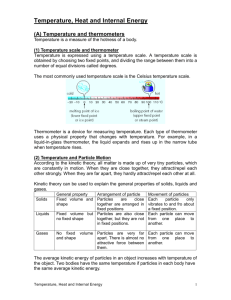
Unit 2 –Energy & States of Matter – Part 1 - Objectives 1. Relate observations of Show on a particle level how a gas diffuses from the diffusion to particle motion center of the room to the whole room. Do the same and collision in the gas for food coloring in water. and liquid phases. 2. Relate observations regarding the addition of energy by warming to increased particle motion. With pictures show on the particle level the difference between a cold and a hot material. 3. Describe the characteristics of solids, liquids and gases in terms of particles and their: arrangement: use particle diagrams to account for motion and density differences; describe the process of how the arrangement of matter particles changes during phase changes. Use pictures to show how particles are arranged in a solid, liquid, and gas. Show then a picture at the particle level of melting and of boiling. 4. Relate temperature to the thermal energy (Etherm) of particles in motion. Show particles with low thermal energy and those with high thermal energy. 5. Explain, at the particle level, how a thermometer measures the temperature of the system. Show particles in a thermometer that is cold and one that is hot. Modeling Chemistry 1 U2 obj v2.0 6. Explain the basis for the Celsius temperature scale. Show a thermometer with the major temperatures. 7. State the basic tents of Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT). What are the three things about matter that explains the states and changes. 8. The 3 variables P, V and T are interrelated. Any factor that affects the number of collisions has an effect on the pressure. You should be able to: Predict the effect of changing P, V or T on any of the other variables. 1 P P T V T V Solve for the following situations: 1) A gas at 50 ml is heated from 30 C to 90 C. Explain (in terms of the collisions of particles) why the change has the effect you predicted. 2) A gas at 50 mL an 120 kPa is increased to 360 kPa. 3) A gas at 90 kPa is heated from 20 C to 80 C. 4) A gas in a balloon at 50 mL has 150 particles. It is then filled with 450 particles. What is the new volume? Explain the basis for the Kelvin scale. Use the absolute temperature scale 5) A gas at 400 mL and 100 kPa leaks. The mass to solve gas problems. drops from 4.5 grams to 1.5 grams but the size is still 400 mL. What is the new pressure? Use factors to calculate the new P, V or T. Make a decision as to how the change affects the variable you are looking for. Modeling Chemistry 2 U2 obj v2.0