Cell Multi
advertisement

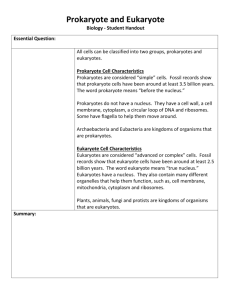
Cell Multi-cellular - First cell to evolve was prokaryote (3.5 billion years ago) - Prokaryotes started to evolve when the number of prokaryotes increased to the point there was limited resources (food). - Prokaryotes evolved into eukaryotes – How? Current theory is called the Symbiotic (Big Gulp) Theory. 1) Prokaryote (A) can’t make food but is large 2) Prokaryote (B) can make food but is small and can’t protect itself 3) Prokaryote (B) starts to live inside of (A) 4) Prokaryote (A) protects (B) and (B) makes food for (A) 5) Prokaryotes (A & B) now can survive better then other cells 6) Over time (millions of years) prokaryote (B) becomes a permanent part of prokaryote (A). 7) Over time – prokaryote (B) will not need certain structures due to prokaryote (A) will do the functions for prokaryote (B). Ex: structures for moving, processing, etc. 8) Prokaryote (A) now has a membrane-bound organelle and now becomes a eukaryote - Eukaryotes evolved into colonial organisms (genetically identical cells living together in group). - Colonial organisms evolved into multi-cellular organisms when the cells in the colonial organisms started to differentiate. Ex: The outer cells would do only movement with cilia and the cells inside would lose their cilia and produce more energy for themselves and the outer cells.