Your Name (Print carefully) Total Correct___________
advertisement

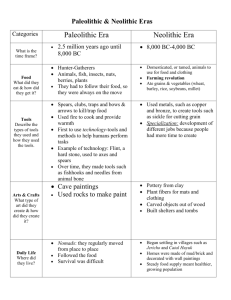
Your Name ________________________(Print carefully) (last name first, please) Total Correct___________ Milestone Quiz 4, ANTH A103, Zimmerman section There are 23 questions (20 regular, 3 bonus) on both sides of the sheet. Be sure to answer all of them! Circle the best answer within the context of this course. Each is worth 1 point. (Max score on this quiz, 23 points). 1. As anatomically modern humans left Africa, one climatic factor that made their movements ‘easier’ was the lowering of sea levels during the last period of glacial advance allowing them to move into Australia as early as 60,000 years and North America by at least 12-20,000 years ago. True False 2. Domestication is an evolutionary process whereby humans intentionally or unintentionally modify the genetic makeup of plants or animals and is a kind of interdependence between species. True False 3. With the Upper Paleolithic and anatomically modern humans, there was an “explosion” of tool types and other cultural activities. True False 4. Trade networks seem to be a decisive factor in the developments of states. True False 5. The Incan civilization of Peru and the Andes would be considered a state except for the fact that they didn’t have a system of writing and mathematics. True False 6. Upper Paleolithic rock art and cave painting “hands” indicate that there was a growing sense of individual identity. True False 7. The widespread use of pottery during the Neolithic implies sedentary communities, but does not require a particularly high degree of technological sophistication. True False 8. Which of the following is not one of kinds of evidence from which archaeologists recognize the stratified nature of civilizations? a. Complex burials and grave goods b. Large size and multi-room dwellings c. Specialized art forms d. Written documents e. All of the above indicate stratification 2 9. One issue that makes human paleontology so controversial is that it seeks to understand the origins and evolution of those who study it and what it means to be human. That leaves it open to all of the social, political, racial, and religious ramifications of what it means to be human. True False 10. Generally speaking, the study of cave painting and Upper Paleolithic art is nearly gender free. True False 11. Civilization is a higher quality, more comfortable life style than hunting and gathering. Which of the following reasons suggest that this may not be true? a. The difference between the two may be a matter of differences in cultural preferences about what ‘higher quality’ or ‘more comfortable’ mean. b. To produce their food, hunter/gatherers spend fewer hours working every day than those growing crops or raising livestock and have more leisure time than those in ‘civilized’ cultures. c. ‘Civilized’ life styles actually bring more diseases related to poor diet and stress than hunting/gathering lifestyles. d. ‘Civilized’ cultures require more energy to stay organized and may in fact create ‘energy sinks.’ e. All of the above may be reasons. 12. Cultivars are wild plants with some level of selection by the people who use them. This selection may eventually turn the plant into a cultigen. True False 13. Archaeologists have proposed several hypotheses to explain Upper Paleolithic cave art. Which of the following is not one of the hypotheses? Cave art may be: a. Hunting magic and training b. Shamanic mental images c. Totemic symbols d. Binary oppositions reflecting society e. All of the above are hypotheses archaeologists have proposed. 14. Which of the following is not one of the major culture changes that marked the transition from Neolithic villages to civilization? a. Relatively complex, theistic religions provided ideological underpinnings for state systems. b. Diversification of labor occurred as part of population growth in cities. c. The emergence of central governments provided an authority to deal with the complex problems of cities. d. Social stratification and the emergence of social classes. e. All of the above occurred with the transition. 3 15. Which of the following is not one of the processes of the multiplier effect? a. The greater the population, the faster the rate of change. b. The greater the ideological diversity, the faster the rate of change. c. The greater the environmental instability, the faster the rate of change. d. The greater the amount of intercultural contact, the faster the rate of change. e. The greater the existing variety, the faster the rate of change 16. Pleistocene overkill is probably the best explanation for the die-off of large mammals near the end of the Ice Ages. True False 17. Struggle for control of key resources such as obsidian, bitumen, and lapis lazuli may be associated with the collapse of early civilizations. True False 18. Archaeologists believe that early civilizations represent progress and advancement over the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic cultures. True False 19. No evidence has been found indicating that religion or government was a centrally organized institution during the Neolithic. True False 20. Like biological adaptation, cultural adaptation is always a local problem. True False Bonus: 21: Among pastoralists, grazing animals in low areas in winter and moving them to high pastures in summer is called ___________________. 22. ‘Venus figurines,’ a form mobilary art, are sometimes hypothesized to be teaching models relating to pregnancy. Another explanation is that they are fertility symbols. True False 23. In terms of selective pressures leading to domesticated plants, which of the following was not an important question? a. Will the food source be reliable? b. Will the plant produce adequate quantities to meet population needs? c. Will the plant meet nutritional requirements in terms of calories, vitamins, and minerals? d. Will the food store easily? e. Will the food be palatable, that is, will it taste reasonably good?