Zoo/Bot 3333
advertisement
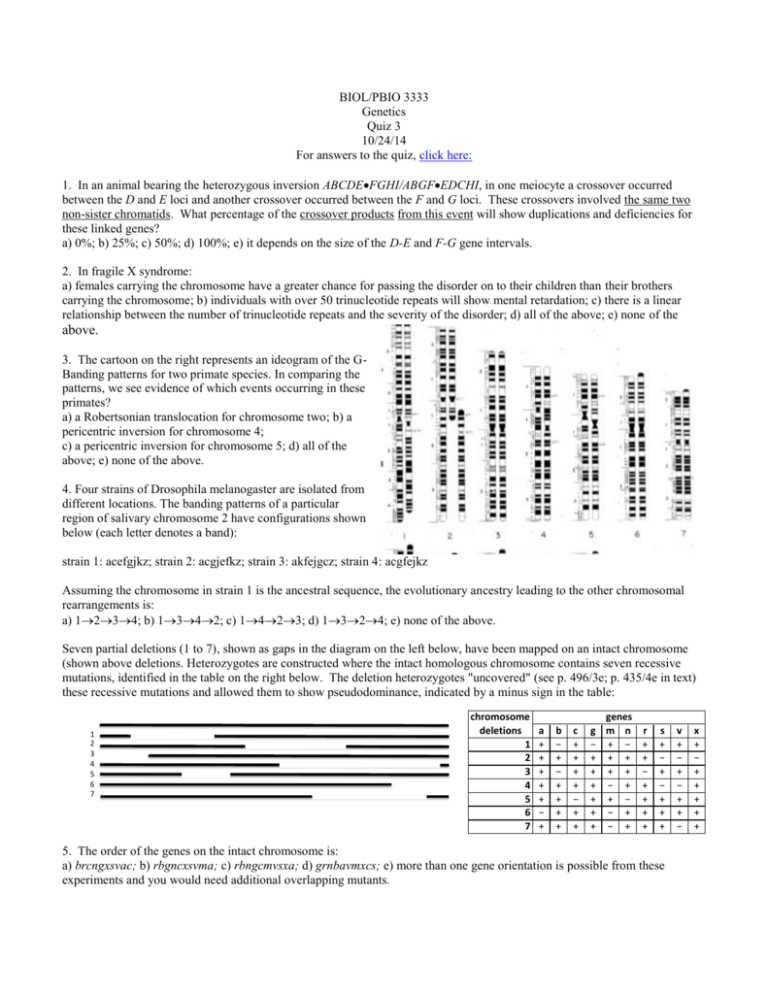
BIOL/PBIO 3333 Genetics Quiz 3 10/24/14 For answers to the quiz, click here: 1. In an animal bearing the heterozygous inversion ABCDEFGHI/ABGFEDCHI, in one meiocyte a crossover occurred between the D and E loci and another crossover occurred between the F and G loci. These crossovers involved the same two non-sister chromatids. What percentage of the crossover products from this event will show duplications and deficiencies for these linked genes? a) 0%; b) 25%; c) 50%; d) 100%; e) it depends on the size of the D-E and F-G gene intervals. 2. In fragile X syndrome: a) females carrying the chromosome have a greater chance for passing the disorder on to their children than their brothers carrying the chromosome; b) individuals with over 50 trinucleotide repeats will show mental retardation; c) there is a linear relationship between the number of trinucleotide repeats and the severity of the disorder; d) all of the above; e) none of the above. 3. The cartoon on the right represents an ideogram of the GBanding patterns for two primate species. In comparing the patterns, we see evidence of which events occurring in these primates? a) a Robertsonian translocation for chromosome two; b) a pericentric inversion for chromosome 4; c) a pericentric inversion for chromosome 5; d) all of the above; e) none of the above. 4. Four strains of Drosophila melanogaster are isolated from different locations. The banding patterns of a particular region of salivary chromosome 2 have configurations shown below (each letter denotes a band): strain 1: acefgjkz; strain 2: acgjefkz; strain 3: akfejgcz; strain 4: acgfejkz Assuming the chromosome in strain 1 is the ancestral sequence, the evolutionary ancestry leading to the other chromosomal rearrangements is: a) 1234; b) 1342; c) 1423; d) 1324; e) none of the above. Seven partial deletions (1 to 7), shown as gaps in the diagram on the left below, have been mapped on an intact chromosome (shown above deletions. Heterozygotes are constructed where the intact homologous chromosome contains seven recessive mutations, identified in the table on the right below. The deletion heterozygotes "uncovered" (see p. 496/3e; p. 435/4e in text) these recessive mutations and allowed them to show pseudodominance, indicated by a minus sign in the table: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 chromosome deletions 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 a + + + + + − + b − + − + + + + c + + + + − + + genes g m n − + − + + + + + + + − + + + − + − + + − + r + + − + + + + s + − + − + + + 5. The order of the genes on the intact chromosome is: a) brcngxsvac; b) rbgncxsvma; c) rbngcmvsxa; d) grnbavmxcs; e) more than one gene orientation is possible from these experiments and you would need additional overlapping mutants. v + − + − + + − x + − + + + + + 6. From the above data set, one can determine: a) r is further from b than v is from a; b) c and s are the closest genes to one another; c) a heterozygote between deletions 1 and 2 would likely be inviable; d) all of the above; e) none of the above. Questions 7 and 8 pertain to the following. Four E. coli strains of genotype a+b− are labeled 1, 2, 3, 4. Four strains of genotype a−b+ are labeled 5, 6, 7 and 8. The two genotypes are mixed in all possible combinations and (after incubation) are plated to determine the frequency of a+b+ recombinants. The results indicated in the table are obtained, where M = many recombinants, L = low numbers of recombinants, and 0 = no recombinants. The strains can be classified as 3 sex types: either F−, F+ or Hfr with regard to a and b gene transfer. strains 5 6 7 8 1 L 0 0 L 2 M 0 0 M 3 0 M L 0 4 M 0 0 M 7. The F− cells present in this data set are represented by: a) 1 and 7; b) 2 and 4; c) 6 and 7; d) 7 only; e) none of the above. 8. True or false. Suppose after mixing strains 5 and 2 the culture was left to grow on medium containing the nutrients needed by both the a- and b- mutants. The progenitor cells arising from this experiment would be expected to be able to form pili if examined under the electron microscope. Questions 9-10 pertain to the following. An Hfr strain of the genotype s+t+u+v+strs is mated with a female strain of the genotype s−t−u−v−strr. At various times the culture is disrupted in a blender to separate the mating pairs. The cells are then plated on agar of the following four agar types (see table below, right), where nutrient S allows the growth of s− auxotrophs, nutrient T allows for the growth of t− autxotrophs, etc. As indicated, all types contain streptomycin (Str). A (+) indicates the presence of the nutrient or drug, a (-) indicates its absence. Timings of Samples 0 2.5 5 7.5 10 12.5 15 17.5 20 25 30 35 Number of Colonies of Agar of Type 1 2 3 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 32 44 48 0 0 0 3 60 113 139 164 180 183 186 189 0 0 0 0 2 56 87 114 122 135 143 146 0 4 68 136 222 318 371 396 414 416 420 425 Agar Type 1 2 3 4 Str + + + + S + + − + T + + + − U − + + + V + − + + The table on the left shows the number of colonies on each type of agar for samples taken at various times after the samples are mixed: 9. Relative to their proximity to the F factor origin of replication (the first gene listed below is closest) the gene order of these four genes is: a) s-t-u-v; b) t-v-s-u; c) t-u-s-v; d) v-s-t-u; e) none of the above. 10. The genes that map closest together in this experiment are: a) v and u; b) t and v; c) v and s; d) t and s; e) there is a closer gene pair that is not listed.