Supplementary Materials and Methods (doc 23K)
advertisement

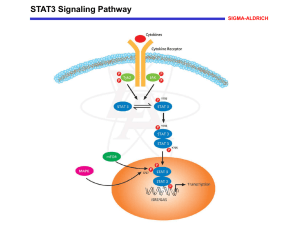
Supplementary Materials and methods shRNA sequences, lentiviral preparation and cells infection pSUPER-derived expression vectors for small interfering RNAs against STAT3 were designed according Chatterjee M et al (Blood, 2004). The sense strand of the STAT3 short hairpin RNA (shRNA) sequence is: gatccccCTTCAGACCCGTCAACAAAttcaagagaTTTGTTGACGGGTCTGAAG 5'tttttggaaa -3' (based on positions 823 to 841 of human STAT3) (named thereafter S1). The 19–nucleotide (nt) STAT3 target sequences are indicated in uppercase letters, whereas the hairpin and the sequences necessary for the directional cloning are depicted in lowercase letters. As a control (C), S1 sequence was mutated in 3 nucleotides. Cassettes containing the H1 promoter and shSTAT3 sequences were subcloned into the EcoRV-XhoI sites of the vector pCCL.sin.PPT.hPGK.GFPWpre, kindly provided by Dr Luigi Naldini (San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan, Italy). An additional shRNA against human STAT3 (named S2 ) was obtained from the Lentiviral Expression Arrest-TRC library (Open Biosystems) (Moffat J et al, Cell, 2006). Self-inactivating lentiviral particles were produced as previously described (Piva R et al, J Clin Invest, 2006). Efficacy of the constructs was tested through transduction into Sup-M2-TS cells. Cells were seeded at a density of 50000 cells/well in a 24-well assay plate, infected using 25 l of unconcentrated shRNA lentiviral supernatants, incubated for 24 hours and treated with 2 g/mL puromycin for additional 3 days. All lentiviral infections were tested in duplicate, one replicate to monitor expression of -actin, STAT3, and oligoadenylate synthetase 1 by Quantitative-RT-PCR, the other replicate was assayed by Western blot analysis with anti-STAT3 and -tubulin –specific antibodies. For the quantitative RT-PCR, total RNA was extracted using the RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Milan, Italy). cDNA was transcribed using SuperScript III (Invitrogen) following the manufacturer’s instructions. RT-PCR analysis was performed on a Thermal iCycler (BioRad, Milan, Italy) using the QuantiFast SYBR Green PCR protocol (Qiagen) and the QuantiTect validated primer sets (Qiagen). The percentages of infected cells were assessed for GFP expression on a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ). The CELLQuest(TM) software (Becton Dickinson) was used for the data acquisition and analysis. Wild type ST4 and Molt4 cells (ST4-WT and Molt4-WT) were infected with the lentiviral vectors delivering the S1 and C shRNAs to generate, respectively, cell lines devoid of STAT3 (ST4-S1 and Molt4-S1), or control cell lines (ST4-C and Molt4-C). The efficiency of infection was evaluated by flow cytometry and, simultaneously, STAT3 expression was checked by Western blot analysis. To improve silencing, infected cells were sorted for high GFP expression (MoFlo HighPerformance Cell Sorter, DakoCytomation, Glostrup, Denmark) and re-infected. The control cell lines were generated in a similar way, using the scrambled shRNA sequence. ST4 and Molt4 cells were also infected with puromycin-resistant lentiviral vectors delivering different shRNA against STAT3 (S2). Cells were infected twice and selected using increasing amounts of puromycin (20 and 30 g/mL). Efficient silencing could only be obtained in Molt4 cells, the so-generated Molt4-S2 cell line was then used in the following experiments.