Ch. 7 - Ltcconline.net
advertisement

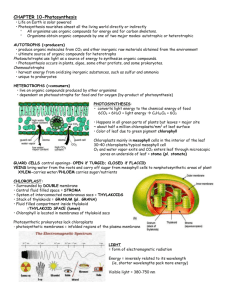
Bio 110 Intro to cell and molecular biology Lake Tahoe Community College Instructor: Sue Kloss ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Chapter 7 - Photosynthesis ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ I. Overview of Photosynthesis (Ps) A. Autotrophs are producers of biosphere 1. producers 2. fixation 3. plants, algae and some bacteria are photosynthetic B. Ps occurs in chloroplasts 1. all green parts of plants have chloroplasts 2. site of Ps 3. O2 produced in Ps comes from splitting of water C. Ps is a redox process 1. When water molecules are split, they are oxidized 2. CO2 is reduced to sugar 3. cell respiration does the opposite to release chem energy 4. Ps involves a food producing redox reaction D. Ps occurs in 2 stages linked by ATP and NADH 1. 2 steps of Ps are light reactions and Calvin Cycle or light independent reactions 2. light reactions convert light energy to chem energy and produce O2 gas as waste 3. Calvin cycle assembles sugar molecule 4. Photo = light, synthesis = putting together (sugar) 5. light reactions occur in grana on thylakoid membranes 6. light absorbed by chlorophyll furnishes energy to power sugar production in Ps 7. Light energy makes ATP from ADP and P; also makes NADP+ into NADPH 8. sugar is made in the Calvin cycle in the stroma. 9. CO2 is reduced - change from gas state to solid - called carbon fixation 10. NADPH provides hi energy electrons 15. ATP from light reactions provides chem energy for Calvin cycle 16. Calvin cycle does not require light directly II. Light Reactions: Converting Solar energy to Chemical energy A. Visible radiation drives light reactions 1. sunlight is a type of energy called electromagnetic radiation 2. light reactions use only certain wavelengths (colors). 3. light absorbing pigments absorb different length waves B. Photosystems capture solar power 1. waves describe energy 2. photon is fixed quantity of energy 3. electron is raised from ground to excited state 4. excited state is very unstable 5. electron transfer is first step of light reactions 6. called reaction center 7. all the pigment molecules = antenna molecules 8. photosystem 9. Photosystems are light harvesting units C. In the light reactions, electron transport chains (etc) generate ATP, NADPH and O2 1. In the light reactions 2. Etc = Electron Transport Chain 3. carrier molecules are arranged in thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast 4. both photosystems absorb energy D. Chemiosmosis powers ATP synthesis in the light reactions 1. photosystems release energy in electron flow 3. excited electrons pass along series of electron carriers 4. some electron carriers use energy released from electrons to actively transport H+ ions 5. concentration gradient of H+ ions build up inside thylakoid 6. energy stored in this concentration 7. photophosphorylation 8. final electron acceptor 9. O2 is produced when H2O is split III. The Calvin cycle converts CO2 to sugar A. ATP and NADPH power sugar synthesis 1. Calvin cycle is a sugar factory 2. CO2 ATP and NADPH are used 3. plant constructs G3P IV. Photosynthesis reviewed and extended A. C4 and CAM plants B. Ps uses light energy to make food molecules Lesson Objectives for Chapter 7 Meeting 1 Week 6 1. Define terms autotroph and producer. 2. Describe structure and location of chloroplasts in a leaf. 3. Explain how plants produce oxygen. 4. Explain how Ps is based on redox reactions. 5. Describe in VERY general terms the overall processes of light reactions and Calvin cycle. Meeting 2 Week 6 6. Explain how photosystems capture solar energy. 7. Explain how the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis in the light reactions generate ATP, NADPH and O2. 8. Describe the reactants and products in Calvin cycle. Explain why this cycle is dependent on light reactions. 9. Draw a model to explain Photosynthesis. Relate the model to the equation for Photosynthesis. Show entry and locations of products and reactants in Calvin Cycle and light reactions. Explain how the term photosynthesis relates to these functions. 10. Contrast and compare regular photosynthesis with C4 and CAM photosynthesis