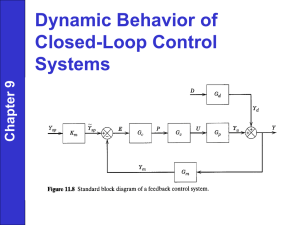
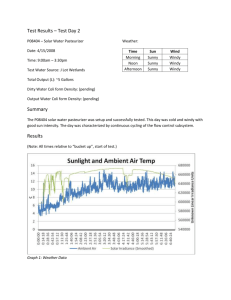
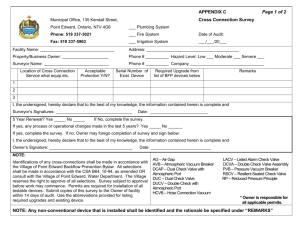
PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure
advertisement

RESTRICTED May 2007 Document ID: PR-1047 Filing Key: Business Control Petroleum Development Oman L.L.C. Well Engineering Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure User Note: The requirements of this document are mandatory. Non-compliance shall only be authorised by the Document Authority or his Delegate through STEP-OUT approval. A controlled copy of the current version of this document is on PDO's EDMS. Before making reference to this document, it is the user's responsibility to ensure that any hard copy, or electronic copy, is current. For assistance, contact the Document Custodian or the Document Controller. Users are encouraged to participate in the ongoing improvement of this document by providing constructive feedback. Please familiarise yourself with the Document Security Classification Definitions They also apply to this Document! This document can be accessed via the following link: http://sww3.pdo.shell.om/getdoc?dataid=95049 (PDO Intranet) Keywords: WIT, Wellhead Integrity Test, SIT, Subsurface Integrity Test, Well Failure Model, Well type, gas lift wells, steam injection wells, free flowing wells This document is the property of Petroleum Development Oman, LLC. Neither the whole nor any part of this document may be disclosed to others or reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form by any means (electronic, mechanical, reprographic recording or otherwise) without prior written consent of the owner. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 This page was intentionally left blank Page 2 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 i Petroleum Development Oman LLC Document Authorisation Authorised For Issue: May 2007 Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 3 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 ii Revision History The following is a brief summary of the 4 most recent revisions to this document. Details of all revisions prior to these are held on file by the issuing department. Note that changes made as part of Document Maintenance (correction of broken hyperlinks) will not be recorded in this Revision Table. Revision No. 2 Date April 2007 Author/ Editor Obaid Al Farsi (UWXZ/4) Christian Koepchen (UWH/2), Changes/ Remarks Alignment of Well Integrity Maintenance Procedures with the Well Failure Model Robin Gardiner (UPT/2) 1 01/01/2002 TWM/92 UOW 1 0 14/10/1998 TM Services – OTW/1 Initial Issue, post merger of Well Services & Well Engineering.1 Initial Issue iii Related Business Processes Code EP.63 Business Process (EPBM V.4.0) Design, Drill, Modify, Service and Abandon Well iv Related Corporate Management Frame Work (CMF) Documents The related CMF Documents can be retrieved from the CMF Business Control Portal. Other, non-CMF documents and links to information relevant to Well Engineering can be found on the Well Engineering Documentation Page. Page 4 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC TABLE OF CONTENTS i Document Authorisation ......................................................................................................... 3 ii Revision History ..................................................................................................................... 4 iii Related Business Processes ................................................................................................. 4 iv Related Corporate Management Frame Work (CMF) Documents ........................................ 4 1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................ 7 2 1.1 Background ...................................................................................................................... 7 1.2 Purpose ............................................................................................................................ 8 1.3 Scope ............................................................................................................................... 8 1.4 Distribution/Target Audience ............................................................................................ 8 1.5 Review and Improvement ................................................................................................ 8 1.6 Step-out and Approval ..................................................................................................... 8 Procedure Description ........................................................................................................... 9 2.1 Wellhead Integrity Test (WIT) ........................................................................................ 10 2.1.1 Suspended Wells.......................................................................................... 10 2.1.2 Well Type 1 (High Pressure Wells or high GLR or H2S Wells) .................... 12 2.1.3 Well Type 2 (Free Flowing Low Pressure Oil Wells, < 20,000 kPa) ............ 20 2.1.4 Well Type 3 (Gas lift Wells) .......................................................................... 27 2.1.5 Well Type 4 (Steam Injection Wells) ............................................................ 33 2.1.6 Well Type 5 (Sub-hydrostatic, pumped wells) .............................................. 40 2.1.7 Well Types 6 and 7 (Water Injection/ Disposal wells with/ without tubing) .. 46 2.2 Subsurface Integrity Test (SIT) ...................................................................................... 52 2.2.1 Well Type 1 (High Pressure Wells or high GLR or H2S Wells) .................... 52 2.2.2 Well Type 2 (Free Flowing Low Pressure Oil Wells, < 20,000 kPa) ............ 63 2.2.3 Well Type 3 (Gas lift Wells) .......................................................................... 74 2.2.4 Well Type 4 (Steam Injection with Packer) .................................................. 85 2.2.5 Well Type 5 (Sub-hydrostatic, pumped wells) .............................................. 91 2.2.6 Well Types 6 and 7 (Water Injection/ Disposal wells with/ without tubing) 102 2.3 Subsurface Integrity Test (SIT), Maintenance ............................................................. 113 2.3.1 Well Type 1 (High Pressure Wells or high GLR or H2S Wells) .................. 113 2.3.2 Well Type 2 (Free Flowing Low Pressure Oil Wells, < 20,000 kPa) .......... 114 2.3.3 Well Type 3 (Gas lift Wells) ........................................................................ 115 2.3.4 Well Type 4 (Steam Injection with Packer) ................................................ 116 2.3.5 Well Type 5 (Sub-hydrostatic, pumped wells) ............................................ 117 2.3.6 Well Types 6 and 7 (Water Injection/ Disposal wells with/ without tubing) 118 2.4 Preventive Well Maintenance of Wellhead related Surface Equipment ....................... 119 2.4.1 Preventive Maintenance of OTIS Control Panels ....................................... 119 2.4.2 Preventive Maintenance of Beam Pumps .................................................. 119 Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 5 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.5 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Corrective Well Maintenance ....................................................................................... 122 2.5.1 General Checks .......................................................................................... 122 2.5.2 Christmas Tree Change-Out ...................................................................... 123 2.5.3 Corrective Maintenance of Christmas Tree Valves and Components ....... 131 2.6 Procedure for acid soaking to clean Tubing hanger BPV thread profile ...................... 145 2.6.1 Safety Precautions while attempting acid soak. ......................................... 145 2.6.2 Procedure for filling acid in Christmas tree ................................................ 146 3 Identified Hazards and Threats .......................................................................................... 147 4 Roles and Responsibilities as referred to in this document ............................................... 149 5 Appendices ........................................................................................................................ 150 5.1 Appendix 1, Forms and Reports .................................................................................. 150 5.2 Appendix 2, Glossary of Terms, Abbreviations and Definitions ................................... 150 5.3 Appendix 3, Related Business Control Documents and References ........................... 151 5.4 Wellhead Maintenance Guides .................................................................................... 153 5.4.1 Cameron ..................................................................................................... 153 5.4.2 FMC ............................................................................................................ 157 5.4.3 Ingram Cactus ............................................................................................ 159 5.4.4 McEvoy Model ‘C’ Style ‘Y’ Blocks ............................................................. 161 TABLE OF FIGURES (Double-click to view in presentation mode) Figure 2-1, Stem Packing with Check Valve ............................................................................. 141 Figure 2-2, Low Pressure Grease Fitting .................................................................................. 141 Figure 2-3, Explosion Drawing of Valve .................................................................................... 142 Figure 5-1, Valve Drawing Sealant and Body Filler Connections ............................................. 163 LIST OF TABLES Table 1-1, Well Types and Colour Coding .................................................................................... 7 Table 2-1, SCSSSV Control line pressure Limits in kPa............................................................. 13 Table 2-2, SCSSSV Control line pressure Limits in kPa............................................................. 21 Table 2-3, Test Pressures for Annuli Tests ................................................................................. 53 Table 2-4, FLS Gate Valve, Description of Parts ...................................................................... 141 Table 4-1, Roles and Responsibilities ....................................................................................... 149 Table 5-1, Glossary of Terms, Abbreviations and Definitions ................................................... 150 Table 5-2, Related Business Control Documents and References .......................................... 151 LIST OF EQUATIONS N/A Page 6 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 1 Introduction 1.1 Background In April 2004 PDO introduced SP-2017, Well Failure Model as the Standard in which PDO’s Well Integrity related requirements are defined, this in line with CP-118, Well Life Cycle Integrity Code of Practice (WLICoP). Since then both these documents have been under continuous development incorporating ideas and challenges brought forward by the members of the Well Integrity Working Group resulting in new versions of these documents. It should be noted that all legacy Well Maintenance related documents, notably PR-1037, PR1472, PR-1474, PR-1477, PR-1484 shall be deemed withdrawn with the official endorsement of this Procedure. The Well Failure Model distinguishes the following categories of well integrity related activities and specifies these for 7 well types in terms of frequency and scope. Well Integrity Testing (Preventive / Planned Maintenance) Wellhead Integrity Test (WIT) (See Chapter 2.1 below) Note: Subsurface Integrity Test (SIT) (See Chapter 2.2 below) Note: The WIT comprises the flow-wetted parts of the completion The WIT comprises all the flow-wetted parts of the completion. WIT and SIT are intended to be interventionless. However it has been recognized that, in order to acquire true knowledge of whether or not a valve can be considered a barrier as per the definition given in SP-1217, Well Control Barriers, there may be a need to set plugs in the completion or the wellhead and pressure test against these to establish their integrity. Such a test would be called a Pressure Integrity Test, PIT. It is PDO’s aim to move to interventionless integrity testing using novel technologies. Subsurface Integrity Test (SIT), Maintenance (Chapter 2.3) The seven Well Types are1: Table 1-1, Well Types and Colour Coding Well Types Color Coding in this document Well Type 1 High Pressure Well - >20,000 kPa (Actual CITHP) or high GLR (>300:1 gas to liquid ratio) or high H2S (>500ppm) Well Type 2 Free Flowing low pressure Oil Well - < 20,000 kPa Well Type 3 Gaslift Well Well Type 4 Steam Injection well Well Type 5 Sub-hydrostatic pumped well, minimum one casing string with or without packer The Colour Coding was introduced to prevent the user from accidentally “slipping” into the wrong well type, this as the procedures are similar yet different in the detail. 1 Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 7 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Well Types Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Color Coding in this document Well Types 6 and 7 1) Water Injection / Disposal Well (with tubing) 2) Water Disposal Well (no tubing) Suspended Wells (not listed as separate Well Type in the Well Failure Model) This Procedure further covers: 1) Preventive Well Maintenance of Wellhead related Surface Equipment (Chapter 2.4) 2) Corrective Well Maintenance (Chapter 2.5) 3) Procedure for acid soaking to clean Tubing hanger BPV thread profile (Chapter 2.6) 1.2 Purpose This Procedure sets out the standards which all Well Maintenance related operations have to conform to. It forms the framework from which detailed work practice procedures can be developed and maintained by PDO and contractor companies who perform operations on behalf of PDO. 1.3 Scope This Procedure is applicable to all Well Integrity related operations conducted either by PDO or Contractor personnel on all PDO well equipment. 1.4 Distribution/Target Audience This document will be distributed to all PDO Section Heads who have interfaces with the Well Services Operations, all Well Services Supervisors and Contractor Supervisors. 1.5 Review and Improvement Any user of this document who wishes to provide constructive feedback, or who encounters a mistake or confusing entry is requested to immediately notify the Document Custodian. This document shall be reviewed as necessary by theDocument Custodian, but no less frequently than every four years. Triggers for full or partial review of this Procedure are listed in PR-1444, Well Engineering Management Framework in Chapter 5.2.4, Document Review. 1.6 Step-out and Approval Step-Outs shall be managed as described in PR-1444, Well Engineering Management Framework in Chapter 5.2.1, Variance from a Standard (Step-Out) The Step-Out Request Form can be downloaded from here. Page 8 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2 Procedure Description Whenever a SIT is carried out it shall be combined with a WIT. Where pressure exists for testing, a differential pressure shall be applied across the valve being tested by blowing down the flow line or downstream fixed volume to the minimum pressure practical. Where it is not possible to blow down the flow line fully, the minimum pressure differential (ΔP) at the start of test shall be 1.2 times the Allowable Leak Rate by valve size as stated above. Note : The reasoning behind this rule is that the purpose of leak testing valves is to assess their likely performance in the worst case scenario; for a Christmas Tree valve this is isolation of the well in case of a flow line rupture. In a failure situation, a greater pressure differential would exist across the valve than under test conditions; so a “pass” under test conditions demonstrates integrity. A “fail” under these conditions will also have occurred before the valve has equalised; therefore this method is deemed to be a valid test method. Where no well pressure exists in lieu of testing, the valve shall be cycled and maintained in accordance with manufacturers instructions; this shall be deemed a test ‘Pass’. Note: Whenever a SIT is carried out in conjunction with a WIT, the valves will be tested using applied pressure above LMV, if fitted, or UMV. The decision not to set a Two-Way Check Valve below the tree (which would give information on the integrity of the lowest Master Valve) is based on a Risk/ Cost/ Value judgement; the value of knowing the result of the Master Valve’s status is outweighed by the effort/ cost of achieving a valid test. In risk term this judgement leads to a rating of C2 on the PDO Risk Matrix. In situations where CITHP is > 0 but corresponding to < 1.2 x Allowable Leak Rate, pressure equalisation across the valve within the test period will be deemed a test ‘Fail’ as it demonstrates condition degradation. The Pressure Measurement Method can be either by Pressure Build-up within an enclosed volume or by Bleed-off from an enclosed volume. Note: When a valve test is carried out it is vital to maintain a small positive pressure in the cavity to be tested, this to ensure a. that there is no zero error on the gauge b. that the cavity to be tested is already filled with fluid Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 9 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.1 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Wellhead Integrity Test (WIT) 2.1.1 Suspended Wells When a well of any type has been suspended, the following test shall be carried out to confirm suspension and valve(s) integrity. Where a tree is still fitted, the standard tree test shall be carried prior to the Suspension Plug test below. WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test Suspension Valve(s)” 2.1.1.1 ALL WELL TYPES TASK CODE SUVIW/ SUVOW TASK DECRIPTION Leak-off test Suspension Valve(s) 1) Ensure the Suspension Valve is closed. 2) Bleed off downstream pressure. 3) Install the Test Manifold and a secured flexible bleed line from the appropriate Valve to a portable waste container in accordance with . 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Open the Suspension Valve to check for pressure. a. Where no pressure exists for testing, maintain the valve(s) as per the Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. b. Where pressure exists for testing, close the Outer or only Suspension Valve. 6) Bleed Suspension Valve downstream pressure. 7) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) Measure the pressure build-up above the Suspension Valve over 10 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate. 9) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 10) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 11) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 12) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.1.1.2 Carry out Steps 6 to 12 for the second valve where two valves are fitted! WIT Task “Leak-off Test Down-Hole Plug” ALL WELL TYPES TASK CODE SUPW TASK DECRIPTION Leak-off test Down-Hole Plug 1) Open the Suspension Valve(s). 2) Bleed off the pressure above the plug in stages to a portable waste drum; monitor returns. Note: Where returns are gas, bleed off to atmosphere if safe to do so (e.g. no H2S) 3) Where pressure cannot be bled down or where the returns are in excess of available Page 10 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC ALL WELL TYPES TASK CODE SUPW TASK DECRIPTION Leak-off test Down-Hole Plug storage capacity, abort the test and record test as ‘Fail’. Note: Record the type of returned fluid in the ‘free text’ field in the WIMS WIT Checklist to aid the investigation. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up in the tubing and the Tree Cavity over 4 hours as described in the note below. Use the Well Failure Model ‘Leak Rate Equation’ to determine if the leak rate is acceptable. Note: Where a well is plugged or suspended, first carry out the Tree Valve Leak-off test using any pressure that has built up above the plug. Then bleed off the pressure above the plug, close in the bleed and carry out and extended (4 hour) inflow test on the plug recording the results at ½ hour average over the test period (i.e. one eighth of the observed rise over the 4 hour test period). Simply cycle and maintain the tree valves where no pressure is initially seen above the plug. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. Note: Printed 15/02/16 WIMS Master Data for the well will be adapted to include allowable leak rates for any plugs fitted. So check WIMS to confirm the calculated allowable leak rate! PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 11 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.1.2 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Well Type 1 (High Pressure Wells or high GLR or H2S Wells) The Testing Frequency is as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.1.2.1 Safety Precautions 2.1.2.1.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.1.2.1.2 H2S Well Type 1, High Risk Wells, comprises H2S wells. This Chapter highlights the particularities relating to H2S wells and provides links to Reference Documents. 1) Comply with all items outlined in SP-1219, Drilling Specification Hydrogen Sulphide. 2) A calibrated pressure gauge fitted to the tree cap with bleed facility (in line with H2S controls) maybe bled off to outside fence downwind of the work area. 2.1.2.2 General Preparation 1) Fit a calibrated pressure gauge with bleed facility to the tree cap. Pressure can be bled off to a portable waste drum. 2) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 3) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 2.1.2.3 Notes of Guidance 1. The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 2. Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes; SCSSSV test leak test durations are 30 minutes. 3. Where a valve to be tested is NOT fitted, omit the respective task. 4. The test pressure can be replenished from the reservoir (by opening the Master Valves) or using an external pump unit. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages as listed below: a. Pumping ...................... keeps UMV test barrier intact but introduces HSE risks associated with mechanical tie in to sour HP well b. Cycling UMV ............... avoids mechanical tie-in risk but breaks UMV tested barrier. Note: Page 12 Either method can be used provided risks are considered. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 5. The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). 6. Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test 7. Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions. 2 Table 2-1, SCSSSV Control line pressure Limits in kPa Minimum Pressure to activate flapper to open 3.5”, 13.7 lbs/ft Completion String 3.5”, 10.2 lb/ft Completion String 4.5”, 16.9 lb/ft Completion String Minimum pressure to activate the flapper to open = expected CITHP + 12,500 kPa (Flapper Opening Pressure) + 3,500 kPa (Safety Factor for Equalization) Minimum pressure to activate the flapper to open = expected CITHP + 16,900 kPa (Flapper Opening Pressure) + 3,500 kPa (Safety Factor for Equalization) Minimum pressure to activate the flapper to open = expected CITHP + 15,200 kPa (Flapper Opening Pressure) + 3,500 kPa (Safety Factor for Equalization) The maximum pressure for the control line used in PDO under SAP # 1000004564 is 182,000 kPa. 2.1.2.4 Testing 2.1.2.4.1 WIT Task “Carry out External Leak Test” WELL TYPE 1 WIT TASK CODE ELCW /CAPW TASK DESCRIPTION Carry out external leak check 1) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 2) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: 2.1.2.4.2 Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps WIT Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines….” WELL TYPE 1 WIT TASK CODE ILFW/ PRT/ PRA/ PRB/ PRC TASK DESCRIPTION Flush instrument Impulse Lines & Check Pressure Reading Equipment (Local and remote) 1) Shut in production at the choke, close the HIPPS valve (if fitted), shut in FWV, UMV and LMV to isolate the wellhead from the reservoir and the flow line pressure. Use a hand pump and control line fluid to ensure that all ‘pressure reading’ lines, i.e. those in contact with well fluid, are free from obstruction. 2) Where transmitters are fitted, ensure that actual local pressure gauge readings agree with remote readings. Where differences occur, rectify or note the problem in the ‘free text’ area 2 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term reliability based maintenance frequency. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 13 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC TASK CODE TASK DESCRIPTION Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 1 WIT ILFW/ PRT/ PRA/ PRB/ PRC Flush instrument Impulse Lines & Check Pressure Reading Equipment (Local and remote) of the WIT Checklist. 3) Install a secured flexiline to allow safe pressure bleed-off of sour fluids from the wellhead to a downwind location outside the well site fence area3. 4) Check pressure rating, condition and specification of needle valves and replace as required. Note: Replace all non-standard needle valves with double block and bleed valves. Attention! Industry pressure release incidents have been caused by impulse lines being blocked, leading to actual pressures in annuli not being shown on the gauges. The blockages can be due to either ingress of well fluids or build-up of valve grease. It is therefore vital to ensure impulse lines are clear before attempting any tests or maintenance activities. 2.1.2.4.3 WIT Task “Function/ leak-off test Flow Wing Valve (Inner or only)” WELL TYPE 1 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW/ FWVOW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve (Inner or only) Note: This method assumes that a combination of LMV and UMV provides a leak-tight seal. 1) Shut in production at the choke and close HIPPS valve (to be done remotely by Production Operations). 2) ‘Zero check’ the ‘methanol line’ or ‘flow line’ pressure gauge, ensuring the line to the gauge is open. 3) ‘Zero check’ the Swab Valve Pressure Gauge, ensuring that the Swab Valve and the line to Gauge are open. 4) Close LMV and UMV. 5) Open FWV. 6) Bleed off pressure between HIPPS, where fitted, or Location and wellhead through KWV. 7) Close KWV and FWV. 8) Replenish Tree Cavity pressure by either pumping or cycling LMV and UMV. 9) Record “Test Start” pressure at the swab pressure gauge in the WIMS Checklist. 10) Measure the pressure drop in the enclosed tree cavity over 10 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate. a. Monitor the pressure rise in the enclosed flow line section between the HIPPS and the FWV, using the ‘methanol line’ or ‘flow line’ Pressure Gauge. Note: If the pressure rise observed on the monitoring gauge exceeds the pressure rise corresponding to the ‘Allowable Leak Rate’, specified in the Well Failure Model (‘Allowable leak rate’ sheet), the FWV is recorded as a ‘Fail’; such a result also suggests that the combination of UMV/ LMV is also a ’Fail’. In this instance, grease all valves and re-test FWV. If the result is the same then the Well Services Supervisor or the Asset Well Integrity Engineer must be 3 All Harweel well sites are equipped with permanent H2S and noise monitors which may trigger audible alarms and HIPPS / SSV closure. Page 14 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 1 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW/ FWVOW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve (Inner or only) informed before taking any further action. 11) Record Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 12) If the test result is within the allowable leak rate for the tested valve’s size, record the test as a ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 13) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 14) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressure’ and number of tests done. 2.1.2.4.4 WIT Task “Function/ leak off test Swab Valve” WELL TYPE 1 WIT TASK CODE TASK DESCRIPTION 1) Close SV. SVW Function/ Leak-off test Swab Valve 2) Open UMV and LMV. 3) Bleed SV downstream cavity. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record the test ‘‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up above the SV over 10 minutes using using a gauge known to be accurate. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.2.4.5 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only)” WELL TYPE 1 WIT TASK CODE KWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only) 1) Close KWVI if not already closed. 2) Bleed down KWVI downstream cavity and install a pressure gauge and double block and Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 15 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC TASK CODE TASK DESCRIPTION bleed system. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 1 WIT KWVIW Function / Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only) 3) Re-pressurize the tree body if required by the chosen method and allow the pressure in the tree body to stabilize. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record test ‘‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the KWVI over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.1.2.4.6 Repeat this Procedure for the KWVO, if fitted. WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Upper Master Valve UMV” TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 1) Close UMV WELL TYPE 1 WIT UMVW Function/ Leak-off test Upper Master Valve 2) Open SV or KWV (dependent on where the measurement will be taken) 3) Open the bleed facility to bleed down the Tree Cavity to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record the test ‘‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up in the Tree Cavity over 10 minutes. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Page 16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.1.2.4.7 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Lower Master Valve LMV” WELL TYPE 1 WIT TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 1) Close LMV. LMVW Function/ Leak-off test Lower Master Valve 2) Open UMV. 3) Open the bleed facility to bleed down the Tree Cavity to as near zero as possible; maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record the test ‘‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up over 10 minutes. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.2.4.8 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Down-Hole Safety Valve” WELL TYPE 1 WIT TASK CODE SSSVW/ APRW/ CLA TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak-off test Down-Hole Safety Valve e.g. SCSSSV/ ICV/ Storm Choke or Plug 1) Open the LMV, record the CITHP. 2) Close the SCSSSV by trip function locally. 3) Open the FWV. 4) Using the choke, bleed off the pressure above the closed SCSSSV in stages to flow line pressure. 5) Close FWV. 6) Bleed off the remaining pressure through the flexiline, hooked up to the KWV. 7) Close in the bleed point. 8) Record the A annulus pressures at the start of the test. 9) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 10) Measure the pressure build-up in the tubing and the Tree Cavity over 30 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate; use the Well Failure Model ‘Leak Rate Equation’ to determine if the leak rate is acceptable. 11) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 12) Record the A Annulus pressure at the end of the test. 13) Whilst conducting the above build-up survey, confirm (e.g. by looking, listening and feeling) Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 17 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 1 WIT SSSVW/ APRW/ CLA Function/ Leak-off test Down-Hole Safety Valve e.g. SCSSSV/ ICV/ Storm Choke or Plug that there is no communication with the reservoir through the Control Line. TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 14) If the first test fails, cycle the valve and re-test it until the test results in a ‘Pass’ or no improvement in results is seen. Ensure that the pressure across the SCSSSV is equalized before cycling. A pump may be required to obtain pressure above the SCSSSV. 15) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including the ‘‘Start’ and the ‘Finish’ pressure and the ‘Number of Tests done’. 16) Bleed off any built-up pressure through the chosen bleed point. 17) Maintain (e.g. grease or lubricate) all Tree Valves. 18) Re-open the SCSSSV. 19) Adjust the Control Line pressure to within the limits stated and record the pressure in the WIT Checklist. Recommend control line pressures, but do not adjust at the Wellhead Panel. Notes: 1.) WIMS Master Data for the well will be adapted to include allowable leak rates for SSSV’s. So check WIMS to confirm the calculated allowable leak rate! 2.) Where a well is plugged or suspended, first carry out the Tree Valve Leak-off test using any pressure that has built up above the plug. Then bleed off the pressure above the plug, close in the bleed and carry out and extended (4 hour) inflow test on the plug recording the results at ½ hour average over the test period (i.e. one eighth of the observed rise over the 4 hour test period). Simply cycle and maintain the tree valves where no pressure is initially seen above the plug. 3.) For SCSSSV’s with no equalizing feature it will be necessary to equalise the pressure across the valve with inhibited water by means of a high pressure pump hooked up to the kill wing valve. 2.1.2.4.9 WIT Task “Visual Inspection instrumentation or fitting weeps” of condition/ deflection / clashes / WELL TYPE 1 WIT VIW Visual Inspection of the condition/ deflection / clashes instrumentation or fitting weeps 1) Visually inspect all tree components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the WIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 2) Visually inspect wind socks and other related well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as required. Note: As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. 2.1.2.4.10 WIT Task “Function/ Maintain remaining Annulus Valves” TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION WELL TYPE 1 WIT MAVW/ MTVW Function / Maintain all Tree Valves and remaining Annulus Valves Page 18 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 1 WIT TASK CODE MAVW/ MTVW TASK DECRIPTION Function / Maintain all Tree Valves and remaining Annulus Valves 1) Lubricate or grease all tree and annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. Note: Printed 15/02/16 To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves (especially tree valves) are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of test result. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 19 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.1.3 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Well Type 2 (Free Flowing Low Pressure Oil Wells, < 20,000 kPa) The Testing Frequency is as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.1.3.1 Safety Precautions 2.1.3.1.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.1.3.2 General Preparation 1) Fit a calibrated pressure gauge with bleed facility to the tree cap. Pressure can be bled off to a portable waste drum. 2) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 3) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 2.1.3.3 Notes of Guidance 1. The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 2. Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes; SCSSSV test leak test durations are 30 minutes. 3. Where a valve to be tested is NOT fitted, omit the respective task. 4. The test pressure can be replenished from the reservoir (by opening the Master Valves) or using an external pump unit. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages as listed below: a. Pumping..................... keeps UMV test barrier intact but introduces HSE risks associated with mechanical tie in to sour HP well b. Cycling UMV .............. avoids mechanical tie-in risk but breaks UMV tested barrier. Note: Either method can be used provided risks are considered. 5. The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). 6. Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test 7. Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions. 4 4 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term reliability based maintenance frequency. Page 20 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Table 2-2, SCSSSV Control line pressure Limits in kPa Minimum Pressure to activate flapper to open 3.5”, 13.7 lbs/ft Completion String 3.5”, 10.2 lb/ft Completion String 4.5”, 16.9 lb/ft Completion String Minimum pressure to activate the flapper to open = expected CITHP + 12,500 kPa (Flapper Opening Pressure) + 3,500 kPa (Safety Factor for Equalization) Minimum pressure to activate the flapper to open = expected CITHP + 16,900 kPa (Flapper Opening Pressure) + 3,500 kPa (Safety Factor for Equalization) Minimum pressure to activate the flapper to open = expected CITHP + 15,200 kPa (Flapper Opening Pressure) + 3,500 kPa (Safety Factor for Equalization) The maximum pressure for the control line used in PDO under SAP # 1000004564 is 182,000 kPa. 2.1.3.4 Testing 2.1.3.4.1 WIT Task “Carry out External Leak Test” WELL TYPE 2 WIT TASK CODE ELCW /CAPW TASK DESCRIPTION Carry out external leak check 1) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 2) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: 2.1.3.4.2 Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps WIT Task “Visual Inspection instrumentation or fitting weeps” of condition/ deflection / clashes / WELL TYPE 2 WIT VIW Visual Inspection of the condition/ deflection / clashes instrumentation or fitting weeps 1) Visually inspect all tree components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the WIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 2) Visually inspect well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as required. Note: Printed 15/02/16 As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 21 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.1.3.4.3 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WIT Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines….” WELL TYPE 2 WIT TASK CODE ILFW/ PRT/ PRA/ PRB/ PRC TASK DESCRIPTION Flush instrument Impulse Lines & Check Pressure Reading Equipment (Local and remote) 1) Shut in production at the choke, close the HIPPS valve (if fitted), shut in FWV, UMV and LMV to isolate the wellhead from the reservoir and the flow line pressure. Use a hand pump and control line fluid to ensure that all ‘pressure reading’ lines, i.e. those in contact with well fluid, are free from obstruction. 2) Where transmitters are fitted, ensure that actual local pressure gauge readings agree with remote readings. Where differences occur, rectify or note the problem in the ‘free text’ area of the WIT Checklist. 3) Install a secured flexiline to allow safe pressure bleed-off of fluids from the wellhead to a portable waste drum. 4) Check pressure rating, condition and specification of needle valves and replace as required. Note: Replace all non-standard needle valves with double block and bleed valves. Attention! Industry pressure release incidents have been caused by impulse lines being blocked, leading to actual pressures in annuli not being shown on the gauges. The blockages can be due to either ingress of well fluids or build-up of valve grease. It is therefore vital to ensure impulse lines are clear before attempting any tests or maintenance activities. 2.1.3.4.4 WIT Task “Function/ leak-off test Flow Wing Valve (Inner or only)” WELL TYPE 2 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW/ FWVOW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve (Inner or only) Note: This method assumes that a combination of LMV and UMV provides a leaktight seal. 1) Shut in production at the choke (if fitted), close the ESD Valve or the FWV and close the Location Valve. 2) ‘Zero check’ the ‘flow line’ pressure gauge (if fitted), ensuring the line to the gauge is open. 3) ‘Zero check’ the Swab Valve Pressure Gauge, ensuring that the Swab Valve and the line to the gauge are open. 4) Close UMV and LMV, if fitted. 5) Open FWV. 6) Bleed off pressure between the Location Valve and the Wellhead through the fixed flexible bleed line. 7) Close KWV and FWV. 8) Replenish Tree Cavity pressure by either pumping or cycling UMV and LMV, if fitted. 9) Record Test ‘Start’ pressure at the swab pressure gauge in the WIMS Checklist. 10) Measure the pressure drop in the enclosed tree cavity over 10 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate. a. Monitor the pressure rise in the enclosed flow line section between the FWV and the Location Valve using the Flow line Pressure Gauge. Note: Page 22 If the pressure rise observed on the monitoring gauge exceeds the pressure rise corresponding to the ‘Allowable Leak Rate’, specified in the Well Failure PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 2 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW/ FWVOW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve (Inner or only) Model (‘Allowable leak rate’ sheet), the FWV is recorded as a ‘Fail’; such a result also suggests that the combination of UMV/ LMV is also a ’Fail’. In this instance, grease all valves and re-test FWV. If the result is the same then the Well Services Supervisor or the Asset Well Integrity Engineer must be informed before taking any further action. 11) Record Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 12) If the test result is within the allowable leak rate for the tested valve’s size, record the test as a ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 13) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 14) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressure’ and number of tests done. 2.1.3.4.5 WIT Task “Function/ leak off test Swab Valve” WELL TYPE 2 WIT TASK CODE TASK DESCRIPTION 1) Close SV. SVW Function/ Leak-off test Swab Valve 2) Open UMV and LMV. 3) Bleed SV downstream cavity. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up above the SV over 10 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 23 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.1.3.4.6 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only)” WELL TYPE 2 WIT TASK CODE KWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only) 1) Close KWVI if not already closed. 2) Bleed KWVI downstream cavity and install a pressure gauge and double block and bleed system. 3) Re-pressurize the tree body if required by the chosen method and allow the pressure in the tree body to stabilize. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the KWVI over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.3.4.7 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Upper Master Valve UMV” WELL TYPE 2 WIT TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 1) Close UMV UMVW Function/ Leak-off test Upper Master Valve 2) Open SV or KWV (dependent on where the measurement will be taken) 3) Open the bleed facility to bleed down the Tree Cavity to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up in the Tree Cavity over 10 minutes. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Page 24 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.1.3.4.8 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Lower Master Valve LMV” TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 1) Close LMV. WELL TYPE 2 WIT LMVW Function/ Leak-off test Lower Master Valve (if fitted) 2) Open UMV. 3) Open the bleed facility to bleed the Tree Cavity to as near zero as possible; maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up over 10 minutes. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.3.4.9 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Down-Hole Safety Valve” WELL TYPE 2 WIT TASK CODE SSSVW/ APRW/ CLA TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak-off test Down-Hole Safety Valve e.g. SCSSSV 1) Open the LMV or UMV, record the CITHP. 2) Close the SCSSSV by trip function locally. 3) Open the FWV. 4) Using the choke, bleed off the pressure above the closed SCSSSV in stages to flow line pressure. 5) Close FWV. 6) Bleed off the remaining pressure through the secured flexiline. 7) Close in the bleed point. 8) Record the A annulus pressures at the start of the test. 9) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 10) Measure the pressure build-up in the tubing and the Tree Cavity over 30 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate; use the Well Failure Model ‘Leak Rate Equation’ to determine if the leak rate is acceptable. 11) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 25 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 2 WIT TASK CODE SSSVW/ APRW/ CLA TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak-off test Down-Hole Safety Valve e.g. SCSSSV 12) Record the A Annulus pressure at the end of the test. 13) Whilst conducting the above build-up survey, confirm (e.g. by looking, listening and feeling) that there is no communication with the reservoir through the Control Line. 14) If the first test fails, cycle the valve and re-test it until the test results in a ‘Pass’ or no improvement in results is seen. Ensure that the pressure across the SCSSSV is equalized before cycling. A pump may be required to obtain pressure above the SCSSSV. 15) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including the ‘Start’ and the ‘Finish’ pressure and the ‘Number of Tests done’. 16) Bleed off any built-up pressure through the chosen bleed point. 17) Maintain (e.g. grease or lubricate) all Tree Valves. 18) Re-open the SCSSSV. 19) Adjust the Control Line pressure to within the limits stated and record the pressure in the WIT Checklist. Recommend control line pressures, but do not adjust at the Framo Panel. Notes: 1.) WIMS Master Data for the well will be adapted to include allowable leak rates for SSSV’s. So check WIMS to confirm the calculated allowable leak rate! 2.) Where a well is plugged or suspended, first carry out the Tree Valve Leak-off test using any pressure that has built up above the plug. Then bleed off the pressure above the plug, close in the bleed and carry out and extended (4 hour) inflow test on the plug recording the results at ½ hour average over the test period (i.e. one eighth of the observed rise over the 4 hour test period). Simply cycle and maintain the tree valves where no pressure is initially seen above the plug. 3.) For SCSSSV’s with no equalizing feature it will be necessary to equalise the pressure across the valve with inhibited sea water by means of a high pressure pump hooked up to the kill wing valve. 2.1.3.4.10 WIT Task “Function/ Maintain remaining Annulus Valves” WELL TYPE 2 WIT TASK CODE MAVW/ MTVW TASK DECRIPTION Function / Maintain all Tree Valves and remaining Annulus Valves 1) Lubricate or grease all tree and annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. Note: Page 26 To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves (especially tree valves) are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of test result. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.1.4 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Well Type 3 (Gas lift Wells) The Testing Frequency as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.1.4.1 Safety Precautions 2.1.4.1.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.1.4.2 General Preparation 1) Fit a calibrated pressure gauge with bleed facility to the tree cap. Pressure can be bled off to a portable waste drum. 2) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 3) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 2.1.4.3 Notes of Guidance 1. The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 2. Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes. 3. If CITHP drops to below the required ΔP (1.2 times the Allowable Leak Rate) during the test, then replenish CITHP using gas lift pressure. Note: Valve tests shall be carried out with gas lift supply isolated to prevent annulus overpressurization or bullheading into the reservoir. 4. FWV and KWV tests can be carried out at the same time to reduce deferment but SV should be monitored during test to see any decay. 5. Where a valve to be tested is NOT fitted, omit the respective task. 6. The test pressure can be replenished from the reservoir (by opening the Master Valves) or using an external pump unit. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages as listed below: a. Pumping .................... keeps UMV test barrier intact but introduces HSE risks associated with mechanical tie in to sour HP well b. Cycling UMV.............. avoids mechanical tie-in risk but breaks UMV tested barrier. Note: Printed 15/02/16 Either method can be used provided risks are considered. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 27 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 7. The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). 8. Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test 9. Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions. 5 2.1.4.4 Testing 2.1.4.4.1 WIT Task “Carry out External Leak Test” WELL TYPE 3 WIT TASK CODE ELCW /CAPW TASK DESCRIPTION Carry out external leak check 1) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 2) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: 2.1.4.4.2 Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps WIT Task “Visual Inspection instrumentation or fitting weeps” of condition/ deflection / clashes / WELL TYPE 3 WIT TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION VIW Visual Inspection of the condition/ deflection / clashes instrumentation or fitting weeps 1) Visually inspect all tree components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the WIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. 2) Visually inspect well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as required. Note: As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. 5 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term reliability based maintenance frequency. Page 28 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.1.4.4.3 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WIT Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines….” WELL TYPE 3 WIT TASK CODE ILFW/ PRT/ PRA/ PRB/ PRC TASK DESCRIPTION Flush instrument Impulse Lines & Check Pressure Reading Equipment (Local and remote) 1) Shut in production at the choke, close FWV, UMV and LMV to isolate the wellhead from the reservoir and the flow line from the gas lift supply. Use a hand pump and control line fluid to ensure that all ‘pressure reading’ lines, i.e. those in contact with well fluid, are free from obstruction. 2) Where transmitters are fitted, ensure that actual local pressure gauge readings agree with remote readings. Where differences occur, rectify or note the problem in the ‘free text’ area of the WIT Checklist. 3) Install a secured flexiline to allow safe pressure bleed-off of fluids from the wellhead to a portable waste drum. 4) Check pressure rating, condition and specification of needle valves and replace as required. Note: Replace all non-standard needle valves with double block and bleed valves. Attention! Industry pressure release incidents have been caused by impulse lines being blocked, leading to actual pressures in annuli not being shown on the gauges. The blockages can be due to either ingress of well fluids or build-up of valve grease. It is therefore vital to ensure impulse lines are clear before attempting any tests or maintenance activities. 2.1.4.4.4 WIT Task “Function/ leak-off test Flow Wing Valve (Inner or only)” WELL TYPE 3 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve 1) Shut in production at the choke (if fitted) and the FWV. 2) Isolate the gas lift supply by closing the annulus valves. 3) Close the Location Valve. 4) ‘Zero check’ the ‘flow line’ pressure gauge (if fitted), ensuring the line to the gauge is open. 5) ‘Zero check’ the Swab Valve Pressure Gauge, ensuring that the Swab Valve and the line to the gauge are open. Note: Monitoring CITHP during FWV test makes test pressure decay noticeable. 6) Bleed off pressure between the Location Valve and the Wellhead through a fixed flexible bleed line into a portable waste drum. 7) Record Test ‘Start’ pressure at the flow line pressure gauge in the WIMS Checklist. 8) Measure the build-up in the flow line between the FWV and Location valve using the flow line Pressure Gauge. Note: If the integrity of the FWV is suspect continue the Integrity test with the Master Valve. 9) Record Test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 10) If the test result is within the allowable leak rate for the tested valve’s size, record the test as a ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 29 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 3 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve 11) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 12) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressure’ and number of tests done. 2.1.4.4.5 WIT Task “Function/ leak off test Swab Valve” WELL TYPE 3 WIT TASK CODE TASK DESCRIPTION 1) Close SV. SVW Function/ Leak-off test Swab Valve 2) Bleed SV downstream cavity. 3) Close in the bleed point. 4) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up above the SV over 10 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate. 6) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.4.4.6 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only)” WELL TYPE 3 WIT TASK CODE KWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only) 1) Close KWVI if not already closed. 2) Bleed KWVI downstream cavity and install a pressure gauge and double block and bleed system. 3) Close in the bleed point. 4) Record test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the KWVI over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the Page 30 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 3 WIT TASK CODE KWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only) result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.4.4.7 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Upper Master Valve UMV” TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 1) Close UMV WELL TYPE 3 WIT UMVW Function/ Leak-off test Upper Master Valve 2) Open SV or KWV (dependent on where the measurement will be taken) 3) Open the bleed facility to bleed down the Tree Cavity to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up in the Tree Cavity over 10 minutes. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.4.4.8 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Lower Master Valve LMV” TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 1) Close LMV. WELL TYPE 3 WIT LMVW Function/ Leak-off test Lower Master Valve (if fitted) 2) Open UMV. 3) Open the bleed facility to bleed the Tree Cavity to as near zero as possible; maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Close in the bleed point. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 31 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 3 WIT TASK CODE LMVW TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak-off test Lower Master Valve (if fitted) 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up over 10 minutes. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.4.4.9 WIT Task “Function/ Maintain remaining Annulus Valves” WELL TYPE 3 WIT TASK CODE MAVW/ MTVW TASK DECRIPTION Function / Maintain all Tree Valves and remaining Annulus Valves 1) Lubricate or grease all tree and annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. Note: Page 32 To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves (especially tree valves) are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of test result. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.1.5 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Well Type 4 (Steam Injection Wells) The Testing Frequency as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.1.5.1 Safety Precautions 2.1.5.1.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.1.5.2 General Preparation 1) Fit a calibrated pressure gauge with bleed facility to the tree cap. Pressure can be bled off to a portable waste drum. 2) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 3) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 2.1.5.3 Notes of Guidance 1. The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 2. Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes. 3. FWV and KWV tests can be carried out at the same time to reduce deferment but SV should be monitored during test to see any decay. 4. Where a valve to be tested is NOT fitted, omit the respective task. 5. The well to be tested must be closed in well in advance prior to the test in order to cool down sufficiently to allow intervention by personnel. Experience shows that the required cooling period may vary between ‘over night’ in the winter and up to three days in the summer. This must be taken into account when planning a WIT or SIT on a steam well. 6. The test pressure must only be replenished from the reservoir (by opening the Master Valves). If a fluid was used and subsequently accidentally trapped in any valve cavity, temperature increase during production could lead to fluid evaporation, associated with an uncontrolled pressure increase. This in turn could lead to compromising the well integrity. 7. The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 33 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 8. Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test 9. Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions. 6 2.1.5.4 Testing 2.1.5.4.1 WIT Task “Carry out External Leak Test” WELL TYPE 4 WIT TASK CODE ELCW /CAPW TASK DESCRIPTION Carry out external leak check 1) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 2) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: 2.1.5.4.2 Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps WIT Task “Visual Inspection instrumentation or fitting weeps” of condition/ deflection / clashes / WELL TYPE 4 WIT TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION VIW Visual Inspection of the condition/ deflection / clashes instrumentation or fitting weeps 1) Visually inspect all tree components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the WIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. 2) Visually inspect well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as required. Note: 2.1.5.4.3 As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. WIT Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines….” WELL TYPE 4 WIT TASK CODE ILFW/ PRT/ PRA/ PRB/ PRC TASK DESCRIPTION Flush instrument Impulse Lines & Check Pressure Reading Equipment (Local and remote) 1) Shut in production at the choke, close FWV, UMV and LMV to isolate the wellhead from the reservoir and the flow line from the gas lift supply. Use a hand pump and control line fluid to ensure that all ‘pressure reading’ lines, i.e. those in contact with well fluid, are free from obstruction. 2) Where transmitters are fitted, ensure that actual local pressure gauge readings agree with remote readings. Where differences occur, rectify or note the problem in the ‘free text’ area 6 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term reliability based maintenance frequency. Page 34 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC TASK CODE TASK DESCRIPTION WELL TYPE 4 WIT ILFW/ PRT/ PRA/ PRB/ PRC Flush instrument Impulse Lines & Check Pressure Reading Equipment (Local and remote) of the WIT Checklist. 3) Install a secured flexiline to allow safe pressure bleed-off of fluids from the wellhead to a portable waste drum. 4) Check pressure rating, condition and specification of needle valves and replace as required. Note: Replace all non-standard needle valves with double block and bleed valves. Attention! Industry pressure release incidents have been caused by impulse lines being blocked, leading to actual pressures in annuli not being shown on the gauges. The blockages can be due to either ingress of well fluids or build-up of valve grease. It is therefore vital to ensure impulse lines are clear before attempting any tests or maintenance activities. 2.1.5.4.4 WIT Task “Function/ leak-off test Flow Wing Valve (Inner or only)” WELL TYPE 4 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve Note: This method assumes that the Master Valve provides a leak-tight seal. 1) Shut in production at the choke (if fitted) and the FWV. 2) Close the Location Valve. 3) ‘Zero check’ the ‘flow line’ pressure gauge (if fitted), ensuring the line to the gauge is open. 4) ‘Zero check’ the Swab Valve Pressure Gauge, ensuring that the Swab Valve and the line to the gauge are open. Note: Monitoring CITHP during FWV test makes test pressure decay noticeable. 5) Bleed off pressure between the Location Valve and the Wellhead through a fixed flexible bleed line into a portable waste drum. 6) Record Test ‘Start’ pressure at the flow line pressure gauge in the WIMS Checklist. 7) Measure the build-up in the flow line between the FWV and Location valve using the flow line Pressure Gauge. Note: If the pressure rise observed on the monitoring gauge exceeds the pressure rise corresponding to the ‘Allowable Leak Rate’, specified in the Well Failure Model (‘Allowable leak rate’ sheet), the FWV is recorded as a ‘Fail’; such a result also suggests that the Location Valve is also a ’Fail’. In this instance, grease all valves and re-test FWV. If the result is the same then the Well Services Supervisor or the Asset Well Integrity Engineer must be informed before taking any further action. 8) Record Test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 9) If the test result is within the allowable leak rate for the tested valve’s size, record the test as a ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 10) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 35 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 4 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve 11) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressure’ and number of tests done. 2.1.5.4.5 WIT Task “Function/ leak off test Swab Valve” TASK CODE TASK DESCRIPTION 1) Close SV. WELL TYPE 4 WIT SVW Function/ Leak-off test Swab Valve 2) Bleed SV downstream cavity. 3) Close in the bleed point. 4) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up above the SV over 10 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate. 6) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.5.4.6 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only)” WELL TYPE 4 WIT TASK CODE KWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only) 1) Close KWVI if not already closed. 2) Bleed KWVI downstream cavity and install a pressure gauge and double block and bleed system. 3) Close in the bleed point. 4) Record test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the KWVI over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. Page 36 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 4 WIT TASK CODE KWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only) b. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.5.4.7 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Upper Master Valve UMV” WELL TYPE 4 WIT TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 1) Close UMV UMVW Function/ Leak-off test Upper Master Valve 2) Open SV or KWV (dependent on where the measurement will be taken) 3) Open the bleed facility to bleed down the Tree Cavity to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up in the Tree Cavity over 10 minutes. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. b. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.5.4.8 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Lower Master Valve LMV” TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 1) Close LMV. WELL TYPE 4 WIT LMVW Function/ Leak-off test Lower Master Valve (if fitted) 2) Open UMV. 3) Open the bleed facility to bleed the Tree Cavity to as near zero as possible; maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Close in the bleed point. 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up over 10 minutes. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 37 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 4 WIT TASK CODE LMVW TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak-off test Lower Master Valve (if fitted) number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. b. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.5.4.9 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test Downhole Plugs (if fitted)” WELL TYPE 4 WIT TASK CODE SSSVW/ APRW/ CLA TASK DECRIPTION Leak-off test Down-Hole Plug (if fitted) 1) Open the LMV or UMV, record the CITHP. 2) Open the FWV. 3) Using the choke, bleed off the pressure above the closed SCSSSV in stages to flow line pressure. 4) Close FWV. 5) Bleed off the remaining pressure through the secured flexiline. 6) Close in the bleed point. 7) Record the A annulus pressures at the start of the test. 8) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 9) Measure the pressure build-up in the tubing and the Tree Cavity over 4 hours as described in the note below. Use the Well Failure Model ‘Leak Rate Equation’ to determine if the leak rate is acceptable. Note: Where a well is plugged or suspended, first carry out the Tree Valve Leak-off test using any pressure that has built up above the plug. Then bleed off the pressure above the plug, close in the bleed and carry out and extended (4 hour) inflow test on the plug recording the results at ½ hour average over the test period (i.e. one eighth of the observed rise over the 4 hour test period). Simply cycle and maintain the tree valves where no pressure is initially seen above the plug. 10) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 11) Record the A Annulus pressure at the end of the test. 12) Bleed off any built-up pressure through the chosen bleed point. Note: WIMS Master Data for the well will be adapted to include allowable leak rates for any plugs fitted. So check WIMS to confirm the calculated allowable leak rate! 2.1.5.4.10 WIT Task “Function/ Maintain remaining Annulus Valves” TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION WELL TYPE 4 WIT MAVW/ MTVW Function / Maintain all Tree Valves and remaining Annulus Valves Page 38 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 4 WIT TASK CODE MAVW/ MTVW TASK DECRIPTION Function / Maintain all Tree Valves and remaining Annulus Valves 1) Lubricate or grease all tree and annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. Note: Printed 15/02/16 To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves (especially tree valves) are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of test result. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 39 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.1.6 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Well Type 5 (Sub-hydrostatic, pumped wells) Pumped water supply wells are included in this well type. The Testing Frequency as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.1.6.1 Well type specific risks Flow is controlled electrically rather than hydraulically Peforming a test with the pump running on the SV and KWV. 2.1.6.2 Safety Precautions 2.1.6.2.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.1.6.3 General Preparation 1) Fit a calibrated pressure gauge with bleed facility to the tree cap. Pressure can be bled off to a portable waste drum. 2) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 3) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 4) Ensure that the pump has been electrically isolated prior to start of the WIT in accordance with PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure and SP-1104, Electrical Safety Rules. 2.1.6.4 Notes of Guidance 1. On pumped wells, pressure is unlikely to exist for testing purposes; the primary purpose of a WIT on this well type is therefore to assess the condition and maintain the valves. 2. The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 3. Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes. 4. Where a valve to be tested is NOT fitted, omit the respective task. 5. The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). 6. Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test Page 40 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 7. Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions.7 2.1.6.5 Testing 2.1.6.5.1 WIT Task “Adjust Stuffing Box Seals” WELL TYPE 5 WIT TASK CODE SPSA TASK DECRIPTION Adjust Stuffing Box Seals This task is specific to rod-pumps 1) Monitor the external leakage from the stuffing box with the pump running. 2) If the Leak rate exceeds those specified in the Well Failure Model, stop the pump and adjust the stuffing box, this to give optimum sealing capability without binding. 3) Restart the pump and re-check leakage. 4) Continue steps 2 to 3 until the observed leak rate is within limits or no further improvement is achieved. 5) Record the result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Inspect the vitraulic joint and report any condition degradation in the ‘Free Text’ box in the WIMS Checklist. 7) Inspect the polished rod and report any condition degradation in the ‘Free Text’ box in the WIMS Checklist. 2.1.6.5.2 WIT Task “Carry out External Leak Test” WELL TYPE 5 WIT TASK CODE ELCW /CAPW TASK DESCRIPTION Carry out external leak check 1) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 2) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: 2.1.6.5.3 Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps WIT Task “Visual Inspection instrumentation or fitting weeps” of condition/ deflection / clashes / WELL TYPE 5 WIT VIW Visual Inspection of the condition/ deflection / clashes instrumentation or fitting weeps 1) Visually inspect all tree components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the WIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 2) Visually inspect well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as 7 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term reliability based maintenance frequency. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 41 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 5 WIT VIW Visual Inspection of the condition/ deflection / clashes instrumentation or fitting weeps required. Note: 2.1.6.5.4 As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. WIT Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines….” WELL TYPE 5 WIT TASK CODE ILFW/ PRT/ PRA/ PRB/ PRC TASK DESCRIPTION Flush instrument Impulse Lines & Check Pressure Reading Equipment (Local and remote) 1) This test shall be carried out with the pump running. 2) Use a hand pump and control line fluid to ensure that all ‘pressure reading’ lines, i.e. those in contact with well fluid, are free from obstruction. 3) Where transmitters are fitted, ensure that actual local pressure gauge readings agree with remote readings. Where differences occur, rectify or note the problem in the ‘free text’ area of the WIT Checklist. 4) Install a secured flexiline to allow safe pressure bleed-off of fluids from the wellhead to a portable waste drum. 5) Check pressure rating, condition and specification of needle valves and replace as required. Note: Replace all non-standard needle valves with double block and bleed valves. Attention! Industry pressure release incidents have been caused by impulse lines being blocked, leading to actual pressures in annuli not being shown on the gauges. The blockages can be due to either ingress of well fluids or build-up of valve grease. It is therefore vital to ensure impulse lines are clear before attempting any tests or maintenance activities. 2.1.6.5.5 WIT Task “Function/ leak off test Swab Valve” WELL TYPE 5 WIT TASK CODE SVW TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off test Swab Valve Note: This test applies to pumped wells without rods 1) This test shall be carried out with the pump running! 2) Close SV. 3) Bleed SV downstream cavity. 4) Close in the bleed point and install Test Manifold. 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up above the SV over 10 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the Page 42 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 5 WIT TASK CODE SVW TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off test Swab Valve number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. The pump must be isolated for greasing and/ or flushing! 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.6.5.6 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only)” WELL TYPE 5 WIT TASK CODE KWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only) Note: This test applies to all types of pumped wells 1) This test shall be carried out with the pump running! 2) Close KWV. 3) Bleed KWV downstream cavity. 4) Close in the bleed point and install Test Manifold. 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up above the KWV over 10 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. The pump must be isolated for greasing and/ or flushing! 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.6.5.7 WIT Task “Function/ leak-off test Flow Wing Valve (Inner or only)” WELL TYPE 5 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve 1) Shut down and electrically isolate the pump 2) Function and maintain the valve in line with the relevant Maintenance Guide. a. Enter ‘Pass’ in the WIMS Checklist where the valve functions correctly. b. Enter ‘Fail’ in the WIMS Checklinst where the valve fails to function and where this Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 43 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 5 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve condition cannot be rectified by the test crew. 2.1.6.5.8 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Upper Master Valve UMV” WELL TYPE 5 WIT TASK CODE UMVW TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak-off test Upper Master Valve Warning: Do NOT function any Master Valve on a rod-type pumped well A: Task Description for non-rod type wells 1) Function and maintain the valve in line with the relevant Maintenance Guide. a. Enter ‘Pass’ in the WIMS Checklist where the valve functions correctly. b. Enter ‘Fail’ in the WIMS Checklinst where the valve fails to function and where this condition cannot be rectified by the test crew B: Task Description for rod type wells 1) Close the valve a maximum of 2 turns to confirm the valve is not seized. Do NOT apply more than 2 turns to the valve as the valve’s gate may impinge on the rod. 2) Maintain the valve in line with the relevant Maintenance Guide. 3) Re-open the valve. 2.1.6.5.9 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Upper Master Valve LMV” WELL TYPE 5 WIT TASK CODE LMVW TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak-off test Upper Master Valve Warning: Do NOT function any Master Valve on a rod-type pumped well A: Task Description for non-rod type wells 1) Function and maintain the valve in line with the relevant Maintenance Guide. a. Enter ‘Pass’ in the WIMS Checklist where the valve functions correctly. b. Enter ‘Fail’ in the WIMS Checklinst where the valve fails to function and where this condition cannot be rectified by the test crew B: Task Description for rod type wells 1) Close the valve a maximum of 2 turns to confirm the valve is not seized. Do NOT apply more than 2 turns to the valve as the valve’s gate may impinge on the rod. 2) Maintain the valve in line with the relevant Maintenance Guide. 3) Re-open the valve. 2.1.6.5.10 WIT Task “Function/ Maintain remaining Annulus Valves” WELL TYPE 5 WIT Page 44 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC TASK CODE MAVW/ MTVW TASK DECRIPTION Function / Maintain all Tree Valves and remaining Annulus Valves 1) Lubricate or grease all tree and annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. Note: To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves (especially tree valves) are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of the test result. 3) Hand over the well to Production Operations for De-isolation and re-start (if required). Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 45 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.1.7 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Well Types 6 and 7 (Water Injection/ Disposal wells with/ without tubing) The Testing Frequency as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.1.7.1 Safety Precautions 2.1.7.1.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.1.7.2 General Preparation 1) Fit a calibrated pressure gauge with bleed facility to the tree cap. Pressure can be bled off to a portable waste drum. 2) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 3) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 2.1.7.3 Notes of Guidance 1. The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 2. Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes. Note: For water leak tests flow rather than pressure build-up can be used, if desired. 3. Where a valve to be tested is NOT fitted, omit the respective task. 4. The test pressure can be replenished from the reservoir (by opening the Master Valves) or using an external pump unit. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages as listed below: a. Pumping .................... keeps UMV test barrier intact but introduces HSE risks associated with mechanical tie in to sour HP well b. Cycling UMV.............. avoids mechanical tie-in risk but breaks UMV tested barrier. Note: Either method can be used provided risks are considered. 5. The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). 6. Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test 7. Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions. 8 8 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term reliability based maintenance frequency. Page 46 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.1.7.4 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Testing 2.1.7.4.1 WIT Task “Carry out External Leak Test” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT TASK CODE ELCW /CAPW TASK DESCRIPTION Carry out external leak check 1) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 2) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: 2.1.7.4.2 Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps WIT Task “Visual Inspection instrumentation or fitting weeps” of condition/ deflection / clashes / WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION VIW Visual Inspection of the condition/ deflection / clashes instrumentation or fitting weeps 1) Visually inspect all tree components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the WIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. 2) Visually inspect well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as required. Note: Printed 15/02/16 As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 47 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.1.7.4.3 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WIT Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines….” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT TASK CODE ILFW/ PRT/ PRA/ PRB/ PRC TASK DESCRIPTION Flush instrument Impulse Lines & Check Pressure Reading Equipment (Local and remote) 1) Shut in inection at the choke (if fitted) and the FWV. Close in UMV to isolate the wellhead from the reservoir and the flow line pressure. Use a hand pump and control line fluid to ensure that all ‘pressure reading’ lines, i.e. those in contact with well fluid, are free from obstruction. 2) Where transmitters are fitted, ensure that actual local pressure gauge readings agree with remote readings. Where differences occur, rectify or note the problem in the ‘free text’ area of the WIT Checklist. 3) Install a secured flexiline to allow safe pressure bleed-off of fluids from the wellhead to a portable waste drum. 4) Check pressure rating, condition and specification of needle valves and replace as required. Note: Replace all non-standard needle valves with double block and bleed valves. Attention! Industry pressure release incidents have been caused by impulse lines being blocked, leading to actual pressures in annuli not being shown on the gauges. The blockages can be due to either ingress of well fluids or build-up of valve grease. It is therefore vital to ensure impulse lines are clear before attempting any tests or maintenance activities. 2.1.7.4.4 WIT Task “Function/ leak off test Swab Valve” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT TASK CODE SVW TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off test Swab Valve 1) This test shall be carried out whilst the well is injecting. 2) Close SV. 3) Bleed SV downstream cavity. 4) Close in the bleed point and install Test Manifold. 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up above the SV over 10 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. The well must be closed in prior to greasing or flushing of valves! 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Page 48 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.1.7.4.5 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only)” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT TASK CODE KWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / Leak-off test Kill Wing Valve Inner (or only) 1) This test shall be carried out whilst the well is injecting. 2) Close KWV. 3) Bleed KWV downstream cavity. 4) Close in the bleed point and install Test Manifold. 5) Record the test ‘Start’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 6) Measure the pressure build-up above the KWV over 10 minutes using a gauge known to be accurate. 7) Record the test ‘Finish’ pressure in the WIMS Checklist. 8) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the Valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. The well must be closed in prior to greasing or flushing of valves! 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including ‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. 2.1.7.4.6 WIT Task “Function/ leak-off test Flow Wing Valve” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve 1) Shut in injection at the choke (if fitted) and the FWV. 2) Close the Location Valve. 3) ‘Zero check’ the ‘flow line’ pressure gauge (if fitted), ensuring the line to the gauge is open. 4) ‘Zero check’ the Swab Valve Pressure Gauge, ensuring that the Swab Valve and the line to the gauge are open. Note: Monitoring CITHP during FWV test makes test pressure decay noticeable. 5) Bleed off pressure between the Location Valve and the Wellhead through a fixed flexible bleed line into a portable waste drum. 6) Once flow has stabilized, start measuring the outflow into a graduated container. 7) Measure the quantity of fluid collected during the 10 minute test and calculate the average flow per minute. Note: If the integrity of the FWV is suspect continue the Integrity test with the Master Valve. 8) If the test result is within the allowable leak rate for the tested valve’s size, record the test as a ‘Pass’ with the average flow rate in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 49 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT TASK CODE FWVIW TASK DESCRIPTION Function / leak-off test Flow Wing Valve 9) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 10) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including the average flow rate and number of tests done. 11) Close in the bleed point. 2.1.7.4.7 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Upper Master Valve UMV” TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 1) Close UMV WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT UMVW Function/ Leak-off test Upper Master Valve 2) Open SV or KWV (dependent on where the measurement will be taken) 3) Bleed off pressure above the UMV through a fixed flexible bleed line into a portable waste drum. 4) Once flow has stabilized, start measuring the outflow into a graduated container. 5) Measure the quantity of fluid collected during the 10 minute test and calculate the average flow per minute. 6) If the test result is within the allowable leak rate for the tested valve’s size, record the test as a ‘Pass’ with the average flow rate in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 7) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 8) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including the average flow rate and number of tests done. 9) Close in the bleed point. 2.1.7.4.8 WIT Task “Function/ Leak-off test the Lower Master Valve LMV” TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 1) Open UMV. WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT LMVW Function/ Leak-off test Lower Master Valve (if fitted) 2) Close LMV. 3) Open SV or KWV (dependent on where the measurement will be taken) 4) Bleed off pressure above the LMV through a fixed flexible bleed line into a portable waste drum. 5) Once flow has stabilized, start measuring the outflow into a graduated container. 6) Measure the quantity of fluid collected during the 10 minute test and calculate the average Page 50 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION flow per minute. Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT LMVW Function/ Leak-off test Lower Master Valve (if fitted) 7) If the test result is within the allowable leak rate for the tested valve’s size, record the test as a ‘Pass’ with the average flow rate in the WIMS WIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. a. Flush the valve Cavity after two failed tests using flushing liquid. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS WIT Checklist including the average flow rate and number of tests done. 10) Close in the bleed poin and re-open LMV. 2.1.7.4.9 WIT Task “Function/ Maintain remaining Annulus Valves” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT TASK CODE MAVW/ MTVW TASK DECRIPTION Function / Maintain all Tree Valves and remaining Annulus Valves 1) Lubricate or grease all tree and annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. Note: Printed 15/02/16 To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves (especially tree valves) are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of test result. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 51 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.2 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Subsurface Integrity Test (SIT) The purpose of the Subsurface Integrity Test is to confirm that the well’s operating envelop is intact and to confirm wellhead, tubing and annular integrity by application of pressure. 2.2.1 Well Type 1 (High Pressure Wells or high GLR or H2S Wells) The testing frequencies are as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.2.1.1 Safety Precautions 1) Perform tool box talks as per PDO’s Toolbox Talk Prompt Card. 2.2.1.1.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.2.1.1.2 H2S Well Type 1, High Risk Wells, comprises H2S wells. This Chapter highlights the particularities relating to H2S wells and provides links to Reference Documents. 1) Comply with all items outlined in SP-1219, Drilling Specification Hydrogen Sulphide. 2) A calibrated pressure gauge fitted to the tree cap with bleed facility (in line with H2S controls) maybe bled off to the outside fence downwind of the work area. 2.2.1.2 General Preparation 1) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record the Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 2) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 3) Pick the correct top-up fluid for annuli testing from WIMS. 2.2.1.3 Notes of Guidance Valve Naming Convention: In the WIMS Checklist, valves are referred to as LEFT (L) and RIGHT (R), when looking at the wellhead from the valve handle side. 1. The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 2. Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes 3. Valve leak tests shall be conducted in the direction of outflow. 4. Where pressure exists for valve testing, a differential pressure shall be applied across the valve being tested by blowing down the fixed downstream volume to the minimum pressure practical. Where it is not possible to blow down fully, the minimum pressure differential (ΔP) at the start of the test shall be 1.2 times the ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ by valve size as stated above. Note: The reasoning behind this rule is that the purpose of leak testing valves is to assess their likely performance in the worst case scenario. In a failure situation, a greater Page 52 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC ΔP would exist across the valve than under test conditions; so a ‘Pass’ under test conditions demonstrates integrity. A “fail” under these conditions will also have occurred before the valve has equalised; therefore this method is deemed to be a valid test method. 5. Where no pressure exists for testing, the annuli have to be topped up with the fluid stipulated in WIMS. 6. The pressure to be applied to the annuli shall be as per Table 2-3Error! Reference source not found.. Table 2-3, Test Pressures for Annuli Tests Annulus A B C D Test Pressure 80 % of MAASP or as defined by the Well Integrity Focal Point 80 % of MAASP or as defined by the Well Integrity Focal Point 80 % of MAASP or as defined by the Well Integrity Focal Point 80 % of MAASP or as defined by the Well Integrity Focal Point Note: Where the observed annulus pressure is above MAASP, a full annulus investigation will be instigated by the WIMS. a. Where the above applies, the test shall be suspended until an annulus investigation has been completed. b. Ensure that the tubing, annulus and the wellhead void pressures are captured before leaving the worksite; this data is required as background information to base the annulus investigation upon. 7. The Pressure Measurement Method shall be ‘Pressure Build-up’ within an enclosed volume for valve tests and ‘Bleed-off‘ from an enclosed volume for annulus tests. Note: Where pressure cannot be maintained in the annulus, cycling and maintaining only (greasing or lubricating) of the annulus valve(s) shall be deemed a test ‘Pass’. 8. Hook up Chicksan lines to the annuli valves. 9. Record the CITHP and all annular pressures as found in the WIMS Checklist. 10. The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). 11. Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test 12. Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions. 9 9 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term maintenance frequency. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 53 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.2.1.4 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Testing SIT Task “Check no external leaks” 2.2.1.4.1 WELL TYPE 1 SIT TASK CODE ELCS TASK DESCRIPTION Check no external leaks 1) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 2) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: 2.2.1.5 Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps Testing 2.2.1.5.1 SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test A annulusulus” WELL TYPE 1 SIT TASK CODE APT TASK DESCRIPTION Pressure Containment Test A Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Bleed off any pressure in all annuli to as low as practical above zero in order to remove any gas caps that may have formed. Note: If it is not possible to bleed down the annulus, abort the test and initiate an annulus investigation. 2) Lubricate all annuli to surface using the fluid stipulated in WIMS, recording volumes pumped in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Note: Where it is not possible to fill the annulus, ensure that 110% of the annular volume has been added prior to aborting the test on that particular annulus. 3) Pressure up the A annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 4) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 5) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 7) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 8) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Packer Depth. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. Page 54 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.2.1.5.2 Petroleum Development Oman LLC SIT Task “Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 1 SIT TASK CODE AVRIS/ AVRO/ AVLIS/ AVLOS TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.1.5.3 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. IT Task “Pressure Containment Test B Annulus” WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE BPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test B Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the B annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 55 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE BPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test B Annulus Notes: 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.1.5.4 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test B Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE BVRI/ BVRO/ BVLI/ BVLO TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test B Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.1.5.5 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test C Annulus” WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE CPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test C Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may Page 56 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE CPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test C Annulus result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the C annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. Notes: 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.1.5.6 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE CVR/ CVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 57 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE CVR/ CVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test D Annulus” 2.2.1.5.7 WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE DPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test D Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the D annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. Notes: 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.1.5.8 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE DVR/ DVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – Page 58 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE DVR/ DVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.1.5.9 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Leak check A to B annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE ABW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check A to B annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where tubing and A annulusulus and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.1.5.10 SIT Task “Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE BCW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 59 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION SIT Checklist. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 1SIT BCW Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 2) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 3) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where A and B Annuli and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.1.5.11 SIT Task “Leak check C to D annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE CDW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check C to D annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where B and C Annuli and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.1.5.12 SIT Task “Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity” WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE TAWS TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: Page 60 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE TAWS TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Tubing and A Annulus and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.1.5.13 SIT Task “Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted” WELL TYPE 1SIT TTCS Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Tubing and Adaptor Flange and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.1.5.14 SIT Task “Leak off test Adaptor Flange to Tubing Head Connection if fitted” WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE ATC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Adaptor Flange to Tubing Head Connection if fitted 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Adaptor Flange and Tubing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 61 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 2.2.1.5.15 SIT Task “Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void” WELL TYPE 1SIT TASK CODE SCWC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: Page 62 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Casing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.2.2 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Well Type 2 (Free Flowing Low Pressure Oil Wells, < 20,000 kPa) The testing frequencies are as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.2.2.1 Safety Precautions 2) Perform tool box talks as per PDO’s Toolbox Talk Prompt Card. 2.2.2.1.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.2.2.1.2 H2S Well Type 1, High Risk Wells, comprises H2S wells. This Chapter highlights the particularities relating to H2S wells and provides links to Reference Documents. 3) Comply with all items outlined in SP-1219, Drilling Specification Hydrogen Sulphide. 4) A calibrated pressure gauge fitted to the tree cap with bleed facility (in line with H2S controls) maybe bled off to the outside fence downwind of the work area. 2.2.2.2 General Preparation 4) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record the Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 5) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 6) Pick the correct top-up fluid for annuli testing from WIMS. 2.2.2.3 Notes of Guidance Valve Naming Convention: In the WIMS Checklist, valves are referred to as LEFT (L) and RIGHT (R), when looking at the wellhead from the valve handle side. 13. The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 14. Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes 15. Valve leak tests shall be conducted in the direction of outflow. 16. Where pressure exists for valve testing, a differential pressure shall be applied across the valve being tested by blowing down the fixed downstream volume to the minimum pressure practical. Where it is not possible to blow down fully, the minimum pressure differential (ΔP) at the start of the test shall be 1.2 times the ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ by valve size as stated above. Note: The reasoning behind this rule is that the purpose of leak testing valves is to assess their likely performance in the worst case scenario. In a failure situation, a greater ΔP would exist across the valve than under test conditions; so a ‘Pass’ under test conditions demonstrates integrity. A “fail” under these conditions will also have Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 63 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 occurred before the valve has equalised; therefore this method is deemed to be a valid test method. 17. Where no pressure exists for testing, the annuli have to be topped up with the fluid stipulated in WIMS. 18. The pressure to be applied to the annuli shall be as per Table 2-3 above. Note: Where the observed annulus pressure is above MAASP, a full annulus investigation will be instigated by the WIMS. c. Where the above applies, the test shall be suspended until an annulus investigation has been completed. d. Ensure that the tubing, annulus and the wellhead void pressures are captured before leaving the worksite; this data is required as background information to base the annulus investigation upon. 19. The Pressure Measurement Method shall be ‘Pressure Build-up’ within an enclosed volume for valve tests and ‘Bleed-off‘ from an enclosed volume for annulus tests. Note: Where pressure cannot be maintained in the annulus, cycling and maintaining only (greasing or lubricating) of the annulus valve(s) shall be deemed a test ‘Pass’. 20. Hook up Chicksan lines to the annuli valves. 21. Record the CITHP and all annular pressures as found in the WIMS Checklist. 22. The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). 23. Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test 24. Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions. 10 2.2.2.4 2.2.2.4.1 Testing SIT Task “Check no external leaks” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE ELCS TASK DESCRIPTION Check no external leaks 3) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 4) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps 10 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term maintenance frequency. Page 64 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.2.2.5 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Testing SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test A annulusulus” 2.2.2.5.1 WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE APT TASK DESCRIPTION Pressure Containment Test A Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 9) Bleed off any pressure in all annuli to as low as practical above zero in order to remove any gas caps that may have formed. Note: If it is not possible to bleed down the annulus, abort the test and initiate an annulus investigation. 10) Lubricate all annuli to surface using the fluid stipulated in WIMS, recording volumes pumped in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Note: Where it is not possible to fill the annulus, ensure that 110% of the annular volume has been added prior to aborting the test on that particular annulus. 11) Pressure up the A annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 12) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 13) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 14) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 15) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 16) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. Notes: 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Packer Depth. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.2.5.2 SIT Task “Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE AVRIS/ AVRO/ AVLIS/ AVLOS TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 10) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 11) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 65 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE AVRIS/ AVRO/ AVLIS/ AVLOS TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve 12) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 13) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 14) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 15) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 16) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 17) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 18) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. 2.2.2.5.3 IT Task “Pressure Containment Test B Annulus” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE BPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test B Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 7) Pressure up the B annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 8) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 9) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 10) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 11) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 12) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. Page 66 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.2.2.5.4 Petroleum Development Oman LLC SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test B Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE BVRI/ BVRO/ BVLI/ BVLO TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test B Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 10) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 11) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 12) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 13) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 14) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 15) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 16) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 17) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 18) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.2.5.5 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test C Annulus” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE CPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test C Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 7) Pressure up the C annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 8) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 9) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 10) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 11) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 12) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 67 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE CPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test C Annulus Notes: 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.2.5.6 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE CVR/ CVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 10) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 11) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 12) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 13) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 14) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 15) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 16) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 17) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 18) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.2.5.7 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test D Annulus” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE DPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test D Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may Page 68 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE DPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test D Annulus result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 7) Pressure up the D annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 8) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 9) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 10) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 11) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 12) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. Notes: 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.2.5.8 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE DVR/ DVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 10) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 11) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 12) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 13) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 14) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 15) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 16) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 17) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 18) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 69 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE DVR/ DVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.2.5.9 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Leak check A to B annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE ABW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check A to B annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 7) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 8) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 9) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 10) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 11) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 12) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where tubing and A annulusulus and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.2.5.10 SIT Task “Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE BCW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: Page 70 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where A and B Annuli and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.2.2.5.11 SIT Task “Leak check C to D annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE CDW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check C to D annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 7) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 8) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 9) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 10) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 11) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 12) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where B and C Annuli and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.2.5.12 SIT Task “Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE TAWS TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Tubing and A Annulus and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.2.5.13 SIT Task “Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TTCS Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 71 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 2 SIT TTCS Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Tubing and Adaptor Flange and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.2.5.14 SIT Task “Leak off test Adaptor Flange to Tubing Head Connection if fitted” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE ATC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Adaptor Flange to Tubing Head Connection if fitted 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Adaptor Flange and Tubing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.2.5.15 SIT Task “Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void” WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE SCWC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. Page 72 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 2 SIT TASK CODE SCWC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Casing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 73 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.2.3 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Well Type 3 (Gas lift Wells) The testing frequencies are as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.2.3.1 Safety Precautions 1) Perform tool box talks as per PDO’s Toolbox Talk Prompt Card. 2.2.3.1.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.2.3.1.2 H2S Well Type 1, High Risk Wells, comprises H2S wells. This Chapter highlights the particularities relating to H2S wells and provides links to Reference Documents. 1) Comply with all items outlined in SP-1219, Drilling Specification Hydrogen Sulphide. 2) A calibrated pressure gauge fitted to the tree cap with bleed facility (in line with H2S controls) maybe bled off to the outside fence downwind of the work area. 2.2.3.2 General Preparation 1) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record the Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 2) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 3) Pick the correct top-up fluid for annuli testing from WIMS. 2.2.3.3 Notes of Guidance Valve Naming Convention: In the WIMS Checklist, valves are referred to as LEFT (L) and RIGHT (R), when looking at the wellhead from the valve handle side. 1. The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 2. Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes 3. Valve leak tests shall be conducted in the direction of outflow. 4. Where pressure exists for valve testing, a differential pressure shall be applied across the valve being tested by blowing down the fixed downstream volume to the minimum pressure practical. Where it is not possible to blow down fully, the minimum pressure differential (ΔP) at the start of the test shall be 1.2 times the ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ by valve size as stated above. Note: The reasoning behind this rule is that the purpose of leak testing valves is to assess their likely performance in the worst case scenario. In a failure situation, a greater ΔP would exist across the valve than under test conditions; so a ‘Pass’ under test conditions demonstrates integrity. A “fail” under these conditions will also have Page 74 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC occurred before the valve has equalised; therefore this method is deemed to be a valid test method. 5. Where no pressure exists for testing, the annuli have to be topped up with the fluid stipulated in WIMS. 6. The pressure to be applied to the annuli shall be as per Table 2-3. Note: Where the observed annulus pressure is above MAASP, a full annulus investigation will be instigated by the WIMS. e. Where the above applies, the test shall be suspended until an annulus investigation has been completed. f. Ensure that the tubing, annulus and the wellhead void pressures are captured before leaving the worksite; this data is required as background information to base the annulus investigation upon. 7. The Pressure Measurement Method shall be ‘Pressure Build-up’ within an enclosed volume for valve tests and ‘Bleed-off‘ from an enclosed volume for annulus tests. Note: Where pressure cannot be maintained in the annulus, cycling and maintaining only (greasing or lubricating) of the annulus valve(s) shall be deemed a test ‘Pass’. 8. Hook up Chicksan lines to the annuli valves. 9. Record the CITHP and all annular pressures as found in the WIMS Checklist. 10. The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). 11. Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test 12. Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions. 11 2.2.3.4 2.2.3.4.1 Testing SIT Task “Check no external leaks” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE ELCS TASK DESCRIPTION Check no external leaks 1) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 2) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps 11 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term maintenance frequency. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 75 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.2.3.5 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Testing 2.2.3.5.1 SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test A Annulus” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE APT TASK DESCRIPTION Pressure Containment Test A Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. B annulus (and others) must be topped up in advance but bled to just above zero in order to not collapse the casing when de-pressurised and monitored for pressure build up in advance. 1) Close the well on FWV and leave the gas lift supply open to allow pressure to build up in the A Annulus and tubing. Note: If the well was isolated prior to the test, the possibility of using gas to carry out test must be confirmed in advance.. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise. 3) Isolate the gas lift supply flow line at location and bleed contents of line between location valve and side outlet valves. Note: This is to prevent a spurious pressure build up from the supply side that caould result in a false fail test result. 4) Bleed off pressure in the A annulus to as near zero as possible ensuring D.P. at start of test is above 1.2 times allowable leak rate. Note: Fast bleed required first in order to close and seal the gas lift valve check vales 5) Once annulus pressure is at zero or minimum stated, close in bleed and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Allow annulus to stabilise for 15 mins 7) Record start pressure in WIMS checklist and monitor pressure pressure in A Annulus for 30 minutes. 8) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 9) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Packer Depth. Possible cases: 1. A Annulus bled to zero / minimum ok and pressure build up over 30 minutes is below allowable leak rate – Pass (No additional investigation required) 2. Unable bleed A Annulus to zero / minimum means annulus is being pressurised from reservoir - Fail (Additional investigation is required to assess what component is leaking and / repair) 3. A Annulus pressure build up after 30 minutes is above allowable leak rate – Fail (Additional investigation is required to assess what component is leaking and / repair) Page 76 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.2.3.5.2 Petroleum Development Oman LLC SIT Task “Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE AVRIS/ AVRO/ AVLIS/ AVLOS TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.3.5.3 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. IT Task “Pressure Containment Test B Annulus” WELL TYPE 3SIT TASK CODE BPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test B Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the B annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 77 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 3SIT TASK CODE BPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test B Annulus Notes: 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.3.5.4 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test B Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE BVRI/ BVRO/ BVLI/ BVLO TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test B Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.3.5.5 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test C Annulus” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE CPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test C Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may Page 78 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE CPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test C Annulus result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the C annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. Notes: 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.3.5.6 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE CVR/ CVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 79 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE CVR/ CVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test D Annulus” 2.2.3.5.7 WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE DPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test D Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the D annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. Notes: 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.3.5.8 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE DVR/ DVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – Page 80 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE DVR/ DVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.3.5.9 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Leak check A to B annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE ABW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check A to B annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where tubing and A annulus and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.3.5.10 SIT Task “Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE BCW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 81 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION SIT Checklist. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 3 SIT BCW Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where A and B Annuli and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.3.5.11 SIT Task “Leak check C to D annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE CDW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check C to D annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where B and C Annuli and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.3.5.12 SIT Task “Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE TAWS TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: Page 82 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE TAWS TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Tubing and A Annulus and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.3.5.13 SIT Task “Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TTCS Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Tubing and Adaptor Flange and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.3.5.14 SIT Task “Leak off test Adaptor Flange to Tubing Head Connection if fitted” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE ATC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Adaptor Flange to Tubing Head Connection if fitted 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Adaptor Flange and Tubing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 83 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 2.2.3.5.15 SIT Task “Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void” WELL TYPE 3 SIT TASK CODE SCWC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: Page 84 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Casing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.2.4 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Well Type 4 (Steam Injection with Packer) The testing frequencies are as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.2.4.1 Safety Precautions 1) Perform tool box talks as per PDO’s Toolbox Talk Prompt Card. 2) Prior to commence SIT on Steam Injector wells steam injection must be closed-in one day prior to start to allow Christmas tree to cool down. Special precautions must be taken to prevent scorch burns due to handling hot equipment. 3) On completion of all pressure tests vent lines are to be left open to prevent pressure build up in test cavity due to thermal expansion. 2.2.4.1.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.2.4.1.2 H2S Well Type 1, High Risk Wells, comprises H2S wells. This Chapter highlights the particularities relating to H2S wells and provides links to Reference Documents. 1) Comply with all items outlined in SP-1219, Drilling Specification Hydrogen Sulphide. 2) A calibrated pressure gauge fitted to the tree cap with bleed facility (in line with H2S controls) maybe bled off to the outside fence downwind of the work area. 2.2.4.2 General Preparation 1) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record the Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 2) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 3) Pick the correct top-up fluid for annuli testing from WIMS. 2.2.4.3 Notes of Guidance Valve Naming Convention: In the WIMS Checklist, valves are referred to as LEFT (L) and RIGHT (R), when looking at the wellhead from the valve handle side. 1) The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 2) Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes 3) Valve leak tests shall be conducted in the direction of outflow. 4) Where pressure exists for valve testing, a differential pressure shall be applied across the valve being tested by blowing down the fixed downstream volume to the minimum pressure practical. Where it is not possible to blow down fully, the minimum pressure differential (ΔP) at the start of the test shall be 1.2 times the ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ by valve size as stated above. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 85 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Note: The reasoning behind this rule is that the purpose of leak testing valves is to assess their likely performance in the worst case scenario. In a failure situation, a greater ΔP would exist across the valve than under test conditions; so a ‘Pass’ under test conditions demonstrates integrity. A “fail” under these conditions will also have occurred before the valve has equalised; therefore this method is deemed to be a valid test method. 5) Where no pressure exists for testing, the annuli have to be topped up with the fluid stipulated in WIMS. 6) The pressure to be applied to the annuli shall be as per Table 2-3 above. Note: Where the observed annulus pressure is above MAASP, a full annulus investigation will be instigated by the WIMS. g. Where the above applies, the test shall be suspended until an annulus investigation has been completed. h. Ensure that the tubing, annulus and the wellhead void pressures are captured before leaving the worksite; this data is required as background information to base the annulus investigation upon. 7) The Pressure Measurement Method shall be ‘Pressure Build-up’ within an enclosed volume for valve tests and ‘Bleed-off‘ from an enclosed volume for annulus tests. Note: Where pressure cannot be maintained in the annulus, cycling and maintaining only (greasing or lubricating) of the annulus valve(s) shall be deemed a test ‘Pass’. 8) Hook up Chicksan lines to the annuli valves. 9) Record the CITHP and all annular pressures as found in the WIMS Checklist. 10) The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). 11) Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test 12) Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions. 12 2.2.4.4 2.2.4.4.1 Testing SIT Task “Check no external leaks” WELL TYPE 4 SIT TASK CODE ELCS TASK DESCRIPTION Check no external leaks Safety Note: Prior to commence SIT on Steam Injector wells steam injection must be closed-in three days prior to start to allow Christmas tree to cool down. Special precautions must be taken to prevent scorch 12 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term maintenance frequency. Page 86 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 4 SIT TASK CODE ELCS TASK DESCRIPTION Check no external leaks burns due to handling hot equipment. 1) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 2) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps 2.2.4.5 Testing 2.2.4.5.1 SIT Task “Check no external leaks” WELL TYPE 4 SIT TASK CODE CBTS TASK DESCRIPTION ChecK Tighten all Bolts and Nuts 1) All casing bowl flange bolts need to be retightened on wellhead cooling in order to prevent a steam leak upon restart of steam injection. Note: Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps 2.2.4.6 Testing 2.2.4.6.1 SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test A annulusulus” WELL TYPE 4 SIT TASK CODE BPT TASK DESCRIPTION Pressure Containment Test B Annulus Note: 1. Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached.. 2. Ensure correct testing fluids are used as stipulated in WIMS (Inhibited fresh water or diesel ???) 1) Bleed off any pressure in all annuli to as low as practical above zero in order to remove any gas caps that may have formed. Note: If it is not possible to bleed down the annulus, abort the test and initiate an annulus investigation. 2) Lubricate all annuli to surface using the fluid stipulated in WIMS, recording volumes pumped in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Note: Printed 15/02/16 Where it is not possible to fill the annulus, ensure that 110% of the annular volume has been added prior to aborting the test on that particular annulus. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 87 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 4 SIT TASK CODE BPT TASK DESCRIPTION Pressure Containment Test B Annulus 3) Pressure up the B annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 4) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 5) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 7) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 8) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. Notes: 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement Depth. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.4.6.2 SIT Task “Leak off test DSAF to Tubing spool ring gasket void (if fitted) or Christmas tree to tubing spool.” WELL TYPE 4 SIT TASK CODE TRGVS TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test DSAF to Tubing spool ring gasket void (if fitted) or Christmas tree to tubing spool. 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) Bleed off test pressures and leave bleed point open. Notes: Page 88 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Casing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 3. Test bleed points are left open after tests to allow fluid to boil off. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.2.4.6.3 Petroleum Development Oman LLC SIT Task “Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 4 SIT TASK CODE BVRIS/ BVRO/ BVLIS/ BVLOS TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off Test B Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.4.6.4 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void” WELL TYPE 4SIT TASK CODE SCWC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void (if fitted) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) Bleed off test pressures and leave bleed point open. Notes: 1. Printed 15/02/16 Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 89 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 4SIT TASK CODE SCWC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void (if fitted) Annulus Investigation. Page 90 2. Where Casing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 3. Test bleed points are left open after tests to allow fluid to boil off. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.2.5 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Well Type 5 (Sub-hydrostatic, pumped wells) The testing frequencies are as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.2.5.1 Safety Precautions 1) Perform tool box talks as per PDO’s Toolbox Talk Prompt Card. 2.2.5.1.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.2.5.1.2 H2S Well Type 1, High Risk Wells, comprises H2S wells. This Chapter highlights the particularities relating to H2S wells and provides links to Reference Documents. 1) Comply with all items outlined in SP-1219, Drilling Specification Hydrogen Sulphide. 2) A calibrated pressure gauge fitted to the tree cap with bleed facility (in line with H2S controls) maybe bled off to the outside fence downwind of the work area. 2.2.5.2 General Preparation 1) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record the Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 2) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 3) Pick the correct top-up fluid for annuli testing from WIMS. 2.2.5.3 Notes of Guidance Valve Naming Convention: In the WIMS Checklist, valves are referred to as LEFT (L) and RIGHT (R), when looking at the wellhead from the valve handle side. 1) The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 2) Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes 3) Valve leak tests shall be conducted in the direction of outflow. 4) Where pressure exists for valve testing, a differential pressure shall be applied across the valve being tested by blowing down the fixed downstream volume to the minimum pressure practical. Where it is not possible to blow down fully, the minimum pressure differential (ΔP) at the start of the test shall be 1.2 times the ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ by valve size as stated above. Note: The reasoning behind this rule is that the purpose of leak testing valves is to assess their likely performance in the worst case scenario. In a failure situation, a greater ΔP would exist across the valve than under test conditions; so a ‘Pass’ under test conditions demonstrates integrity. A “fail” under these conditions will also have Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 91 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 occurred before the valve has equalised; therefore this method is deemed to be a valid test method. 5) Where no pressure exists for testing, the annuli have to be topped up with the fluid stipulated in WIMS. 6) The pressure to be applied to the annuli shall be as per Table 2-3 above. Note: Where the observed annulus pressure is above MAASP, a full annulus investigation will be instigated by the WIMS. i. Where the above applies, the test shall be suspended until an annulus investigation has been completed. j. Ensure that the tubing, annulus and the wellhead void pressures are captured before leaving the worksite; this data is required as background information to base the annulus investigation upon. 7) The Pressure Measurement Method shall be ‘Pressure Build-up’ within an enclosed volume for valve tests and ‘Bleed-off‘ from an enclosed volume for annulus tests. Note: Where pressure cannot be maintained in the annulus, cycling and maintaining only (greasing or lubricating) of the annulus valve(s) shall be deemed a test ‘Pass’. 8) Hook up Chicksan lines to the annuli valves. 9) Record the CITHP and all annular pressures as found in the WIMS Checklist. 10) The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). 11) Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test 12) Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions. 13 2.2.5.4 2.2.5.4.1 Testing SIT Task “Check no external leaks” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE ELCS TASK DESCRIPTION Check no external leaks 1) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 2) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps 13 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term maintenance frequency. Page 92 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.2.5.5 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Testing SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test A annulusulus” 2.2.5.5.1 WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE APT TASK DESCRIPTION Pressure Containment Test A Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Bleed off any pressure in all annuli to as low as practical above zero in order to remove any gas caps that may have formed. Note: If it is not possible to bleed down the annulus, abort the test and initiate an annulus investigation. 2) Lubricate all annuli to surface using the fluid stipulated in WIMS, recording volumes pumped in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Note: Where it is not possible to fill the annulus, ensure that 110% of the annular volume has been added prior to aborting the test on that particular annulus. 3) Pressure up the A annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 4) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 5) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 7) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 8) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. Notes: 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Packer Depth. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.5.5.2 SIT Task “Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE AVRIS/ AVRO/ AVLIS/ AVLOS TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 93 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE AVRIS/ AVRO/ AVLIS/ AVLOS TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. 2.2.5.5.3 IT Task “Pressure Containment Test B Annulus” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE BPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test B Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the B annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. Page 94 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.2.5.5.4 Petroleum Development Oman LLC SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test B Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE BVRI/ BVRO/ BVLI/ BVLO TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test B Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.5.5.5 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test C Annulus” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE CPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test C Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the C annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 95 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE CPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test C Annulus Notes: 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.5.5.6 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE CVR/ CVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.5.5.7 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test D Annulus” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE DPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test D Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may Page 96 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE DPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test D Annulus result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the D annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. Notes: 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.5.5.8 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE DVR/ DVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 97 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE DVR/ DVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.5.5.9 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Leak check A to B annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE ABW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check A to B annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where tubing and A annulusulus and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.5.5.10 SIT Task “Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE BCW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 8) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 9) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: Page 98 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where A and B Annuli and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.2.5.5.11 SIT Task “Leak check C to D annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE CDW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check C to D annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where B and C Annuli and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.5.5.12 SIT Task “Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE TAWS TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Tubing and A Annulus and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.5.5.13 SIT Task “Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TTCS Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 99 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPE 5 SIT TTCS Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Tubing and Adaptor Flange and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.5.5.14 SIT Task “Leak off test Adaptor Flange to Tubing Head Connection if fitted” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE ATC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Adaptor Flange to Tubing Head Connection if fitted 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Adaptor Flange and Tubing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.5.5.15 SIT Task “Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void” WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE SCWC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. Page 100 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPE 5 SIT TASK CODE SCWC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Casing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 101 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.2.6 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Well Types 6 and 7 (Water Injection/ Disposal wells with/ without tubing) The testing frequencies are as per SP-2017, Well Failure Model 2.2.6.1 Safety Precautions 1) Perform tool box talks as per PDO’s Toolbox Talk Prompt Card. 2.2.6.1.1 Permit to Work Ensure that PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure is followed. 2.2.6.1.2 H2S Well Type 1, High Risk Wells, comprises H2S wells. This Chapter highlights the particularities relating to H2S wells and provides links to Reference Documents. 1) Comply with all items outlined in SP-1219, Drilling Specification Hydrogen Sulphide. 2) A calibrated pressure gauge fitted to the tree cap with bleed facility (in line with H2S controls) maybe bled off to the outside fence downwind of the work area. 2.2.6.2 General Preparation 1) Establish the Valve Manufacturer, type and size and check same against data recorded in DIMS. For Solid Block Trees also record the Part Number and check same against data recorded in DIMS. 2) Pick the correct Wellhead Maintenance Guide from the following: a. Cameron (see Chapter 5.4.1 b. FMC (see Chapter 5.4.2) c. Ingram Cactus (see Chapter 5.4.3) d. McEvoy (see Chapter 5.4.4) 3) Pick the correct top-up fluid for annuli testing from WIMS. 2.2.6.3 Notes of Guidance Valve Naming Convention: In the WIMS Checklist, valves are referred to as LEFT (L) and RIGHT (R), when looking at the wellhead from the valve handle side. 1) The allowable Leak Rates for Valves are listed by valve size in the “Allowable leak rates” tab of SP-2017, Well Failure Model. 2) Valve leak test durations are 10 minutes 3) Valve leak tests shall be conducted in the direction of outflow. 4) Where pressure exists for valve testing, a differential pressure shall be applied across the valve being tested by blowing down the fixed downstream volume to the minimum pressure practical. Where it is not possible to blow down fully, the minimum pressure differential (ΔP) at the start of the test shall be 1.2 times the ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ by valve size as stated above. Note: The reasoning behind this rule is that the purpose of leak testing valves is to assess their likely performance in the worst case scenario. In a failure situation, a greater ΔP would exist across the valve than under test conditions; so a ‘Pass’ under test conditions demonstrates integrity. A “fail” under these conditions will also have occurred before the valve has equalised; therefore this method is deemed to be a valid test method. Page 102 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 5) Where no pressure exists for testing, the annuli have to be topped up with the fluid stipulated in WIMS. 6) The pressure to be applied to the annuli shall be as per Table 2-3 above. Note: Where the observed annulus pressure is above MAASP, a full annulus investigation will be instigated by the WIMS. k. Where the above applies, the test shall be suspended until an annulus investigation has been completed. l. Ensure that the tubing, annulus and the wellhead void pressures are captured before leaving the worksite; this data is required as background information to base the annulus investigation upon. 7) The Pressure Measurement Method shall be ‘Pressure Build-up’ within an enclosed volume for valve tests and ‘Bleed-off‘ from an enclosed volume for annulus tests. Note: Where pressure cannot be maintained in the annulus, cycling and maintaining only (greasing or lubricating) of the annulus valve(s) shall be deemed a test ‘Pass’. 8) Hook up Chicksan lines to the annuli valves. 9) Record the CITHP and all annular pressures as found in the WIMS Checklist. 10) The tests and the work to be carried out are defined, for each individual well type, in the Well Failure Model, in the worksheet titled ‘Well Integrity Testing/ Maintenance Matrix’ (ensure work is carried out based on the approved version of the Well Failure Model). 11) Tests must be carried out in the order stated below as the valve status is assumed ‘as left’ from the previous test 12) Valves must not be greased before testing. Valve maintenance will be carried out after the initial test, not before (irrespective of whether the test results is a ‘pass’ or ‘fail’), this to allow the condition ‘as found’ to be analysed in terms of failure rates for both ‘as found’ and ‘as left’ conditions. 14 2.2.6.4 2.2.6.4.1 Testing SIT Task “Check no external leaks” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 WIT TASK CODE ELCS TASK DESCRIPTION Check no external leaks 1) Check all gaskets, flanged, bolted connections and packings for leakage and rectify as required. 2) Measure and record all annulus pressures and the closed in tubing pressure (CITHP). Note: Pressure within bolted or flanged connections must be bled off prior to attempting to pull up any minor weeps 14 If the number of tests performed and recorded in WIMS equals 1 the condition as found can be concluded to have been within limits. The data obtained in this manner will allow analysis of valve performance with a view to establishing the appropriate long-term maintenance frequency. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 103 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.2.6.5 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Testing SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test A annulusulus” 2.2.6.5.1 WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE APT TASK DESCRIPTION Pressure Containment Test A Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Bleed off any pressure in all annuli to as low as practical above zero in order to remove any gas caps that may have formed. Note: If it is not possible to bleed down the annulus, abort the test and initiate an annulus investigation. 2) Lubricate all annuli to surface using the fluid stipulated in WIMS, recording volumes pumped in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Note: Where it is not possible to fill the annulus, ensure that 110% of the annular volume has been added prior to aborting the test on that particular annulus. 3) Pressure up the A annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 4) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 5) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 7) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 8) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. Notes: 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Packer Depth. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.6.5.2 SIT Task “Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE AVRIS/ AVRO/ AVLIS/ AVLOS TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. Page 104 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE AVRIS/ AVRO/ AVLIS/ AVLOS TASK DESCRIPTION Function/ Leak-off Test A Annulus Valve 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. 2.2.6.5.3 IT Task “Pressure Containment Test B Annulus” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE BPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test B Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the B annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 105 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.2.6.5.4 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test B Annulus Valve” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE BVRI/ BVRO/ BVLI/ BVLO TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test B Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.6.5.5 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test C Annulus” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE CPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test C Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the C annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Page 106 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE CPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test C Annulus Notes: 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.6.5.6 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE CVR/ CVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test C Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.6.5.7 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Pressure Containment Test D Annulus” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE DPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test D Annulus Note: Whilst carrying out all steps of the test below, monitor the adjacent annuli for pressure communication effects and report any observations in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Abort any test if communication between annuli and/ or the tubing may Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 107 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE DPT TASK DECRIPTION Pressure Containment Test D Annulus result in any annulus’ MAASP being breached. 1) Pressure up the D annulus to the test pressure stated in Table 2-3 above. Note: Where it is not possible to achieve the required test pressure, record this fact in the ‘Free text’ area in the WIMS SIT Checklist, recommending further investigation and continue with the test below. 2) Allow the pressure to stabilise for 10 mins 3) Record and enter the ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Monitor the pressure for 30 minutes. 5) Record the Test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 6) Record the test result as ‘Pass’ or ‘Fail’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 1. The ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ must be calculated using the formula provided in the Well Failure Model ‘Subsurface Leak Rates’ in the ‘Allowable leak rates” sheet. Notes: 2. The annular volume must be calculated in m3 based on the Top of Cement. 3. Where the Top of Cement is unknown, use the casing shoe depth in the calculation as the resulting ‘Allowable Leak Rate’ will be more conservative. 2.2.6.5.8 SIT Task “Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE DVR/ DVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve Notes: 1. Annulus Valve testing shall be carried out using the test pressure applied to the annuli or in conjunction with the annulus pressure containment test where possible. 2. Test the outer valve(s) first, then inner or only. 1) Function-test all Annulus valves in accordance with the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Close the respective Annulus valve to be tested. 3) Bleed down the downstream side of the valve to be tested to as near zero as possible – maintain some positive pressure on the gauge. 4) Record the test ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Checklist. 5) Measure the pressure build-up downstream of the valve to be tested over 10 minutes using the installed pressure gauge. 6) Record the test ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 7) If the test result is within the Allowable Leak Rate for the tested valve’s size then record the result as ‘Pass’ with ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish pressures’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist; record the number ‘1’ in the ‘Number of Tests done’ field. 8) If the test results in a ‘Fail’ on the first attempt, grease and cycle the valve and re-test it until a ‘Pass’ test result is achieved or no improvement in results is seen. 9) Record the final test (last test carried out) result in the WIMS SIT Checklist including ‘‘Start’ Page 108 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE DVR/ DVL TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Leak off test D Annulus Valve and ‘Finish’ pressure and number of tests done. Note: 2.2.6.5.9 Repeat this Procedure for all annulus valves fitted as per the instruction in Note 2 above. SIT Task “Leak check A to B annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE ABW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check A to B annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where tubing and A annulusulus and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.6.5.10 SIT Task “Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE BCW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check B to C annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 10) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 11) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 12) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where A and B Annuli and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 109 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 2.2.6.5.11 SIT Task “Leak check C to D annulus integrity at wellhead (seals)” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE CDW TASK DECRIPTION Leak check C to D annulus integrity at wellhead (seals) 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where B and C Annuli and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.6.5.12 SIT Task “Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE TAWS TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Tubing to A Annulus Integrity 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Tubing and A Annulus and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.6.5.13 SIT Task “Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TTCS Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS Page 110 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 TASK CODE TASK DECRIPTION Petroleum Development Oman LLC WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TTCS Leak off test Tree to tubing head/ Adaptor Flange Connection if fitted SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Tubing and Adaptor Flange and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.6.5.14 SIT Task “Leak off test Adaptor Flange to Tubing Head Connection if fitted” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE ATC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Adaptor Flange to Tubing Head Connection if fitted 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Where Adaptor Flange and Tubing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 2.2.6.5.15 SIT Task “Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE SCWC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void 1) Identify the Cavity testing port as per the relevant Wellhead Maintenance Guide. 2) Install the Universal Bleeder Tool and Testing Manifold complete with a recording gauge on the test port. 3) Stab the Cavity testing port and record the pressure found as ‘Start pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. 4) Bleed off the void pressure to zero. 5) Close in the Bleeder port and monitor the build-up for 10 minutes. 6) Record the final pressure as ‘Finish pressure’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 111 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT TASK CODE SCWC TASK DECRIPTION Leak off test Surface Casing Wellhead Connection Void Notes: 1. Where pressure is found in the void, which cannot be bled off, recommend an Annulus Investigation. 2. Page 112 Where Casing and void ‘‘Start’ and ‘Finish’ pressures are ‘zero’, the test is recorded as ‘Pass’ in the WIMS SIT Checklist. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.3 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Subsurface Integrity Test (SIT), Maintenance 2.3.1 Well Type 1 (High Pressure Wells or high GLR or H2S Wells) 2.3.1.1 SIT Maintenance Task “Carry out Visual Inspection” WELL TYPE 1SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE VIS TASK DECRIPTION Carry out Visual Inspection 1) Visually inspect all wellhead components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the SIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. 2) Visually inspect wind socks and other related well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as required. Note: 2.3.1.2 As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. SIT Maintenance Task “Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves” WELL TYPE 1SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE MAVS TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves – stipulate any that fail in the ‘free text’ field of WIMS 1) Lubricate or grease all annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of test result. Note: 2.3.1.3 SIT Maintenance Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines” WELL TYPE 1SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE ILFS TASK DECRIPTION Flush Instrument Impulse Lines 1) Flush the Annulus Impulse lines with the appropriate annulus top-up medium, specified in WIMS, from the gauge panel connection back into the annulus to ensure that any grease left in the valve body void is removed. 2.3.1.4 SIT Maintenance Task “Gauge Replacement as required” WELL TYPE 1SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE GR TASK DECRIPTION Gauge Replacement as required 1) Isolate the faulty gauge from pressure. 2) Bleed off the pressure on the gauge. 3) Replace the faulty gauge with a new gauge. 4) De-isolate the gauge. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 113 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.3.2 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Well Type 2 (Free Flowing Low Pressure Oil Wells, < 20,000 kPa) 2.3.2.1 SIT Maintenance Task “Carry out Visual Inspection” WELL TYPE 2 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE VIS TASK DECRIPTION Carry out Visual Inspection 1) Visually inspect all wellhead components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the SIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. 2) Visually inspect wind socks and other related well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as required. Note: 2.3.2.2 As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. SIT Maintenance Task “Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves” WELL TYPE 2 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE MAVS TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves – stipulate any that fail in the ‘free text’ field of WIMS 1) Lubricate or grease all annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. Note: 2.3.2.3 To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of test result. SIT Maintenance Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines” WELL TYPE 1SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE ILFS TASK DECRIPTION Flush Instrument Impulse Lines 1) Flush the Annulus Impulse lines with the appropriate annulus top-up medium, specified in WIMS, from the gauge panel connection back into the annulus to ensure that any grease left in the valve body void is removed. 2.3.2.4 SIT Maintenance Task “Gauge Replacement as required” WELL TYPE 2 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE GR TASK DECRIPTION Gauge Replacement as required 1) Isolate the faulty gauge from pressure. 2) Bleed off the pressure on the gauge. 3) Replace the faulty gauge with a new gauge. 4) De-isolate the gauge. Page 114 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.3.3 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Well Type 3 (Gas lift Wells) 2.3.3.1 SIT Maintenance Task “Carry out Visual Inspection” WELL TYPE 3 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE VIS TASK DECRIPTION Carry out Visual Inspection 1) Visually inspect all wellhead components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the SIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. 2) Visually inspect wind socks and other related well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as required. Note: 2.3.3.2 As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. SIT Maintenance Task “Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves” WELL TYPE 3 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE MAVS TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves – stipulate any that fail in the ‘free text’ field of WIMS 1) Lubricate or grease all annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of test result. Note: 2.3.3.3 SIT Maintenance Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines” WELL TYPE 3 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE ILFS TASK DECRIPTION Flush Instrument Impulse Lines 1) Flush the Annulus Impulse lines with the appropriate annulus top-up medium, specified in WIMS, from the gauge panel connection back into the annulus to ensure that any grease left in the valve body void is removed. 2.3.3.4 SIT Maintenance Task “Gauge Replacement as required” WELL TYPE 3 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE GR TASK DECRIPTION Gauge Replacement as required 1) Isolate the faulty gauge from pressure. 2) Bleed off the pressure on the gauge. 3) Replace the faulty gauge with a new gauge. 4) De-isolate the gauge. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 115 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.3.4 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Well Type 4 (Steam Injection with Packer) 2.3.4.1 SIT Maintenance Task “Carry out Visual Inspection” WELL TYPE 4 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE VIS TASK DECRIPTION Carry out Visual Inspection 1) Visually inspect all wellhead components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the SIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. 2) Visually inspect wind socks and other related well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as required. Note: 2.3.4.2 As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. SIT Maintenance Task “Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves” WELL TYPE 4 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE MAVS TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves – stipulate any that fail in the ‘free text’ field of WIMS 1) Lubricate or grease all annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. Note: 2.3.4.3 To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of test result. SIT Maintenance Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines” WELL TYPE 4 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE ILFS TASK DECRIPTION Flush Instrument Impulse Lines 1) Flush the Annulus Impulse lines with the appropriate annulus top-up medium, specified in WIMS, from the gauge panel connection back into the annulus to ensure that any grease left in the valve body void is removed. 2.3.4.4 SIT Maintenance Task “Gauge Replacement as required” WELL TYPE 4 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE GR TASK DECRIPTION Gauge Replacement as required 1) Isolate the faulty gauge from pressure. 2) Bleed off the pressure on the gauge. 3) Replace the faulty gauge with a new gauge. 4) De-isolate the gauge. Page 116 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.3.5 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Well Type 5 (Sub-hydrostatic, pumped wells) 2.3.5.1 SIT Maintenance Task “Carry out Visual Inspection” WELL TYPE 5 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE VIS TASK DECRIPTION Carry out Visual Inspection 1) Visually inspect all wellhead components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the SIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. 2) Visually inspect wind socks and other related well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as required. Note: 2.3.5.2 As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. SIT Maintenance Task “Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves” WELL TYPE 5 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE MAVS TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves – stipulate any that fail in the ‘free text’ field of WIMS 1) Lubricate or grease all annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of test result. Note: 2.3.5.3 SIT Maintenance Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines” WELL TYPE 5 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE ILFS TASK DECRIPTION Flush Instrument Impulse Lines 1) Flush the Annulus Impulse lines with the appropriate annulus top-up medium, specified in WIMS, from the gauge panel connection back into the annulus to ensure that any grease left in the valve body void is removed. 2.3.5.4 SIT Maintenance Task “Gauge Replacement as required” WELL TYPE 5 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE GR TASK DECRIPTION Gauge Replacement as required 1) Isolate the faulty gauge from pressure. 2) Bleed off the pressure on the gauge. 3) Replace the faulty gauge with a new gauge. 4) De-isolate the gauge. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 117 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.3.6 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Well Types 6 and 7 (Water Injection/ Disposal wells with/ without tubing) 2.3.6.1 SIT Maintenance Task “Carry out Visual Inspection” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE VIS TASK DECRIPTION Carry out Visual Inspection 1) Visually inspect all wellhead components and report any anomalies or unacceptable degradation through free text format area of the SIT Checklist suggesting possible remedies required. 2) Visually inspect wind socks and other related well site safety equipment; report anomalies and replace equipment as required. Note: 2.3.6.2 As this section is open to interpretation and has no clear pass or fail criteria it is important to describe the problem noted clearly to allow the Well Integrity Engineer to make the decision whether to request follow-up repair or not. SIT Maintenance Task “Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE MAVS TASK DECRIPTION Function/ Maintain remaining annulus valves – stipulate any that fail in the ‘free text’ field of WIMS 1) Lubricate or grease all annulus valves as per Maintenance Guide for the appropriate valve type / manufacturer. 2) Return all valves to operational position. Note: 2.3.6.3 To ensure the valves’ ongoing operability, it is vital that all valves are maintained in line with Manufacturers’ Instructions irrespective of test result. SIT Maintenance Task “Flush Instrument Impulse Lines” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE ILFS TASK DECRIPTION Flush Instrument Impulse Lines 1) Flush the Annulus Impulse lines with the appropriate annulus top-up medium, specified in WIMS, from the gauge panel connection back into the annulus to ensure that any grease left in the valve body void is removed. 2.3.6.4 SIT Maintenance Task “Gauge Replacement as required” WELL TYPES 6 AND 7 SIT MAINTENANCE TASK CODE GR TASK DECRIPTION Gauge Replacement as required 1) Isolate the faulty gauge from pressure. 2) Bleed off the pressure on the gauge. 3) Replace the faulty gauge with a new gauge. 4) De-isolate the gauge. Page 118 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.4 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Preventive Well Maintenance of Wellhead related Surface Equipment 2.4.1 2.4.1.1 Preventive Maintenance of OTIS Control Panels Procedure for "OTIS" Well Head Control Panel Maintenance 1) Check reservoir fluid 2) Change fluid at required intervals 3) Clean fluid filter 4) Clean pneumatic filter 5) Fill pneumatic lubricators 6) Lubricate pneumatic pumps 7) Verify proper relief valve setting 8) Verify proper pressure regulator setting 9) Verify proper pilot valve (sensors) pressure setting 10) Verify proper sequence pilot control setting 11) Verify proper safety system panel control operation 12) Verify proper electrical wiring and connections 13) Preventive Maintenance of OTIS Control Panel: 14) Otis Control Panels will be maintained every three months in North Oman. 15) Check hydraulic fluid level (DO NOT fill hydraulic reservoir while the safety valves are open as the oil reservoir will overflow or the tank will rupture at a later date when the valves are closed. 16) Check the reservoir tank is fitted with a pressure relief valve. 17) Check for hydraulic and pneumatic leaks in the panel. 18) Re-tighten all connection but DO NOT OVER TIGHTEN as this will also cause leaks. 19) Clean and replace hydraulic filter strainers. 20) Replace H2S filter cartridges. 21) Remove the spool from the top of each Haskel pump and coat the O-rings with Haskel Grease. 22) Test the pump function (close control line isolation valves on panel and cycle pump, keeping the return valve to the tank open). 23) Test Dial Pilot function, tripping panel on Hi/Lo pressures. (Bleed off sensing line pressure to check Lo pressure trip and increase pressure by applying Nitrogen pressure from the bottle to test Hi pressure trip). 24) Revert panel back to normal operation after completion of all checks. 25) Fill in the maintenance checklist. 2.4.2 Preventive Maintenance of Beam Pumps 1) Change out or install Valve handles, grease fittings, needle valves, bull plugs, companion flanges and pressure gauges as required and in accordance with PDO’s Wellhead Standards Manual 2) Replace leaking grease nipples on valves after ensuring that the valve body has been completely depressurised. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 119 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 3) Carry out routine gate valve maintenance on all gate valves, involving the injection of grease into the valve body cavity, greasing the stem bearings and injection of sealing compound, as specified in manufactures' maintenance procedures Whilst lubricating the body cavities and stem bearings of all wellhead valves, ensure that the master and swab valves are locked open to prevent fouling of the pump rods. Also, one of the 'A' annulus valves may be the exit point for a stainless steel PTS line, this should not be closed either 4) Observe the operation of the pump and note any unusual noise or vibration. 5) Record the amperage drawn by the pump motor. 6) Switch off and lock the power switch near the pump motor ensuring that the pump is stopped with the counterweights at their lowest position. 7) Isolate and lock off at the control panel the electrical supply. This must be done by the Competent Electrical Person who will sign the Isolation Certificate to that effect. 8) Record the following information for the beam pump unit: Pump : Manufacturer's name and serial number Gearbox : Manufacturer's name and serial number V-belt type V-belt pulley size Counterweight position Stroke length 1) Apply the mechanical lock, if fitted, or secure the counterweight to the pump base with chains or wire rope 2) Close the BOP rams around the polished rod. 3) Check the oil level in the gearbox and check the gearbox for evidence of oil leaks. Collect a sample of oil from the gearbox in a container and label it with the well number, date and point of collection. 4) Clean the breather on the gearbox, if fitted. 5) Check the alignment of the horse head. 6) Check the tension, alignment and condition of the V-belts and, if necessary, adjust the tension or alignment by moving the jacking bolts on the motor. 7) Check the condition and tightness of the brake rod/cable and adjust it if necessary, according to the instructions in the manufacturer's service manual. 8) Grease all the bearings. 9) Check the tightness of all the hold-down bolts. 10) Apply lubricant to the wire rope of the carrier bar sling. 11) Check the alignment of the polished rod with a spirit level and adjust it as necessary by moving the jacking bolts on the horse head or frame. 12) Check the condition of polished rod stuffing box and replace if necessary with New packing. 13) Inspect the Victraulic joint, if fitted. 14) Open the rams on the polished rod BOP and disengage the mechanical lock or remove the restraining chains from the counterweight. 15) De-isolate the electrical supply at the control panel. This has to be done by the Competent Electrical Person who will sign to this effect on the Isolation Certificate. 16) Remove the lock from the power switch near the pump motor and switch on the pump. Monitor the operation of the pump to check there is no abnormal noise or vibration. Page 120 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 17) Adjust the polished rod stuffing box packing to give optimum sealing without leaking or binding 18) Return all valves, especially valves closed for isolation purposes, to their original status, as found upon commencement of the maintenance 19) Report any changes to the status of the wellhead and any safety hazards encountered on the Well Location Custodianship Transfer Form and inform the Well Services Supervisor. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 121 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.5 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Corrective Well Maintenance 2.5.1 General Checks Prior to commencing any preventive maintenance at a wellhead location, the following steps and checks shall be taken: SP-2037, Well Engineering Specification for the Use of Equipment in Hazardous Areas. Obtain either a Permit to work or, if applicable a TOC, (transfer of custodianship) TOC needs to be submitted to area authority 24 hrs in advance of planned commencement of the activity. Refer to PR-1098, Well Activity Control and Coordination Procedure where the form is anchored or PR-1444, Well Engineering Management Framework. The Wellhead Maintenance Supervisor must ensure that: 1) The Area Well Services Wellhead Maintenance Supervisor shall contact the Asset Team to advise of the type of maintenance to be done and its expected duration, and will obtain a Well Location Custodianship Transfer Form to carry out the work. 2) The Wellhead Maintenance Senior Foreman will ensure that manufacturer’s maintenance procedures for specific wellhead accessories and equipment are available to the crews as required. 3) A gas test shall be carried out on arrival at the well site, by the Crew Chief, before the maintenance truck enters the location. Note: the maintenance trucks and ancillary equipment shall comply fully with the requirements for the appropriate hazardous area or shall be kept at least 15 meters away from the wellhead, outside the zone 2 hazardous area. Refer to: PR-1043 “General Requirements for Equipment in Hazardous Areas”. 4) Oxygen levels in the well cellar shall also be checked if work is to be done in this area and on H2S gnated locations, a test shall also be conducted to ensure that the H2S level is below 10 ppm Note: If either test is outside acceptable limits, BA sets shall be worn whilst working in the areas concerned. Refer to: PR-1042 “General Operational Safety” PR-1044 “H2S Environment”. 5) A warning sign shall be erected at the location entrance and the Crew Chief shall designate an emergency assembly point on the upwind side of the wellhead. All crewmembers shall wear their PPE and, in H2S areas, activate their personal H2S monitors and deploy their BA escape sets close to where they are working. Refer to the following for general safety and H2S specific requirements to be applied during maintenance activities: PR-1042 “General Operational Safety”; PR-1044 “H2S Environment”. 6) Prior to the commencement of work on pumping wells (beam pump, screw pump and ESP) the electrical supply shall be isolated properly by a competent electrical person and an isolation certificate authorised. 7) All maintenance work on the wellhead shall commence with a thorough visual check for leaks and inspection of the general wellhead condition. If the wellhead is dirty and/or contaminated with oil, it shall be cleaned with a steam cleaner or other appropriate means prior to carrying out further activities. 8) The condition of the ball catcher and location valves shall be checked and reported. 9) A check and report shall be made of the general cellar condition, in particular the following: Page 122 cellar grating - no work shall be carried out on a well without adequate cellar grating; PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC sand or oil fill - the Asset Team shall be informed if cellar requires clearing of sand or oil. The Contractor shall carry out this if instructed by the Company in accordance with the contract. 10) All flange studs and nuts shall be checked to see that they are in place, properly made-up and fully engaged with the studs. Lose studs shall only be made-up after it has been confirmed that the ring joint is fully de-pressurised. 11) All bull plugs, needle valves and pressure gauges shall be checked for correct make-up and tightened if necessary before opening any upstream wellhead gate valves. 12) If installed, the condition and fixtures of the working platform shall be checked for integrity. 13) The tubing and annulus pressures shall be measured and recorded. If either the 'B' or 'C' annulus pressures are greater than 500 kPa they shall be bled down below 500 kPa, providing this can be achieved within a few minutes. This shall be done initially via the flow line then by a line to the downwind side the well site to the point when liquids are produced, only. If the annulus pressures cannot be easily bled down this shall be reported with a recommendation for the provision of additional equipment, e.g. tanks, etc., or the need for further investigation of the problem leading to the possibility of a workover in the severest cases. 2.5.2 Christmas Tree Change-Out 2.5.2.1 Hazards to be managed As change-out of an Christmas Tree on a high pressure gas well is a hazardous activity, it is necessary to define the critical hazards that must be prepared for. The two main hazards are as follows: Leaking tubing barrier plugs after Christmas Tree removal Lifting equipment failure 2.5.2.1.1 Leaking Tubing Barrier Plugs: In the unlikely event of the two tubing barrier plugs simultaneously leaking at surface after removal of the Christmas Tree, this will be managed by having a suspension cap available. The suspension cap will be prepared with an isolation valve pre installed and in the open position, pre-slung, pre-positioned on the well pad and ready to lift immediately onto the wellhead in the event of such a leak. 2.5.2.1.2 Lifting Equipment Failure: The worst case of a lifting equipment failure would be that resulting in the Christmas Tree being dropped onto the wellhead. This will be managed by the following prior to lifting operations commencing: 2.5.2.2 Full inspection of lifting equipment and certification, including crane Determination of crane driver's competence Limitation of lifting height to minimize impact damage in the event of a mechanical failure Preparations To Be Completed Before Commencing Change-Out Of Christmas Tree Prior to commencing change-out of the Christmas Tree all equipment required must be available on-site and checked out by the Well Services Supervisor, to ensure the operation can be completed without interruption. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 123 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 The following equipment checks must therefore be completed before commencing change-out of the Christmas Tree: 2.5.2.2.1 Lifting Equipment: Prior to conducting lifting operations the following items need to be checked. A. Crane Driver: Check that the crane driver has a valid license authorizing him to operate the size and type of crane to be used, and that he is competent to do so. Discuss the method of signaling to be used. Assign a single person to give signals to the crane driver, and check that the crane driver understands the signaling. Prior to moving the crane onto the wellhead area discuss the positioning of the crane with the driver, and brief him on the danger of hitting the Christmas Tree. He must never reverse directly towards the Christmas Tree. Brief the crane driver to limit the lifting height of the Christmas Tree to the required minimum over the wellhead. The Christmas Tree will therefore be lowered to one side of the wellhead to the approximate height required, and then swung round over the wellhead. This is a precautionary measure to limit impact in the event of a lifting equipment failure. B. Crane: Check the certification of the crane to ensure it is valid, and rated for the load to be lifted at the required radius. Check that the crane appears to be in good condition and fit for purpose. The crane driver will carry out a functional check of the crane before starting operations. The Well Services Supervisor must be aware of the location of a back-up crane in the area, to be made available for emergency use in the event of a crane breakdown, as the Christmas Tree must not be left off the well for a prolonged period. C. Slings & Shackles: Check the certification of the slings and shackles to be used. Two sets of lifting slings and shackles are required on site. One for the new tree, which will be pre-slung before starting the Christmas Tree change-out, and one for the Christmas Tree on the well. If a spreader bar is considered necessary two of these should be available and certified for purpose. 2.5.2.2.2 Replacement Christmas Tree: The replacement Christmas Tree will undergo a full visual inspection at the wellsite prior to the change-out commencing, to ensure there is no damage or missing components. This will be done by the manufacturers representative. This will require lifting of the Christmas Tree to inspect the bottom of the Fastlock hub to confirm it is in perfect condition. This can best be done when lifting the tree onto the well pad in preparation for commencing operations. The Christmas Tree valves can also be topped up with grease prior to lifting it onto the well pad. A. CF-13 Ring Joint, SRL Seal, Flange Ring Joints, Studs & Nuts: As a new CF-13 ring joint will be fitted to the wellhead for the replacement Christmas Tree, two of these will be available on site. As a new SRL seal will be fitted to the tubing for the replacement Christmas Tree, two of these will be available on site. Five ring joints type BX- 169 are to be available on site for the 5-1/8" 10,000 psi Christmas Tree flanged outlets. (3 may be required leaving 2 spare) Page 124 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Twenty four (24) spare stud bolts size 9-1/4" x 1-1/8" 8 TPI, and forty eight (48) spare nuts size 1-1/8" 8 TPI will be available on site, should it be necessary to replace those on the flanged outlets. Flogging wrenches for the 1-1/8" nuts and for the Fastlock hub nuts are also required, and must be checked for fit prior to commencing operations. 2.5.2.2.3 Suspension Cap: A suspension cap is required on site prior to commencing operations, as a back up in the event of a problem with the Christmas Tree. The suspension cap will be pre-fitted with a 5-1/8" x 10,000 psi gate valve, which will be left in the open position. The suspension cap will be preslung and positioned on the well pad ready for immediate use, prior to operations commencing. 2.5.2.2.4 High Pressure Greasing Package: A high-pressure grease package is required on site to enable greasing of the Christmas Tree valves. This consists of a high pressure grease pump with grease outlet hose and grease fitting, diesel driven air compressor to power it, 100 ft of air hose to enable the compressor to be located outside the zone two area, and sufficient diesel for the operation. This equipment should be spotted, rigged up and tested prior to commencing tree change-out operations. Cameron diesel resistant high-pressure grease type 713837/02 (MESC 87 61 06 020 9) should only be used. 2.5.2.3 2.5.2.3.1 Replacing the Christmas Tree Barrier Requirements As per SP-1217, Well Control Barrier Specification, Chapter 2.3.1, there must be two barriers for high and medium risk wells and one barrier for low risk wells prior to removing the Christmas Tree. 2.5.2.4 Christmas Tree Change-Out for High-Risk Wells A. Isolation of Flow line Prior to commencing Christmas Tree replacement operations it will be necessary to isolate the flow line from the production system. This will be done by the Production Operations Department, after which custodianship of the well and location will be transferred to the Well Services Supervisor for the Christmas Tree change-out, as outlined in PR-1098, Well Activity Coordination and Control Procedure. The flow line location valve, production control choke and HIPPS valve will all be closed and isolated, as per the Production Operations procedures. B. Hook-up of High Pressure Pump, Choke & Vent Line (See Drawing Appendix 1) An high pressure pump is required on site for pressure testing the Monolock and HE-3- type tubing barrier isolation plugs, for equalizing pressure prior to removing the prongs from these plugs, and for pressure testing the replacement Christmas Tree body, using inhibited water. The pump will be hooked up by rigid steel hoses (Chiksans) to the KWV (kill wing valve), as outlined in hookup drawing Appendix 1. Also required in the hookup is a manual choke and vent line to pit or other safe area, to enable controlled bleed down of the tubing pressure for inflow testing the lower Monolock plug. The line from the pump truck to the KWV, choke and vent shall be wired down and pressure tested to 60,000 kPa for 15 minutes as per standard hook-up and pressure testing procedures. The vent line to pit shall be restrained by use of a concrete saddle block, placed over the top of the vent line at the end, after which the vent line will be wired to the block to prevent pressure whipping. A water tanker will be required on site with +/- 10 m3 inhibited water (with oxygen scavenger) for pressure testing, and filling the tubing above the Monolock plugs. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 125 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 C. Establishing & Testing Annulus Barriers Establish 'A' annulus barriers and pressure integrity prior to commencing change-out of the Christmas Tree as follows: 1) Confirm annulus integrity by bleeding of residual pressure from the ‘A’ annulus and observing zero pressure build up over a period of 30 minutes. (Record returns and initial pressures). 2) Top up annulus with inhibited water, and confirm fluid level remains constant for 3 hours. 3) Confirm integrity of the dual hanger seals by testing all seals as per standard Cameron procedures. D. Installation, Inflow Testing & Pressure Testing of Monolock Plug Tubing Isolation Barriers Isolation from the formation will be achieved by setting a Monolock type Bridge plug in the 41/2" tubing at a depth of +/- 250m (55 m if TRSCSSSV installed). The Monolock plug is designed to withstand differential pressure of up to 10,000 psi (69,000 kPa) from either direction, and is retained in position by slips rather than keys. The sealing element is located above the slips, preventing any debris accumulation around the slip area. The Monolock plug will be inflow tested against full reservoir pressure by depressurizing the tubing above it to 0 kPa, and monitoring the pressure for 4 hours. It will then be pressure tested from above to CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) for 1 hour using inhibited water with oxygen scavenger. A second Monolock type Bridge plug will be set at 50 m (25m if TRSCSSSV installed), and pressure tested from above to CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) for 1 hour using inhibited water with oxygen scavenger. This pressure test should be done through the tree cap, using a small volume pump fed from a calibrated reservoir tank. This will enable measurement of the exact volume pumped in relation to the theoretical volume required, thereby making it easier to observe if the plug leaks. Run and set the lower and upper Monolock plugs as follows: 1) Rig up WL Lubricator to tree cap, with Monolock drift inserted, and pressure test lubricator to CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) against Swab valve for 15 minutes. If the Swab valve is leaking use of a secondary Swab valve will be required. 2) RIH full bore Monolock drift in 5-1/2" tubing to 350 m. POOH. 3) Make-up WL lubricator with Monolock body to tree cap, and pressure test lubricator to CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) against closed Swab valve for 15 minutes 4) RIH Monolock body with DPU & Running Tool and set in 5-1/2" tubing at +/- 250m (55m if TRSCSSSV installed). Stand by for 1 hour whilst the DPU activates. POOH DPU & Running Tool. 5) RIH Monolock prong and set in Monolock body. POOH running tool. 6) Inflow test Monolock, plug by bleeding down tubing slowly to zero pressure in a controlled manner, through the manual choke and vent line. When zero pressure has been achieved and conditions are stable, monitor and record the pressure for a period of four hours. Should a pressure fluctuation occur during this period re-establish a stable zero pressure condition and repeat the four hour monitoring and recording period, until an acceptable test is achieved. The Monolock inflow test must be accepted by the Well Services Supervisor, in which case a copy of the inflow test chart must be sent to him by fax. 7) RIH Monolock body with DPU & Running Tool and set in 5-1/2" tubing at +/- 50m (25m if TRSCSSSV installed). POOH DPU & Running Tool. 8) RIH Monolock prong and set in Monolock body. POOH running tool and rig down WL lubricator. Page 126 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 9) Using the high pressure pump and inhibited fresh water fill the tubing above the upper Monolock plug by pumping +/- 2.5 m3 (+/- 0.25 m3 if plug set at 25m) through the KWV, whilst venting through the Swab valve until all the air is displaced. (Tubing volume +/- 1 m3 per 100 m of 5-1/2" 26 lbs/ft tubing) 10) Pressure test the upper Monolock plug to CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) for 1 hour, and monitor / record the pressure on a chart recorder. This pressure test should be done through the tree cap, using a small volume pump fed from a calibrated reservoir tank. This will enable measurement of the exact volume pumped in relation to the theoretical volume required, thereby making it easier to observe any plug leakage. The Monolock pressure test must be accepted by the Well Services Supervisor, in which case a copy of the pressure test chart must be sent to him by fax. If the pressure test is acceptable, Christmas Tree replacement may commence. E. Replacing the Christmas Tree All Christmas Tree change-out must be supervised by PDO Well Services Supervisors with under direct instruction of vendor personnel. The replacement Christmas Tree and suspension cap, both of which will already be pre-slung, will be lifted onto the well pad in close proximity to the wellhead, before commencing Christmas Tree change out operations. Replace the Christmas Tree as follows: 1) Disconnect Chiksan pump line at KWV. 2) Remove KWV cross-over flange to Weco 2" 1502 3) Break flange at FWV 4) Install lifting equipment onto Christmas Tree, in readiness for lifting it off 5) Nipple down Christmas Tree from Fast-lock hub as per Cameron procedure 6) Lift of Christmas Tree using certified lifting equipment 7) Inspect Fast-lock hub on wellhead and prepare it to receive replacement tree 8) Replace CF-13 and SRL seals 9) Lift replacement Christmas Tree onto wellhead Fast-lock hub and nipple up as per Cameron procedure 10) Carry out pressure tests on CF-13 and SRL seals as per Cameron procedure 11) Make-up Weco 2" 1502 cross-over flange to KWV flange, using a new BX-169 ring joint 12) Make-up pump line to Weco 2" 1502 crossover flange hammer lug union. 13) Pressure test pump line against closed KWV to 60,000 kPa for 15 minutes 14) Grease all Christmas Tree valves as per Cameron procedure (if not already done) 15) Check that valves are in the following positions, then fill the Christmas Tree with inhibited fresh water, pumping into the tree through the KWV and venting through the Swab valve until all air is displaced from the tree. FWV Closed LMV Closed UMV Open KWV Open Swab Open 16) Body test Christmas Tree to 60,000 kPa for 30 minutes as per Cameron procedure and chart record the test. Standard precautions for pressure testing and safeguarding the area to be observed. 17) Make-up FWV flange to flow line. Fill the system with inhibited fresh water, vent off air and pressure test connection using the HT-400 pump, pumping through the Christmas Tree against the closed HIPPS valve. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 127 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 F. Pressure Equalization & Removal of Monolock Plug Tubing Isolation Barriers Now that the integrity of the Christmas Tree body and flange connections are established, the Monolock plugs may be removed as follows: 1) Rig up WL Lubricator to tree cap, and pressure test connections with inhibited water to previously recorded CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) through the Christmas Tree for 15 minutes, using the HT-400 pump. 2) RIH Monolock prong pulling tool to +/- 50 m (+/- 25m if TRSCSSSV installed), pull prong from Monolock plug, and POOH. 3) RIH Monolock body pulling tool to +/- 50m (+/- 25m if TRSCSSSV installed), engage Monolock body and jar plug free. 4) Standby a further 30 minutes whilst the element relaxes, then POOH Monolock body. Observe weight indicator carefully to pre-empt the packing becoming stuck. Note: If the plug is not free after 30 minutes, wait another 30 minutes, as the time required to relax the element is variable, dependant on time in hole, depth and temperature. 5) RIH Monolock prong pulling tool and engage lower Monolock prong at 250 m. (+/- 55m if TRSCSSSV installed), Apply pressure to water column to equalize differential pressure across plug to previously recorded CITHP, then POOH with prong. Stand by whilst well pressure equalizes and stabilizes, before pulling the plug body. 6) RIH Monolock body pulling tool to +/- 250 m (+/- 55m if TRSCSSSV installed), engage Monolock body and jar plug body free. Standby a further 30 minutes whilst element relaxes, then POOH Monolock body. Observe the weight indicator carefully to pre-empt the packing becoming stuck. Note: If the plug is not free after 30 minutes, wait another 30 minutes, as the time required to relax the element is variable, dependant on time in hole, depth and temperature . 7) Close Swab valve and UMGV, rig down WLS lubricator and prepare for inflow testing Christmas Tree valves. G. Inflow Testing Christmas Tree Valves Now that full wellhead pressure is available the pressure integrity of the LMGV, UMGV, FWV, KWV and Swab valve must be tested. To test these valves refer to Chapter 2.1.2 above Ensure that all tests are chart recorded. 2.5.2.5 Christmas Tree Change out for Medium Risk wells 1) Check that for no leak from the location valve 2) Check that the wellhead pressure is zero. If necessary, bleed off any pressure and monitor for build up before proceeding. 3) Confirm annulus integrity by bleeding of residual pressure from the ‘A’ annulus and observing zero pressure build up over a period of 30 minutes. (Record returns and initial pressures). 4) Top up annulus with inhibited water, and confirm fluid level remains constant for 3hours. 5) Confirm integrity of the dual hanger seals by testing all seals as per standard Cameron procedures 6) RIH WL and Install deep plug at lowest nipple; inflow-test the plug as per SP-1217, Well Control Barriers. 7) Rig up the BPV lubricator and install the 2 way Check valve in tubing hanger profile and pressure test to Christmas Tree rating. Rig down the BPV lubricator Page 128 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 8) Break the flange on the downstream side of the Flow wing valve and restrain the flow line to prevent it fouling the tree during removal. 9) Position the crane, fit slings to the Christmas Tree and take up the slack in the lifting cable. 10) Break the flange at the base of the Christmas Tree and remove the tree from the wellhead. Stand well clear of the Christmas Tree while it is being lifted off the wellhead. 11) Fit a new ring gasket in the groove on the top of the tubing spool then pick up the replacement Christmas Tree and lower it into position. Make up the flange at the base of the Christmas Tree. 12) Close the Flow wing valve and kill valve and open the master valve(s). 13) Fill the Christmas Tree with water and connect the air-operated pump to the swab cap needle valve. Pressure-test the bottom flange connection and Christmas Tree assembly to rated working pressure for 30 minutes. Record the test on a chart recorder. 14) Disconnect the pressure testing equipment and make up the flow line flange. 15) Pressure test the flow line. 16) Rig up the BPV lubricator and retrieve the two way check valve. Rig down the BPV lubricator. 17) Equalize the pressure across the isolation plug and retrieve same. 18) Re-install the swab cap. Leave the Christmas Tree with the master valve(s) open and the swab, kill and Flow wing valves closed. 19) Inflow Testing Christmas Tree Valves: Now that full wellhead pressure is available the pressure integrity of the LMGV, UMGV, FWV, KWV and Swab valve must be tested. To test these valves refer to Chapter 2.1.2 above Ensure that all tests are chart recorded. 2.5.2.6 Christmas Tree Change-Out for Low Risks Wells 1) Check that for no leak from the location valve 2) Check that the wellhead pressure is zero. If necessary, bleed off any pressure and monitor for build up before proceeding. 3) Confirm annulus integrity by bleeding of residual pressure from the ‘A’ annulus and observing zero pressure build up over a period of 30 minutes. (Record returns and initial pressures). 4) Top up annulus with inhibited water, and confirm fluid level remains constant for 3hours. 5) Confirm integrity of the dual hanger seals by testing all seals as per standard Cameron procedures 6) Rig up the BPV lubricator and install the 2 way Check valve in tubing hanger profile and pressure test to Christmas Tree rating. Rig down the BPV lubricator. Note: it is also possible to install a deep plug and pressure-test it as per SP-1217, Well Control Barriers 7) Break the flange on the downstream side of the Flow wing valve and restrain the flow line to prevent it fouling the tree during removal. 8) Position the crane, fit slings to the Christmas Tree and take up the slack in the lifting cable. 9) Break the flange at the base of the Christmas Tree and remove the tree from the wellhead. Stand well clear of the Christmas Tree while it is being lifted off the wellhead. 10) Fit a new ring gasket in the groove on the top of the tubing spool then pick up the replacement Christmas Tree and lower it into position. Make up the flange at the base of the Christmas Tree. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 129 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 11) Close the Flow wing valve and kill valve and open the master valve(s). 12) Fill the Christmas Tree with water and connect the air-operated pump to the swab cap needle valve. Pressure test the bottom flange connection and Christmas Tree assembly to rated working pressure for 30 minutes. Record the test on a chart recorder. 13) Disconnect the pressure testing equipment and make up the flow line flange. 14) Pressure test the flow line. 15) Rig up the BPV lubricator and retrieve the two way check valve. Rig down the BPV lubricator and re-install the swab cap. Leave the Christmas Tree with the master valve(s) open and the swab, kill and Flow wing valves closed. Note: In case of solid block Christmas Tree, the P-seals of Christmas Tree bottom flange needs to be de-energised before lifting the tree off the wellhead. The same seals need to be energised and pressure tested to 30 minutes on the new Christmas Tree. Haskel pump or a hand pump may be used for testing. Note: For Medium Risk wells refer to SP-1217, Well Control Barrier Specification, Chapter 2.3.1 . 2.5.2.7 Christmas Tree Change-Out on wells to be fracced On wells which are planned to be fracced the rig installs a Frac tree and after Fraccing this tree has to be replaced with a production Christmas Tree. The Christmas Tree change out will be managed by a PDO supervisor together a representative from the Christmas Tree Vendor As a safety precaution a suspension cap with an isolation valve pre installed in the open position, pre-slung, pre-positioned on the well pad and ready to lift immediately onto the wellhead in the event of such a leak. 2.5.2.7.1 Checks to be carried out prior to changing the Christmas Tree 1) Ensure that both the Crane driver and the crane are licensed and certified for the Purpose 2) Check the certification of the slings and shackles 3) Discuss the method of signalling to be used. Assign a single person to give signals to the crane driver, and check that the crane driver understands the signalling. 4) Prior to moving the crane onto the wellhead area, discuss the positioning of the crane with the driver, and brief him on the danger of hitting the Christmas Tree. He must never reverse directly towards the Christmas Tree. 5) Brief the crane driver to limit the lifting height of the Christmas Tree to the required minimum over the wellhead. The Christmas Tree will therefore be lowered to one side of the wellhead to the approximate height required, and then swung round over the wellhead. This is a precautionary measure to limit impact in the event of a lifting equipment failure. 6) Thoroughly inspect the production tree to ensure there is no damage or missing components. The tree should be lifted to inspect the bottom of the Fastlock hub to confirm it is in perfect condition. . 7) Check that all valves have been greased and function tested prior to leaving the vendor’s factory. 8) Ensure the correct number of replacement parts and back up spares available: -CF-13 Ring Joint, SRL Seal, Flange Ring Joints, Studs & Nuts: 9) Replace tree as follows:10) Disconnect Chiksan pump line at KWV. Page 130 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 11) Remove KWV cross-over flange to Weco 2" 1502 12) Break flange at FWV 13) Install lifting equipment onto Christmas Tree, in readiness for lifting it off 14) Nipple down Christmas Tree from Fast-lock hub as per Cameron procedure 15) Lift Christmas Tree 16) Inspect Fast-lock hub on wellhead and prepare it to receive replacement tree 17) Replace CF-13 and SRL seals 18) Lift replacement Christmas Tree onto wellhead Fast-lock hub and nipple up as per Cameron procedure 19) Carry out pressure tests on CF-13 and SRL seals as per Cameron procedure 20) Make-up Weco 2" 1502 cross-over flange to KWV flange, using a new BX-169 ring joint 21) Make-up pump line to Weco 2" 1502 crossover flange hammer lug union. 22) Pressure test pump line against closed KWV to 60,000 kPa for 15 minutes 23) Grease all Christmas Tree valves as per Cameron procedure (if not already done) 24) Check that valves are in the following positions, then fill the Christmas Tree with inhibited fresh water, pumping into the tree through the KWV and venting through the Swab valve until all air is displaced from the tree. FWV Closed LMV Closed UMV Open KWV Open Swab Open 25) Body test Christmas Tree to 60,000 kPa for 30 minutes as per Cameron procedure and chart record the test. Standard precautions for pressure testing and safeguarding the area to be observed. 26) Make-up FWV flange to flow line. Fill the system with inhibited fresh water, vent off air and pressure test connection using the HT-400 pump, pumping through the Christmas Tree against the closed HIPPS valve. 2.5.3 Corrective Maintenance of Christmas Tree Valves and Components 2.5.3.1 2.5.3.1.1 Low Pressure Wells Corrective Maintenance of Wellhead (Cameron Valves) A. Bearing Inspection 1) Remove bonnet cap (with valve open or shut). 2) Pull off front race and needle bearing. 3) Inspect for corrosion or damage to race. 4) Inspect for freedom of movement of needle rollers. If front bearing is satisfactory refit and replace the BONNET CAP. 5) If the front race and needle bearing is defective and inner race and bearing is suspect the following procedure should be followed: - Remove pin and stem adapter and replace back bearing. B. Change Stem Packing Under Pressure 1) With gate fully closed, back off the bearing cap 4 turns and bump gate closed again. The stem is now back seated. 2) Remove cap from extreme pressure, grease fitting and unseat the check valve with a stinger tool. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 131 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 3) If after a reasonable length of time pressure is still evident, do not continue but inform the Wellhead Maintenance Foreman. 4) Remove hand wheel, bearing cap, stem to adapter pin, bearings, adapter and packing gland. (Do not stand in front of valve). 5) Inject grease through injection point until stem packing comes out. (alternately packing puller may be used) 6) Clear out grease from housing completely and replace a new J-packing half way inside the housing. C. Refit Assembly 1) With new J-packing inserted, screw in the gland packing and nip tight. 2) Fit inner race and bearing. 3) Fit stem adapter and drive in location pin. 4) Fit outer race and bearing. 5) Inspect and fit new O-ring if required. 6) Fit bonnet cap and nip tight. 7) Back off valve slightly too un-back seat and nip tight bonnet cap again. 8) Re-grease at all grease points. 9) Refit injection grease cap. 10) Check that the number of turns to fully open the valve is as specified for that type of valve. D. Complete Overhaul of the Valve 1) With gate in open position, bleed the line pressure and remove bonnet nuts. Turn handwheel clockwise (close), and bonnet lifts off of studs. 2) Rotate bonnet slightly until bolt holes and studs are out of line, and turn handwheel counterclockwise to pull gate assembly out of the body. If assembly is still tight in the body, simply repeat this jacking operation with spacers between studs and bonnet. 3) Flush body cavity, grease thoroughly, and slide in a new assembly all the way to the bottom of the body, being careful not to pinch the seat-to-body seals. Fill with grease, thread in the stem and replace the bonnet. NOTE: 2.5.3.1.2 Please refer to Cameron manual in Wellhead Maintenance Office for troubleshooting information and grease types and quantities. Corrective Maintenance of Wellhead (Wood Group valves) A. Minor Repairs Minor repairs such as replacement of grease fitting and stem bearing on WG model 2200 may be carried out while the valve is in service under pressure by back-seating the valve and depressurizing using a stinger tool. B. Back-seating procedure Close the valve fully. Back off the bearing cap three turns using a pipe wrench. If the valve is under pressure the internal pressure should automatically backseat the valve. If not, grab the hand wheel and pull outward on the stem. This would be approximately 1/8” of movement. Install Stinger tool on grease fitting and bleed off trapped pressure. Do not attempt to carry out any repair on valve if the back seating do not seal. (indicated by continued bleed off) Caution: Trapped pressure may be hazardous depending upon the actual service the valve has seen. On 2,000 psi. through 10,000 psi. valves, the body grease fitting are ½” line pipe. Page 132 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC C. Testing the fitting Loosen the safety cap. If pressure escapes through the weep-holes, retighten the safety cap. D. Replacing the damaged fitting 1) Fully close the valve making sure the gate is in the proper position. 2) Backseat the valve and bleed off all trapped pressure. Note: Take all necessary precautions appropriate for specific valves and service conditions. 3) Using the adjustable wrench, remove the damaged fitting by backing off counter clockwise. 4) Install a new fitting making sure safety cap is tight. 5) Disengage the backseat by fully tightening the bearing cap. 6) Test the fitting to verify it is functioning properly. E. Stem Bearing Replacement It is time to replace the bearings when a grinding is felt during the operation of the stem. If the valve is back seated, this procedure can be performed under pressure. Caution: Take all appropriate safety precautions if such procedures are being performed while the valve is in service and under pressure. Note: Two bearings are found in each model 2200 Gate Valve. Each bearing consists of a thrust bearing with a bearing race on either 1) Fully close and backseat the valve. 2) Bleed off all trapped pressure using a stinger tool. Note: It is not necessary to backseat the valve to remove the steam bearings although it is recommended. 3) Remove hand-wheel split pin and remove hand-wheel. 4) Using a pipe wrench, remove the bearing cap by rotating the cap counter clockwise until it comes free of the bonnet. Lift the bearing cap off of the stem adaptor. 5) Using the hammer and drift punch, carefully drive the drive pin out of the stem adapter with a straight lift. 6) Remove the upper and lower stem bearings and races from the stem adapter. 7) Discard damaged bearings and races. 8) Grease new bearings thoroughly and install them on the stem nut as indicated. 9) Thoroughly clean the end of the stem, inside of the bearing cap, and top of the packing retainer, removing all old contaminated grease and debris. 10) Carefully slide the stem adaptor with bearings over the stem and install the drive pin. Ensure the ends of the drive pin are below the O.D. of the adapter. 11) Lightly grease the inside of the bearing cap and then thread it onto the bonnet with the right hand rotation. Ensure cap is made up to its original position. 12) Reinstall hand wheel. 13) Attach grease gun to Alemite fittings and inject bearings with grease to ensure sufficient lubrication Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 133 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 F. Replacement of Wing Valve or Swab Valve Prior to removing a Flow Wing or Kill Valve two barriers to flow must be in position in line with SP-1217, Well Control Barriers (note this document will be revised to state that a leaking valve cannot be considered a barrier for well intervention). A back pressure valve (BPV) A closed and tested master valve. 1) Close the flow line (location) valve and the master valve(s). Open the Flow wing valve and swab valve. Check that for no leak from the location valve 2) Bleed off the pressure above the master valve and monitor for any leak across the master valve before proceeding. 3) Rig up the BPV lubricator and install the BPV in the tubing hanger profile according to well services procedure. Bleed off the pressure above the BPV then close the master valve(s). 4) If the Flow wing valve is to be replaced, break the flange on the downstream side of the valve and restrain the flow line to prevent it fouling the valve during removal. 5) If the kill valve is to be replaced, remove its companion flange with plug and needle valve after first opening the needle valve to release any trapped pressure. 6) If swab valve is to be replaced, first break flange and remove tree cap. 7) Position the HIAB, fit slings to the valve to be removed and take up the slack in the lifting cable. 8) Break the upstream flange of the valve and remove the valve from the Christmas Tree. 9) Pick up the replacement valve and install it on the Christmas Tree after first inserting a new ring gasket in the flange groove. Make up the flange on the upstream side of the valve. If the valve replaced is swab, reinstall the tree cap and make up the flange making sure a new ring gasket and Teflon insert are placed. 10) Close the Flow wing and kill valves. 11) Rig up Lubricator, open Master valve, pull BPV and install 2-way check valve. 12) Bleed off pressure above 2-way check valve and fill the Christmas Tree with water. Connect the air-operated pump to the swab cap needle valve. Pressure test the newly made-up flange connection to max. WP (working pressure) for 30 minutes. Record the test on a chart recorder. 13) Disconnect the pressure testing equipment and make up the flow line flange (in the case of a wing valve replacement), or install the companion flange assembly (in the case of a kill valve replacement). 14) Rig up the BPV lubricator, open the master valve(s) and retrieve the 2-way check valve. Rig down the BPV lubricator and re-install the swab cap. Leave the Christmas Tree with the master valve(s) open and the swab, kill and wing valves closed. Note: During the pressure test ensure that personnel not directly connected with pressure testing are clear of test area. G. Repair hydraulic wire cutting actuators in situ The Hydraulic actuators fitted to upper master valve may be repaired while under pressure. 1) Close in the lower master and Flow wing valve and bleed off pressure through the swab valve. 2) Trip the actuator from the control panel. 3) Ensure the actuator is fully tripped and then disconnect the control line keeping clear of the cylinder fitting. Page 134 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 4) Disassemble the actuator for inspection and accessing the defective parts. 5) Clean thoroughly and replace the defective part/seals. 6) Assemble the actuator. 7) Function test the actuator. Note : 2.5.3.2 Extreme care should be taken while working on actuators as springs are energised with control line pressure applied. Only trained personnel may be allowed to work on actuators. For disassembly refer to manufacturer’s procedure. HP Pressure Wells 2.5.3.2.1 Corrective Maintenance on HPHT Wells Before carrying out any non routine maintenance on High Pressure Christmas Trees it is imperative that the Barrier policy is fully understood. If a valve is recorded in the WIMS data base this does not mean that it is a barrier the actually leakage rate across the valve must be known or it must be inflow tested Leak rates as stipulated in the wellhead failure model are of no relevance to the determination of whether the valve is an acceptable barrier Two tested mechanical barriers must be in place prior to starting non routine valve maintenance activities If the CITHP of a well is too low to effect a satisfactory leak test on a valve (<10,000 kPa), plug(s) must be set in the tubing and tested to ensure compliance with the Barrier Policy The TRSCSSSV is not acceptable as a barrier for non routine maintenance due to its leak potential 1) The Christmas Tree must first be isolated from the flow line by closing the HIPPS valve and the location valve and depressurizing the line between these two valves, 2) The A annulus must be checked for pressure Maintenance on the Swab Valve, the Kill wing valve and the Flow Wing valves can be down by isolating from well bore pressure using Barrier 1: LMGV Barrier 2: UMGV 3) The valves must be inflow tested as described in Chapter2.1.2 above. 4) Close the TRSCSSSV for additional safety if installed 5) After valve maintenance is finished, hook HP pump to the kill line open the UMGV and test the Christmas Tree body to CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) for 30 minutes against the LMGV, using inhibited water. 6) Equalise pressure across the LMGV and open it. 7) De-isolate & pump open TRSCSSSV (where installed) 8) Inflow-test the repaired valve as as per procedures 2.1.2 above. Maintenance on the Upper Master Valve can be down by isolating from well bore pressure using: Barrier 1: Bridge Plug (set at 50 m, inflow & pressure tested Barrier 2: LMGV 1) The bridge plug and LMGV valves must be inflow tested as described in Chapter2.1.2 above. For additional safety if a TRSCSSSV is instaled close it Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 135 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 2) Hook-up pump/Chiksan/vent line to KWV. Open Swab valve to monitor pressure. 3) Open UMGV. 4) Inflow-test LMGV as as described in Chapter2.1.2 above. The leak rate across the LMGV must comply with SP-2017, Well Failure Model. Open the LMGV. 5) Run and set a Bridge plug in the tubing at +/- 50 m and inflow test to 0 kPa for 1 hour. 6) Pressure test Bridge plug from above to CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) for 30 minutes using inhibited water. 7) Depressurise Christmas Tree and close the LMGV. 8) Bleed off pressure to the UMGV actuator hydraulic control line, isolate it and disconnect it from the hydraulic operating system. 9) Leave the KWV connection to the pump/chiksan/vent line open to atmosphere during valve maintenance 10) After valve maintenance is finished, hook HP pump to the kill line open the UMGV and test the Christmas Tree body to CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) for 30 minutes against the LMGV, using inhibited water. 11) Equalise pressure across the LMGV and open it. 12) De-isolate & pump open TRSCSSSV (where installed) 13) Inflow-test the repaired valve as as per the procedures as described in Chapter2.1.2 above. Maintenance on the Lower Master Valve can be done by isolating from well bore pressure using Barrier 1: Bridge Plug set at 250 m (or 55 m if TRSCSSSV installed), Barrier 2: Bridge Plug set at 50 m (or 25 m if TRSCSSSV installed), The lower bridge plug must be inflow tested and pressure tested per SP-1217, Well Control Barriers The upper bridge plug must pressure tested The Annulus must first be tested 1) Hook-up pump/Chiksan/vent line to A annulus Bleed off residual pressure from 'A' annulus, top up using inhibited water with oxygen scavenger, and monitor pressure build-up or water losses for 30 minutes to confirm integrity. (Record pressure) 2) Pressure test ‘A’ annulus to 10,000 kPa for 30 minutes to confirm integrity of the cemented tubing (or packer), tubing hanger seals and other side outlet valves. 3) Hook-up pump/Chiksan/vent line to KWV Open Swab valve to monitor pressure. 4) Open UMGV and isolate hydraulics at control panel. Open LMGV. 5) Run an HWL Monolock or PES (prong type) bridge plug, set it at +/- 250 m (or 55m if TRSCSSSV installed) and inflow test it to 0 kPa for 4 hours. 6) Pressure test from above to CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) for 1 hour, using fresh inhibited water with oxygen scavenger. Bleed off pressure. 7) Run a second HWL Monolock or PES (prong type) bridge plug, set it at +/- 50m (or 25m if TRSCSSSV installed), and pressure test it using inhibited water with oxygen scavenger to CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) for 1 hour. Bleed of pressure. 8) Where installed isolate the TRSCSSSV hydraulics at the control panel. 9) After valve maintenance is finished, open the LMGV and test the Christmas Tree body to CITHP + 2,000 kPa (or 35,000 kPa, whichever is greater) for 30 minutes against the upper bridge plug, using inhibited water. Page 136 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 10) Equalise pressure using pump then remove Bridge plugs 11) De-isolate & pump open TRSCSSSV (where installed) 12) Close and inflow-test the LMGV as outlined in Section 8. 13) De-isolate UMGV hydraulics 2.5.3.2.2 FLS Gate Valve Bonnet Grease Fitting & Buried Check Valve Replacement Two isolation barriers are required and must be in place and tested before removing and replacing the FLS valve grease fitting or buried check valve in the valve bonnet. Back-seating the valve and pressure testing the back seat provides one barrier. The other barrier may be provided by either an inflow tested TRSCSSSV, insertion of a bridge plug at +/- 10 m and inflow or pressure testing it, or closure of an up-stream tree valve(s), e.g. LMGV when removing UMGV grease fitting. Where fitted, the buried check valve on newer style trees provides a barrier if it is pressure tested. A. Changing out a Grease Fitting on a LMGV with a buried Check Valve, on a well with a TRSCSSSV 1) Close and inflow test TRSCSSSV. Leave Christmas Tree depressurised 2) Back-seat the valve as follows: 3) Close LMGV fully. 4) Unscrew the four Allan Screws on the bearing cap then unscrew the bearing cap four complete turns. 5) Turn the hand-wheel clockwise (the closing direction) until the gate firmly contacts the bottom of the cavity and the stem moves outward, contacting the internal backseat shoulder. 6) Bump the hand-wheel in the closing direction 7) Pressure Test Effectiveness of Backseat as follows: 8) Fill the Christmas Tree with inhibited water and pressurise to 3,000 kPa. Maintain pressure 9) Remove cap from the grease fitting 10) Trip the ball in the grease fitting check valve by inserting a 1/8" diameter by 3/4" long pin (bleeder tool) into the run of the fitting. 11) Replace the cap slowly until the ball in the fitting is unseated and the pressure/water trapped by the back-seating process is released. 12) If pressure/water escapes quickly then stops, the backseat is effective. Depressurise tree and change out the grease fitting. Note: If water continues to escape & the pressure drops, the backseat is ineffective. Backseat the valve again as above and repeat test. B. Changing out a Grease Fitting on a LMGV without a buried Check Valve, on a well without a TRSCSSSV 1) Set Bridge plug at +/- 10 m and inflow test to 0 kPa for 30 minutes. 2) Fill tubing with inhibited water and pressurise to 3,000 kPa. Maintain pressure. 3) Remove cap from the grease fitting 4) Trip the ball in the grease fitting check valve by inserting a 1/8" diameter by 3/4" long pin (bleeder tool) into the run of the fitting. 5) Replace the cap slowly until the ball in the fitting is unseated and any trapped pressure is released. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 137 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 6) If pressure escapes quickly then stops, the buried check valve is effective. 7) Depressurise Christmas Tree to 0 kPa. 8) Change out grease fitting 9) Equalise pressure and remove Bridge plug. C. Changing out buried Check Valve in LMGV Bonnet on a well without a TRSCSSSV 1) Set Bridge Plug at +/- 10 m and inflow test to 0 kPa for 30 minutes. Leave Christmas Tree depressurised 2) Backseat LMGV and pressure test effectiveness of backseat by pressurising Christmas Tree with inhibited water, & stinging grease fitting, as outlined above 3) Remove grease fitting 4) Sting buried check valve with bleeder tool to re-test for trapped pressure 5) Depressurise and change out buried check valve 6) Replace the grease fitting and un-backseat the LMGV D. Un-Backseating the LMGV 1) Move the valve gate off the backseat position 2) Tighten the bearing cap. (Torque to approximately 25 ft-lb) 3) Turn the hand wheel counter clockwise (opening direction) one full turn while simultaneously tightening the bearing cap. 4) Tighten the bearing cap to approximately 200 ft-lb. 5) Replace the four Allan screws in the bearing cap. E. Replacing Thrust Bearings 1) Loosen the bearing cap. After two or three turns the cap will rotate freely by hand. Note: If the cap does not rotate freely after three turns, the packing gland may be moving outward with the bearing cap. DO NOT REMOVE THE CAP. Tighten the cap and call out specialist help before proceeding. 2) If the bearing cap rotates freely, remove the cap from the bonnet. 3) Using a punch, drive the stem shear pin from the stem adapter, ensuring that the adapter is not damaged. 4) Remove the adapter from the stem. 5) Remove both sets of bearings and bearing races from the stem adapter. 6) Discard any pitted, cracked, or damaged bearings or races. 7) Discard the stem adapter if either bearing surface on the adapter shoulder is damaged. 8) Pack the bearings with grease 9) Place each bearing between a pair of cleaned races 10) Install one set of bearings and races over the bottom of the adapter and one set over the top of the adapter Note: The adapter ‘O’ ring may be removed temporarily to allow the installation of the top bearing and race assembly. 11) Insert the stem adapter over the end of the stem, and align the pin hole in the adapter with the hole in the stem Page 138 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 12) Using a punch, drive in the stem and ensure that the pin does not protrude over the OD of the adapter shoulder. 13) Replace the stem adapter ‘O’ ring if necessary 14) Inspect the bearing cap to ensure that an extra race, held by grease tension is not retained inside. Clean and install the cap. 15) Rotate the stem adapter counter clockwise to ensure that the gate is off the bottom of the body. This will confirm that the stem back seating shoulder is not contacting the bonnet shoulder. Inject grease through the bearing cap grease fittings until excess grease passes through the bleed port. F. Stem Packing Replacement with Pressure in the Valve 1) Backseat the valve 2) Remove the hand wheel (21) 3) Remove the bearing cap from the bonnet (1) 4) Using a punch, drive the stem shear pin from the stem adapter, ensuring that the adapter is not damaged. (7 & 8) 5) Remove the adapter from the stem (7 & 16) 6) Remove both sets of bearings and bearing races from the stem adapter (3 & 4) 7) Loosen the packing gland (9) 8) Ensure that the threads on the bonnet neck OD are not damaged. 9) Remove the packing gland (9) 10) Remove the stem packing (11) as follows: 11) Use packing sleeve P/N 21168 for 1" stem size and packing sleeve P/N 233842 for 1-1/4" stem size. 12) Thread the packing sleeve into the bonnet packing gland preparation until the sleeve bottoms out. 13) Using a grease gun attached to the bonnet grease fitting, pump the packing out into the recessed area of the packing sleeve. 14) Remove the packing sleeve from the bonnet. 15) If a packing sleeve is not available, remove the stem packing by one of the following methods: 16) Pump the packing out with grease until the grease bypasses or the packing refuses to extrude further. 17) Pull the packing out with a corkscrew. Caution: Do not damage the stem or packing bore 18) Clean the grease from the stuffing box bore (inside bonnet) so that a hydraulic lock will not prevent the installation of new packing 19) Inspect the stuffing box to ensure that the bore is clean and free of pits or scars. 20) Inspect the stem (16) to ensure that the surface is free of burrs and pits. 21) Apply a light coat of grease to: 22) The Stem (16) 23) The stuffing box bore (Inside Bonnet) 24) The ID and OD of the stem packing (11) Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 139 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 25) The nose and threads of the packing gland. 26) Lightly grease the new stem packing. Install it over the stem and into the bonnet as follows: 27) J packing or U packing: Install with rounded nose facing pressure. 28) Varipak packing: Install with open end facing pressure. 29) HT-20 packing: Call Cameron service. (Special tools required; not user replaceable). 30) Using the packing gland as a pushing tool, push the packing into the stuffing box 31) Remove the packing gland and lubricate the stem OD. If a packing back-up ring is required, install it over the stem. 32) Install the packing gland and apply approximately 200 ft-Ib of torque, ensuring that the bonnet threads are not damaged. 33) Inspect the bearings and bearing races on the stem adapter for pits, scores, or cracks. Replace if damaged. 34) Pack the bearings with grease. 35) Place each bearing between a pair of carefully cleaned races. 36) Carefully clean the stem adapter. 37) Install one set of bearings and races over the bottom of the adapter and one set over the top of the adapter. Note: The adapter O-ring may be removed temporarily to allow for the installation of the top bearing and race assembly. 38) Insert the stem adapter over the end of the stem and align the pin-hole in the adapter with the hole in the stem. 39) Using a punch, drive in the stem pin and ensure that the pin does not protrude over the OD of the adapter shoulder. Caution: hammer. Do not strike the bearings, races, or stem adapter with the punch or 40) Replace the stem adapter O-ring if necessary. 41) Inspect the bearing cap to ensure that an extra race, held by grease tension, is not retained inside. 42) Clean the bearing cap and lubricate the threads, 43) Install the cap, and torque to 200 ft-Ib, 44) Rotate the stem adapter counter clockwise to ensure that the gate is off the bottom of the body. This procedure will confirm that the stem back seating shoulder is not contacting the bonnet shoulder. 45) Inject grease through the bearing cap grease fitting until the excess grease passes through the bleed port. 46) Lubricate the body cavity. Page 140 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Figure 2-1, Stem Packing with Check Valve Figure 2-2, Low Pressure Grease Fitting Table 2-4, FLS Gate Valve, Description of Parts Item Qty Item Qty 1. 2. 1 1 Bearing Cap Grease Fitting 12. 13. 8 8 Nut Stud 3. 4. 4 2 Bearing race Bearing 14 15. 1 1 Grease fitting Gasket Printed 15/02/16 Description Description PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 141 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 5. 1 ‘O’ Ring 16. 1 Stem 6. 1 ‘O’ Ring 17. 1 Gate 7. 1 Stem Adapter 18. 2 Seat 8. 1 Dowel Pin 19. 2 Seal Ring 9. 1 Packing Gland 20. 1 Retainer Plate 10. 1 Backup Gland 21. 1 Hand Wheel 11. 1 Stem Packing Figure 2-3, Explosion Drawing of Valve G. Valve Gate and Seat Replacement 1) Isolate the valve from the line pressure 2) Release the cavity pressure by bleeding the bonnet grease fitting 3) Fully open the valve to ensure that the stem is completely within the gate neck. 4) Remove the bonnet nuts. 5) Support the bonnet and turn the hand wheel clockwise until the stem completely backs out of the gate. 6) Remove the bonnet assembly. 7) Pull the gate from the body. 8) Remove the seats. Page 142 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Note: Petroleum Development Oman LLC If the seats are stuck, insert a screwdriver in the groove on the OD of the seats and pry out the seats. 9) Remove the retainer plate from the bottom of the body cavity. 10) Flush the body cavity thoroughly with a suitable solvent and wipe clean with a rag. 11) Inspect the cavity parts for damage. 12) Ensure that the retainer plate is not bent, twisted, or distorted. Important: Solid material should not be built up on the retainer plate surfaces. 13) Ensure that the seal rings are not damaged 14) Ensure that the seats are not cut or damaged 15) Ensure that the gate is not cut or damaged. 16) Replace any damaged parts. 17) Ensure that the body cavity is free of all foreign matter such as solid particles, grit, trash, etc. 18) Clean the body cavity with a suitable cleaning solvent. 19) Apply a thin coat of clean grease to the body cavity, gate, retainer plate, seats, and seat seal rings. 20) Install the U-shaped retainer plate in the bottom of the body cavity. The flat centre part of the retainer plate goes against the cavity bottom, and the semi-circular cut-outs must be aligned with the seat pockets. 21) Install the seal rings into the face groove(s) located in the seats. Note: The FL valve uses one seal ring per seat; the FLS uses two per seat. 22) Install the seats into the seat pockets. Note: The grooved seat face with its seal ring(s) goes against the body seat pocket seal face. Do not apply more than a very thin film of grease to the back face of the seat and seal ring(s) or the seal face on the body seat pocket. 23) Install the gate into the cavity between the seats. 24) Push the gate all the way to the bottom of the cavity and pack the remaining space with grease. 25) Remove the seal ring from the bonnet groove. 26) Clean the grooves and/or seating area of the body and bonnet. 27) Apply a very thin film of clean grease to the bonnet seal ring and groove 28) Install the new seal ring in the bonnet groove. 29) Install the bonnet over the body studs. 30) On valves 10,000 psi WP and above, rotate the bonnet until the grease fitting is 90° from the gate bore. 31) Thread the stem into the gate by turning the hand wheel counter clockwise, 32) Pull the bonnet down over the studs. 33) Hand tighten the bonnet nuts. 34) Ensure that the gate is not on the bottom of the cavity. 35) Evenly tighten the bonnet nuts to a torque of 1,275 ft-lb Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 143 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 The raised bonnet face on valves 10,000 psi and above will fully contact the body face when the bonnet nuts are tight 2.5.3.3 2.5.3.3.1 Corrective Maintenance of OTIS Control Panels Checks prior to embarking on any Corrective Maintenance: 1) Check and ensure that the control line pressure is set normal. 2) Close control line and isolate gas/N2 supply. 3) Trip the panel by pushing on the “pull & pin” shut down valve 4) Open the “block” & “drain” valves of hydraulic system. This ensures that there is no hydraulic pressure and the gas supply pressure is fully blown down. 5) If dial pilot is to be replaced, close flow pressure sensing line isolation valve on panel exterior and depressurise line to dial pilot. 6) Remove the defective component after disconnecting the mounting bolts and input /output and pilot supply lines. 7) Install the new replacement component. 8) Charge the panel. 9) Leak test the newly tightened connections and function test panel. 10) Charge panel, ensure all system pressures are normal and line up by opening all valves previously isolated. Note: 2.5.3.3.2 Only trained personnel are allowed to work on control panels. Before isolating the control line ensure the system is free of any leak on surface or down hole, else the well may trip. Replace the Control Panel 1) Check and ensure that the control line pressure is set normal. 2) Close control line and isolate gas/N2 supply Trip the panel by pushing on the “pull & pin” shut down valve). 3) Isolate fusible plug signal, flow line pressure sensing line to internal pilot, external pilot output signal (and any other signal output lines if connected) by closing valves on the panel external and bleed off trapped pressure in the system with in the panel. 4) Open the “block” & “drain” valves of hydraulic system. This ensures that there is no hydraulic pressure and the gas supply pressure is fully blown down 5) Disconnect all output/input lines to and from control panel upstream of isolation valves by breaking the swage lock connections (this should be done after having made sure that upstream side/towards panel of isolation valves are fully depressurised and that the valves do not leak) 6) Remove panel foundation bolts if provided. 7) Remove Panel from the pad lifting off with a HIAB or crane (check and ensure that the shade/roof above panel do not obstruct lifting) 8) Locate the replacement panel on the pad. 9) Connect up all lines previously disconnected. 10) Open all isolation valves except the control line isolation valves. 11) Charge and function test panel. 12) Open the control line isolation valves after having ensured that the panel is set normal and calibrated correctly as per design parameters (for specifics refer to MRP & ERDs) Page 144 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 2.5.3.3.3 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Pre-commissioning checks on Control Panel 1) Ensure that the control panel is hooked as per Engineering design drawing. 2) Fill the panel reservoir with hydraulic oil (Tellus-37) to the recommended level. 3) Disconnect control lines at the wellhead (ensure the isolation valve of SCSSSV on the wellhead is closed) and purge the lines with N2 to ensure the lines are clear and clean. For this purpose connect N2 bottles to the control line at the panel end. 4) Using the Haskel pumps on the panel flush through the control lines with hydraulic oil until oil appears on the disconnected end of control lines at the wellhead. 5) Hydro-test the control lines to 1.5 times the max working pressure for 30 minutes. 6) Purge all other signal input/output lines of panel with N2 and test to 1.5 times of working pressure. 7) Check and ensure that the external pilot/pilots are correctly calibrated. 8) Calibrate R/Vs of panel hydraulic system. 9) Calibrate dial pilot. 10) Close the control line isolation valve on panel exterior and charge panel. 11) Calibrate ‘on delay’, ‘off delay’ and ‘equalizing delay’ where applicable. 12) On completion of checks and calibration, function test the control panel. 13) Using a test pump check the Hi/Lo tripping functions (connect pump to pilot sensor line). 14) Check tripping of panel on fire protection (simulate by bleeding off signal to fusible plug) 15) Check panel tripping on Hi/Hi or Lo/Lo pressure if provided (by bleeding off signal to external pilot) 16) On satisfactory completion of checks, function test the panel and ensure that the safety valves trips and opens up as per design logic. Ensure that all valves are in operating position and 3-way pilot valves are in ‘pilot’. Note: 2.6 2.6.1 On wells with TRSCSSSV if the valve trips with differential pressure pump truck is required to equalize and open up. The above procedure is only generic Procedure for acid soaking to clean Tubing hanger BPV thread profile Safety Precautions while attempting acid soak. 1) Ensure a wellhead platform or scaffold is available placed in position for acid handling if the Christmas tree height is above 1.5 meters. 2) Ensure appropriate PPE are worn by the personnel handling acid (Neoprene gloves, Rubber apron, plastic gobbles, acid vapour mask, Helmet and Safety Boots) 3) Emergency eye wash station or running water facility available on location. 4) Acid (28% HCL) in plastic container to be transported in wooden box with appropriate warning sign posted on the box and plastic contained identified as containing acid. 5) Always position yourself upwind while handling acid. 6) Ensure the acid is pumped using a HD plastic hand pump and hose and the end of the hose is secured to wellhead to prevent hose falling off and spilling acid. 7) Ensure extreme care while handling acid as it can cause severe burning in contact with skin. 8) Ensure SHOC card is available and displayed. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 145 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 2.6.2 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Procedure for filling acid in Christmas tree 1) Close the master and flow wing valve. Open the swab valve and bleed off pressure above master through the tree cap needle valve. 2) Ensure both the master and wing valves are holding pressure. 3) Remove the tree cap. 4) Pump acid into the tree cavity approximately 2 litres of acid using the hand pump. (Do not attempt to pump acid if master or wing is passing as it can cause acid to spray up) 5) Close the swab and replace the tree cap. 6) Open the master very slowly to equalize and allow for soaking for 30 minutes. If necessary repeat procedure Page 146 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 3 Identified Hazards and Threats The following hazards or threats have been identified as being prevalent during the process covered by this Procedure. These are assessed and the controls to be applied are given in the Hazards Register, which forms Part 5 of Volume 1 of GU-458, Well Engineering Combined Operations HSE Case REF HAZARD H-01.02a Hydrocarbons in Formation / at Surface (drilling ops) H-01.02b Hydrocarbons in Formation / at Surface (well services) H-02.03 Diesel Fuel (fuel source) H-04 Explosives H-05.01 Bottled Gases Under Pressure H-05.04a Air Under High Pressure (drilling ops) H-05.04b Air Under High Pressure (well services) H-05.07a Fluids Under High Pressure (drilling ops) H-05.07b Fluids Under High Pressure (well services) H-06.01a Personnel Working at Heights (drilling ops) H-06.01b Personnel Working at Heights (well service) H-06.01c Personnel Working at Heights (man riding winch) H-06.02 Personnel at Height <2m – Slippery / Uneven Surfaces H-06.03a Overhead Equipment (drilling ops) H-06.03b Overhead Equipment (well services) H-06.03c Overhead Equipment (crane, forklift, air winch ops) H-06.06 Elevated equipment (tubular on pipe rack or catwalk) H-07.01 Objects under tension (wireline cable) H-08.01 On land transport – onsite vehicles H-08.05a Equipment with moving / rotating parts (ex drill floor equipment) H-08.05b Equipment with moving / rotating parts (drill floor equipment) H-08.06 Use of Hazardous Hand Tools H-08.09 Moving or Rotating Equipment (drill floor) H-13.02 Liquid Nitrogen H-15.02 Voltage >50 to 440V in Equipment H-15.03 Voltage >440 Volts H-17 Open Source Radiation H-18 Closed Source H-19.01 Insufficient Oxygen Atmosphere – Confined Space Entry H-20.01 Hydrogen Sulphide Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 147 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC REF HAZARD H-23.01 Hydrofluoric Acid H-23.02 Hydrochloric Acid H-25.01 Manual Materials Handling Page 148 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 4 Roles and Responsibilities as referred to in this document The principle of Single Point Accountability is applied to well testing activities and therefore responsibilities will vary according to the type of well test being conducted (see below). With the introduction of Asset Management in PDO, multi-function teams have been established to control the management of each area. For simplicity, the responsibilities of individual functions within these organisation structures have not been identified but have been referred to collectively as the ‘Asset Team’. Table 4-1, Roles and Responsibilities Role Responsibility Well Integrity Focal Point / Engineer Approve maintenance scheduling changes (WIFP) as Technical Authority (TA2) or CFDH for assigned Directorate Co-ordinate Well Integrity & abandonment programme activities in the asset Report Well Integrity status of Well Stock / KPI’s to Asset Team Carry out / assist in Well Integrity training of staff / communication of changes / updates to CoP / Management Specifications Ensure implementation of Maintenance Strategy in SAP Provide technical support on Well Integrity issues to the asset Ensure integrity data is entered into electronic WIMS Provide support to Function to further develop well integrity management system, e.g. CoP, WFM etc Overall Management of Integrity work execution and document updating. Focal Point for Integrity work planning and execution Senior Well Engineer-Integrity Well Services Operation Engineer Well Services Site Supervisor Printed 15/02/16 Adhere to WLICoP during well construction, repair, modification, intervention and abandonment Carry out maintenance / monitoring activities as defined by Process Maps (see also CP-118, Well Life Cycle Integrity Code of Practice) Ensure test results / work history is reported in electronic WIMS Create Operating Envelope Report by data provision for each new well or well design change Execution of Integrity Work PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Ref. Ind. Asset UWXZ/4 UWXZ/4X UWH/93, UWXZ/31N Page 149 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 5 Appendices 5.1 Appendix 1, Forms and Reports The following forms are used in relation to this Procedure: Step-Out Request Form Well Location Custodianship Transfer Form The PDO Site Supervisor will ensure that a Pre-Stimulation Audit Checklist is completed jointly with the Contractor Stimulation Supervisor, and any shortfalls rectified, before the stimulation operations commence. 5.2 Appendix 2, Glossary of Terms, Abbreviations and Definitions Table 5-1, Glossary of Terms, Abbreviations and Definitions Term/Abbreviation Definition May Indicates one possible course of action Should Indicates a preferred course of action Shall Indicates a mandatory course of action APN Axelson Part Number BOP Blow-Out Preventer BPV Back Pressure Valve CFDH Corporate Functional Discipline Head CITHP Closed-in Tubing Head Pressure CMF Corporate Management Framework CoP Code of Practice DIMS Drilling Information replaced by EDM) ESD Emergency Shut Down FMC Blow-Out Preventer Manufacturer FWV Flow Wing Valve HIPPS High Integrity Pipeline Protection System KPI Key Performance Indicator KWV Kill Wing Valve KWVI Inner Kill Wing Valve KWVO Outer Kill Wing Valve LMGV Lower Master Gate Valve LMV Lower Master Valve MAASP Maximum Allowable Annular Surface Pressure POOH Pull-Out-Of-Hole PTS Pressure Transmission System SCSSSV Surface Controlled Subsurface Safety Valve SSSV Subsurface Safety Valve Page 150 Management PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure System (will be Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Term/Abbreviation Definition SIT Subsurface Integrity Test SV Swab Valve TRSCSSSV Tubing Retrievable Surface Controlled Subsurface Safety Valve UMGV Upper Master Gate Valve UMV Upper Master Valve WFM Well Failure Model WIFP Well Integrity Focal Point WLICoP CP-118, Well Life Cycle Integrity Code of Practice WIMS Well Integrity Management System WIT Wellhead Integrity Test WR-SCSSSV Wireline Retrievable Surface Controlled Subsurface Safety Valve 5.3 Appendix 3, Related Business Control Documents and References Table 5-2, Related Business Control Documents and References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Document CMF Business Control Portal Well Engineering Documentation Page PL-01-11, PDO Policies CP-118, Well Integrity Code of Practice CP-122, Health Safety and Environment Management System Code of Practice Co. PDO PDO PDO PDO PDO CP-123, Emergency Response Code of Practice PR-1065, Emergency Response Documents Part II PR-1287, Emergency Response Document Part III, Contingency Plan Volume II, Well Engineering Operations 9. PR-1444, Well Engineering Management Framework 10. SP-2036, General Operational Safety Specification PDO PDO SP-2017, Well Failure Model Completion Operations Manual SP-1217, Well Control Barriers Wellhead Standards Manual APF/92/70R, Surface Controlled Sub-Surface Safety Valve (SCSSSV) Policy APG/289/96,“LNG Upstream 10K Monobore Standard Completion Design” APG/212/97 “Frac Treatment Shut-down Criteria to Optimise LNG Frac Efficiency” APG/154/97 “Standard LNG Well Frac Initiation Perforating Programme” APG/289/96,“LNG Upstream 10K Monobore Standard Completion Design” APY/9802/5, Well Integrity Data Mapping PDO PDO 6. 7. 8. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Printed 15/02/16 PDO PDO Remark Replaces HSE/96/01, Part 1, Introduction and User Guide Replaces PR-1446 and PR-1042 PDO PDO PDO PDO PDO PDO PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 151 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Document Co. GU-458, Well Engineering Combined Operations HSE 21. PDO Case 22. PR-1172, Permit to Work Procedure 23. PR-1482, Slickline Operations Procedure 24. PR-1036, Coil Tubing Operations Procedure PDO PDO PDO 25. SP-2037, Well Engineering Specification for the Use of PDO Equipment in Hazardous Areas 26. SP-1219, Drilling Specification Hydrogen Sulphide PDO 27. PR-1078, Hydrogen Sulfide Management 28. Safe Handling of Chemicals (SHOC) 29. Well Location Custodianship Transfer Form 30. PR-1098, Well Activity Coordination and Procedure Page 152 PDO Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Remark Replaces Drilling and Well Services Safety Cases (DSC and WSSC) Replaces PR-1456 (HP-CT-001), Coiled Tubing Rig Up & Operations Replaces PR-1043 and PR-1451 Replaces PR-1044 and PR-1452; will probably be replaced by PR-1078, Hydrogen Sulphide Management Procedure which seeks to be a company-wide onestop shop procedure for H2S related issues. The procedure is currently in DRAFT format. Click here to view the latest DRAFT. Out of date, owned by Operations PDO PDO Control PDO PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 5.4 Petroleum Development Oman LLC Wellhead Maintenance Guides 5.4.1 Cameron 5.4.1.1 Christmas Tree Valve Maintenance Routine maintenance entails greasing the valve stem bearings and filling the valve with sealant or grease as applicable, each time the valve is routinely leak tested. It is recommended that this is carried out immediately after the SSSV leak test while the Christmas Tree is de-pressurised. These procedures should be used in conjunction with the OEM operation and maintenance procedures, as well as the following GUIDEXPRO procedures. ‘Well preparation for Christmas Tree Work’ ‘Operation and maintenance of Christmas Trees’ 5.4.1.1.1 Visual Inspection Visually inspect the Christmas Tree assembly for leaks and record any defects. Inspection to include: All Alemite style grease fittings Actuated valve actuator relief/breather ports for leakage Manual valves for stem seal leakage All needle valves, manifolds and instrumentation for leaks or damage Test and bleeder port fittings for leaks Valve bonnet seal areas for leaks XT Cap flanged connection and quick union. Rust preventative to be applied to any exposed metal surfaces or areas of damaged paintwork. 5.4.1.1.2 Valve Operation A. Manual Valve Stroke the valve 2 – 3 times to check for correct operation. Refer to table for number of turns for each size of valve. 2 1/16” 12 1/3 turns Note: 5 1/8” 27.5 6 3/8” 33.75 Manuals valves must be backed off ¼ turn after fully opening or closing to allow the valve to function properly. B. Actuated Valve Function the actuated valve 2 – 3 times to check for correct operation, and confirm full stroke via rising stem or visual indicator. Operation should be smooth over full travel of valve in both directions. Time taken to fully close should be recorded. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 153 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Petroleum Development Oman LLC 5.4.1.1.3 Valve Lubrication Valve Grease Type Bearing Grease Standard Service CI-14 or TF-41 CI-14 or TF-41 HPHT Shearwater TS-41 / Clare 601 TS-41 / Clare 601 Note: In all cases, reference should be made to the Manufacturers Operation and Maintenance Manual. Grease specifications may vary between wells due to particular well characteristics. A. Stem Bearings Stem bearings can be greased while the valve is in the open or closed position, or under pressure. The grease fitting can be found on the bearing cap of the manual valve bonnet. Connect the manual grease pump to the bearing cap grease fitting. Pump until clean grease extrudes from the vent port opposite. B. Valve Grease Injection Max Per Cavity Volume (cu in) Weight (lb) Note : 2 1/6” 43 1.7 5 1/8” 312 12.5 5k 583 23.3 6 3/8” 10k 583 23.3 15k 1,000 40.1 Where possible the valve cavity will be de-pressurised, however, grease may be injected while the valve is under pressure. Grease may be injected into manual valves in either the open or closed position, but preferably in the closed position. Actuated valves must be in the open position while injecting grease. A suitable valve should be installed inline, preferably close to the grease fitting if access allows. This will enable the pump to be removed in the event that the check valve does not re-seat. Valves that are seldom used or do not have fluids flowing past them may not require the full quantity of grease. To avoid blockages of instrumentation, etc with grease, carefully observe the pump pressure on these valves, and stop injecting as soon as a noticeable rise in pressure above the initial injection pressure occurs. If excess grease is a known problem, limit the grease injection to between 10% and 25% of the recommended capacity, irrespective of the pressure indications. 1) Close the manual valve and back-off the stem ¼ turn. 2) Identify the valve grease fitting, and carefully remove the cap. Warning: Use a back-up spanner to prevent the grease fitting from backing out of the bonnet. Trapped pressure may exist under the protective cap of the grease fitting. Back-off the cap carefully and monitor for pressure. If pressure exists, then re-tighten the cap and record details. 3) If the well is still pressurised, record the upstream and downstream pressures. This will determine the pump pressure required to overcome the pressure within the cavity. 4) Connect the grease pump to the fitting and begin to pump the grease until the cavity is filled. At no time should the total amount of grease pumped exceed the recommended capacity of the valve. Warning: At no time should pump pressure exceed the maximum working pressure of the valve. 5) When the required amount of grease has been injected, the pump air supply should be isolated, and the injection hose should be vented via the bleeder fitting, prior to removing from the grease fitting. Page 154 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Warning: Petroleum Development Oman LLC If pressure does not vent off quickly, then the grease fitting internal check valve has not seated. Attempt to reseat by pumping more grease, but if unsuccessful, then close the inline valve and remove the pump. Appropriate physical barriers should be placed around the valve to protect it from impacts until remedial measures are carried out. 6) Replace the grease fitting cap. 7) Return the valve to its normal operating position, ensuring correct operation and full travel. 8) Repeat steps 2 – 7 with the remaining valves. 5.4.1.2 Annulus Valve Maintenance Routine maintenance entails greasing the valve stem bearings and filling the valve with sealant or grease as applicable, each time the valve is routinely leak tested. It is recommended that this is carried out while the respective annulus has been bled down These procedures should be used in conjunction with the OEM operation and maintenance procedures, as well as the following GUIDEXPRO procedures. ‘Well preparation for Christmas Tree Work’ ‘Operation and maintenance of Christmas Trees’ 5.4.1.2.1 Visual Inspection Visually inspect the XT assembly for leaks and record any defects. Inspection to include: All Alemite style grease fittings Actuated valve actuator relief/breather ports for leakage Manual valves for stem seal leakage All needle valves, manifolds and instrumentation for leaks or damage Test and bleeder port fittings for leaks Valve bonnet seal areas for leaks Rust preventative to be applied to any exposed metal surfaces or areas of damaged paintwork. 5.4.1.2.2 Valve Operation A. Manual Valve Stroke the valve 2 – 3 times to check for correct operation. Refer to table for number of turns for each size of valve. 2 1/16” 12 1/3 turns Note: 3 1/8” 18 1/8 turns Manuals valves must be backed off ¼ turn after fully opening or closing to allow the valve to function properly. B. Actuated Valve Function the actuated valve 2 – 3 times to check for correct operation, and confirm full stroke via rising stem or visual indicator. Operation should be smooth over full travel of valve in both directions. Time taken to fully close should be recorded. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 155 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 5.4.1.2.3 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Valve Lubrication Valve Grease Type Bearing Grease Standard Service CI-14 or TF-41 CI-14 or TF-41 HPHT Shearwater TS-41 / Clare 601 TS-41 / Clare 601 Note: In all cases, reference should be made to the Manufacturers Operation and Maintenance Manual. Grease specifications may vary between wells due to particular well characteristics. A. Stem Bearings Stem bearings can be greased while the valve is in the open or closed position, or under pressure. The grease fitting can be found on the bearing cap of the manual valve bonnet. Connect the manual grease pump to the bearing cap grease fitting. Pump until clean grease extrudes from the vent port opposite. B. 4.2 Valve Grease Injection Max Per Cavity Volume (cu in) Weight (lb) Note : 2 1/6” 3 1/8” 43 114 1.7 4.6 Where possible the valve cavity will be de-pressurised, however, grease may be injected while the valve is under pressure. Grease may be injected into manual valves in either the open or closed position, but preferably in the closed position. Actuated valves must be in the open position while injecting grease in order to bypass the automatic backseat facility. A suitable valve should be installed inline, preferably close to the grease fitting if access allows. This will enable the pump to be removed in the event that the check valve does not re-seat. Valves that are seldom used or do not have fluids flowing past them may not require the full quantity of grease. To avoid blockages of instrumentation, etc with grease, carefully observe the pump pressure on these valves, and stop injecting as soon as a noticeable rise in pressure above the initial injection pressure occurs. If excess grease is a known problem, limit the grease injection to between 10% and 25% of the recommended capacity, irrespective of the pressure indications. 1) Close the manual valve and back-off the stem ¼ turn. 2) Identify the valve grease fitting, and carefully remove the cap. Warning: Use a back-up spanner to prevent the grease fitting from backing out of the bonnet. Trapped pressure may exist under the protective cap of the grease fitting. Back-off the cap carefully and monitor for pressure. If pressure exists, then re-tighten the cap and record details. 3) If the annulus is still pressurised, record the upstream and downstream pressures. This will determine the pump pressure required to overcome the pressure within the cavity. 4) Connect the grease pump to the fitting and begin to pump the grease until the cavity is filled. At no time should the total amount of grease pumped exceed the recommended capacity of the valve. Warning: At no time should pump pressure exceed the maximum working pressure of the valve. 5) When the required amount of grease has been injected, the pump air supply should be isolated, and the injection hose should be vented via the bleeder fitting, prior to removing from the grease fitting. Page 156 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Warning: Petroleum Development Oman LLC If pressure does not vent off quickly, then the grease fitting internal check valve has not seated. Attempt to reseat by pumping more grease, but if unsuccessful, then close the inline valve and remove the pump. Appropriate physical barriers should be placed around the valve to protect it from impacts until remedial measures are carried out. 6) Replace the grease fitting cap. 7) Return the valve to its normal operating position, ensuring correct operation and full travel. 8) Repeat steps 2 – 7 with the remaining valves. 5.4.2 FMC 5.4.2.1 Annulus Valve Maintenance Routine maintenance entails greasing the valve stem bearings and filling the valve with sealant or grease as applicable, each time the valve is routinely leak tested. It is recommended that this is carried out while the respective annulus has been bled down. These procedures should be used in conjunction with the OEM operation and maintenance procedures, as well as the following GUIDEXPRO procedures. ‘Well preparation for Christmas Tree Work’ ‘Operation and maintenance of Christmas Trees’ 5.4.2.1.1 Visual Inspection Visually inspect the annulus valves for leaks and record any defects. Inspection to include: All Alemite style grease fittings Actuated valve actuator relief/breather ports for leakage Manual valves for stem seal leakage All needle valves, manifolds and instrumentation for leaks or damage Test and bleeder port fittings for leaks Valve bonnet seal areas for leaks Rust preventative to be applied to any exposed metal surfaces or areas of damaged paintwork. 5.4.2.1.2 Valve Operation A. Manual Valve Stroke the valve 2 – 3 times to check for correct operation. Refer to table for number of turns for each size of valve. 2 1/16” Note: Printed 15/02/16 12.5 turns Manuals valves must be backed off ¼ turn after fully opening or closing to allow the valve to function properly. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 157 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 5.4.2.1.3 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Valve Lubrication Valve Grease Type Bearing Grease FMC G70500 FMC G70500 Note : In all cases, reference should be made to the Manufacturers Operation and Maintenance Manual. Grease specifications may vary between wells due to particular well characteristics. A. Stem Bearings Stem bearings can be greased while the valve is in the open or closed position, or under pressure. The grease fitting can be found on the bearing cap of the manual valve bonnet. 1) Connect the manual grease pump to the bearing cap grease fitting. 2) Pump grease into the bearing cavity, rotating the hand wheel back and forth about ½ a turn to distribute the grease. 3) Disconnect the grease pump 4) Return the valve to its normal operating position. B. 4.2 Valve Grease Injection Max Per Cavity Weight (lb) Note : 2 1/6” 2 lbs Where possible the valve cavity will be de-pressurised, however, grease may be injected while the valve is under pressure. Grease should be injected into manual valves in the closed position. A suitable valve should be installed inline, preferably close to the grease fitting if access allows. This will enable the pump to be removed in the event that the check valve does not re-seat. Valves that are seldom used or do not have fluids flowing past them may not require the full quantity of grease. To avoid blockages of instrumentation, etc with grease, carefully observe the pump pressure on these valves, and stop injecting as soon as a rise in pressure above the initial injection pressure occurs. If excess grease is a known problem, limit the grease injection to between 10% and 25% of the recommended capacity, irrespective of the pressure indications. 1) Close the manual valve and back-off the stem ¼ turn. 2) Identify the valve grease fitting, and carefully remove the cap. Warning: Trapped pressure may exist under the protective cap of the grease fitting. Back-off the cap carefully and monitor for pressure. If pressure exists, then re-tighten the cap and record details. Use a back-up spanner to prevent the grease fitting from backing out of the bonnet. 3) If the annulus is still pressurised, record the upstream and downstream pressures. This will determine the pump pressure required to overcome the pressure within the cavity. 4) Connect the grease pump to the fitting and begin to pump the grease until pressure builds up. Open the valve slightly until the pressure starts to relieve. Warning: At no time should pump pressure exceed the maximum working pressure of the valve. At no time should the total amount of grease pumped exceed the recommended capacity of the valve. 5) When the required amount of grease has been injected, the pump air supply should be isolated, and the injection hose should be vented via the bleeder fitting, prior to removing from the grease fitting. Page 158 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Warning: Petroleum Development Oman LLC If pressure does not vent off quickly, then the grease fitting internal check valve has not seated. Attempt to reseat by pumping more grease, but if unsuccessful, then close the inline valve and remove the pump. Appropriate physical barriers should be placed around the valve to protect it from impacts until remedial measures are carried out. 6) Replace the grease fitting cap. 7) Return the valve to its normal operating position, ensuring correct operation and full travel. 8) Repeat steps 2 – 7 with the remaining valves. 5.4.3 Ingram Cactus Ingram Cactus Valves are installed primarily on some Shell Expro Shearwater Wellheads. 5.4.3.1 Annulus Valve Maintenance Routine maintenance entails greasing the valve stem bearings and filling the valve with sealant or grease as applicable, each time the valve is routinely leak tested. It is recommended that this is carried out while the respective annulus has been bled down. These procedures should be used in conjunction with the OEM operation and maintenance procedures, as well as the following GUIDEXPRO procedures. ‘Well preparation for Christmas Tree Work’ ‘Operation and maintenance of Christmas Trees’ 5.4.3.1.1 Visual Inspection Visually inspect the valve assembly for leaks and record any defects. Inspection to include: All Alemite style grease fittings Manual valves for stem seal leakage All needle valves, manifolds and instrumentation for leaks or damage Test and bleeder port fittings for leaks Valve bonnet seal areas for leaks Rust preventative to be applied to any exposed metal surfaces or areas of damaged paintwork. 5.4.3.1.2 Valve Operation A. Manual Valve Stroke the valve 2 – 3 times to check for correct operation. Refer to table for number of turns for each size of valve. Note: Printed 15/02/16 2 1/16” 18 turns Manuals valves must be backed off 1 full turn after fully opening or closing to allow the valve to function properly. PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 159 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 5.4.3.1.3 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Valve Lubrication Valve Grease Bearing Grease Type Standard Service 700149 700149 HPHT Shearwater 713837 713837 Note : In all cases, reference should be made to the Manufacturers Operation and Maintenance Manual. Grease specifications may vary between wells due to particular well characteristics. A. Stem Bearings Stem bearings can be greased while the valve is in the open or closed position, or under pressure. The grease fitting can be found on the bearing cap of the manual valve bonnet. Connect the manual grease pump to the bearing cap grease fitting. Pump approximately 15 strokes or until pressure builds up. B. 4.2 Valve Grease Injection Max Per Cavity 2 1/6” 3 1/8” Volume (cu in) 43 114 Weight (lb) 1.7 4.6 Notes : 1. Where possible the valve cavity will be de-pressurised, however, grease may be injected while the valve is under pressure. 2. Grease may be injected into manual valves in either the open or closed position, but preferably in the closed position. 3. A suitable valve should be installed inline, preferably close to the grease fitting if access allows. This will enable the pump to be removed in the event that the check valve does not re-seat. 4. Valves that are seldom used or do not have fluids flowing past them may not require the full quantity of grease. To avoid blockages of instrumentation, etc with grease, carefully observe the pump pressure on these valves, and stop injecting as soon as a noticeable rise in pressure above the initial injection pressure occurs. If excess grease is a known problem, limit the grease injection to between 10% and 25% of the recommended capacity, irrespective of the pressure indications. 1) Close the manual valve and back-off the stem 1 full turn. 2) Identify the valve grease fitting, and carefully remove the cap. Warning: Use a back-up spanner to prevent the grease fitting from backing out along with the cap. Trapped pressure may exist under the protective cap of the grease fitting. Back-off the cap carefully and monitor for pressure. If pressure exists, then re-tighten the cap and record details. 3) If the annulus is still pressurised, record the upstream and downstream pressures. This will determine the pump pressure required to overcome the pressure within the cavity. 4) Connect the grease pump to the fitting and begin to pump the grease until the cavity is filled. At no time should the total amount of grease pumped exceed the recommended capacity of the valve. Warning: At no time should pump pressure exceed the maximum working pressure of the valve. 5) When the required amount of grease has been injected, the pump air supply should be isolated, and the injection hose should be vented via the bleeder fitting, prior to removing from the grease fitting. Page 160 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Warning: Petroleum Development Oman LLC If pressure does not vent off quickly, then the grease fitting internal check valve has not seated. Attempt to reseat by pumping more grease, but if unsuccessful, then close the inline valve and remove the pump. Appropriate physical barriers should be placed around the valve to protect it from impacts until remedial measures are carried out. 6) Replace the grease fitting cap. 7) Return the valve to its normal operating position, ensuring correct operation and full travel. 8) Repeat steps 2 – 7 with the remaining valves. 5.4.4 McEvoy Model ‘C’ Style ‘Y’ Blocks 5.4.4.1 Christmas Tree Valve Maintenance Routine maintenance entails greasing the valve stem bearings and filling the valve with sealant or grease as applicable, each time the valve is routinely leak tested. It is recommended that this is carried out immediately after the SSSV leak test while the Christmas Tree is de-pressurised. These procedures should be used in conjunction with the OEM operation and maintenance procedures, as well as the following GUIDEXPRO procedures. ‘Well preparation for Christmas Tree Work’ ‘Operation and maintenance of Christmas Trees’ 5.4.4.1.1 Visual Inspection Visually inspect the Christmas Tree assembly for leaks and record any defects. Inspection to include: All sealant compound and body filler fittings Bonnet bleeder screws Actuated valve actuator relief/breather ports for leakage Manual valves for stem seal leakage All needle valves, manifolds and instrumentation for leaks or damage Test and bleeder port fittings for leaks Valve bonnet seal areas for leaks XT Cap flanged connection and quick union. Rust preventative to be applied to any exposed metal surfaces or areas of damaged paintwork. 5.4.4.1.2 Valve Operation A. Manual Valve Stroke the valve 2 – 3 times to check for correct operation. Refer to table for number of turns for each size of valve. 2 1/16” 13 turns Note: 5 1/8” 20 6 3/8” 25 Manuals valves must be backed off ¼ turn after fully opening or closing to allow the valve to function properly. B. Actuated Valve Function the actuated valve 2 – 3 times to check for correct operation, and confirm full stroke via rising stem or visual indicator. Operation should be smooth over full travel of valve in both directions. Time taken to fully close should be recorded. Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 161 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC 5.4.4.1.3 Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 Valve Lubrication Asset Valve Sealant Type X-184 (5k) X-195 (10k) X-184 Prod X-195 Ann X-184 X-184 X-184 X-195 X-184 X-184 X-184 Brent A,B,C,D Tern A Cormorant A Dunlin A Eider Gannet Fulmar Auk Kittywake Body Filler Bearing Grease15 N/a CI-14 or TF-41 N/a CI-14 or TF-41 N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a N/a CI-14 or TF-41 CI-14 or TF-41 CI-14 or TF-41 CI-14 or TF-41 CI-14 or TF-41 CI-14 or TF-41 CI-14 or TF-41 A. Stem Bearings Stem bearings can be greased while the valve is in the open or closed position, or under pressure. Connect the manual grease pump to the bearing cap grease fitting. Pump until clean grease extrudes from either the outer dust seal or the relief port. B. Valve Sealant Injection Max Per Seat 2 1/6” 5 1/8” 6 3/8” Pump Strokes 18 100 225 Weight of Sealant 1.5 oz 10.8 oz 22 oz Note : 1. Where possible the valve cavity will be de-pressurised, however, sealant may be injected while the valve is under pressure. 2. Sealant may be injected into manual valves in either the open or closed position, but preferably in the closed position. 3. Actuated valves must be in the open position while injecting sealant. 1) Close the manual valve and back-off the stem ¼ turn. 2) Identify the valve sealant compound fittings, and remove the cap from one only. Warning: Use a back-up spanner to prevent the grease fitting from backing out along with the cap. Trapped pressure may exist under the protective cap of the sealant injection fitting. Remove the cap carefully and slowly to allow any trapped pressure to vent off. If pressure does not quickly vent off, then re-tighten the cap and record details. 3) If the well is still pressurised, record the upstream and downstream pressures. This will determine the pump pressure required to overcome the pressure within the cavity. 4) Connect the sealing compound pump to the fitting and begin to pump the sealant until the seat reservoir is filled. The operator should notice a significant increase in pressure when the reservoir is full. At no time should the total amount of sealant pumped exceed the recommended capacity of the valve seat. Warning: At no time should pump pressure exceed the maximum working pressure of the valve. 5) When the required amount of sealant has been injected, the pump air supply should be isolated, and the injection hose should be vented via the bleeder fitting, prior to removing from the sealant injection fitting. 15 Standard Cameron valve grease Page 162 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Revision: 2.0 Effective: May 2007 Warning: Petroleum Development Oman LLC If pressure does not vent off quickly, then the grease fitting internal check valve has not seated. Attempt to reseat by pumping more grease, but if unsuccessful, then close the inline valve and remove the pump. Appropriate physical barriers should be placed around the valve to protect it from impacts until remedial measures are carried out. 6) Replace the sealant injection fitting cap. 7) Repeat steps 2 – 7 with the opposite seat. 8) Return the valve to its normal operating position, ensuring correct operation and full travel. Figure 5-1, Valve Drawing Sealant and Body Filler Connections Printed 15/02/16 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Page 163 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED. Petroleum Development Oman LLC Revision: 2.0 Effective: May2007 This page was intentionally left blank Page 164 PR-1047, Well Integrity Maintenance Procedure Printed 15/02/16 The controlled version of this CMF Document resides online in Livelink®. Printed copies are UNCONTROLLED.