The Sun and the Seasons: Video Guided Notes - vhs-ees-am
advertisement

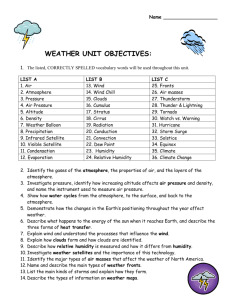
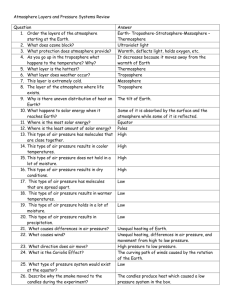
The Sun and the Seasons: Video Guided Notes 1. The sun holds earth in ________and ________ the planet, it provides the _________for winds, evaporation, weather patterns, and our climate. 2. Earth is a _________. This is why the sun’s rays are much more intense in the _________ than in ___________ regions. 3. As Earth orbits the sun, the different ______________ of the globe are exposed to changing amounts of direct sunlight throughout the year, creating the ____________. 4. When a region is in a position to receive more direct sunlight, it experiences ____________. As Earth’s position shifts & that region tilts away from the sun, it will experience_________. 5. As the sun’s rays reach Earth’s atmosphere, much of that energy is scattered back into ________ or absorbed by __________ BONUS: What is this characteristic called, when clouds affect the temperature in the troposphere? 6. When the sun is directly overhead, the intense heat warms the air and evaporates moisture so that the air is laden with water vapor. This sets up _______________ . Hot air _________ and rises, while cool air _______. 7. Rainy seasons in the __________ coincide with the season when the sun is most directly __________. 8. The updrafts of air create a _____________________ along the equator and very ________ winds. In the days of sailing ships, this equatorial zone was called the ___________ because there were so little winds. 9. Once the air is in the upper atmosphere, it begins to ___________ both to the north and south in the form of ______________. How does the sun affect the weather and seasons? The Sun and the Seasons: Video Guided Notes 1. The sun holds earth in ________and ________ the planet, it provides the _________for winds, evaporation, weather patterns, and our climate. 2. Earth is a _________. This is why the sun’s rays are much more intense in the _________ than in ___________ regions. 3. As Earth orbits the sun, the different ______________ of the globe are exposed to changing amounts of direct sunlight throughout the year, creating the ____________. 4. When a region is in a position to receive more direct sunlight, it experiences ____________. As Earth’s position shifts & that region tilts away from the sun, it will experience_________. 5. As the sun’s rays reach Earth’s atmosphere, much of that energy is scattered back into ________ or absorbed by __________ BONUS: What is this characteristic called, when clouds affect the temperature in the troposphere? 6. When the sun is directly overhead, the intense heat warms the air and evaporates moisture so that the air is laden with water vapor. This sets up _______________ . Hot air _________ and rises, while cool air _______. 7. Rainy seasons in the __________ coincide with the season when the sun is most directly __________. 8. The updrafts of air create a _____________________ along the equator and very ________ winds. In the days of sailing ships, this equatorial zone was called the ___________ because there were so little winds. 9. Once the air is in the upper atmosphere, it begins to ___________ both to the north and south in the form of ______________. How does the sun affect the weather and seasons?