Earth Systems Study Guide: Semester A Final Exam
advertisement

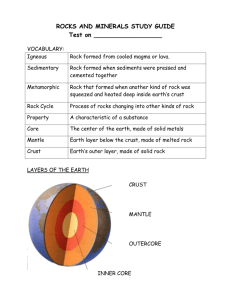
Study Guide for Earth Systems Semester A Final KEY 1. List 5 areas of study found in Earth Science. geology, astronomy, oceanography, meterology, climatology 2. How were the inner planets formed? repeated collisions of asteroid-sized debris 3. According to the nebular hypothesis the solar system was formed by a a rotating cloud made of what 2 gases? helium and hydrogen 4. Name the 4 major spheres of the Earth.hydrosphere, atmosphere, geosphere, biosphere 5. Which of Earth’s spheres include oceans, groundwater, and glaciers?hydrosphere 6. Look in your textbook at the diagram of the Earth layers on p.8. Study the layers you will have a picture of this diagram on the test. 7. What are the 3 main parts of the geosphere?crust, mantle, core 8. The crust and uppermost mantle make up the rigid outer layer of Earth which is called?lithosphere 9. The theory of plate tectonics helps scientists explain what?how eqrthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur 10. What is the driving force for the movement of lithospheric plates?unequal distribution of heat within Earth 11. According to the plate tectonics model what layer of Earth forms the rigid plates?crust and uppermost mantle 12. What are lines of longitude?distance east or west of the prime meridian, measured in degrees 13. What are lines of latitude?distance north or south of the equator, measured in dgrees 14. On the global grid , the prime meridian is at what degrees longitude?0 degrees longitude 15. What type of map shows the differences in elevation best? Topographical map 16. Look on pages 14-15 for an example of a topographic map. Study the map and make sure you understand how to read the map. There will be one on your final exam. 17. On a topographic map, contour lines that form a circle represent what feature?hill 18. What does a map with a scale of 1:24,000 mean? 24000 units on the ground 19. What are the two sources of energy for an Earth system?sun and Earth’s interior 20. The sun’s energy drives what 2 processes? Weather and ocean circulation 21. List an environmental hazard created by humans.air pollution, water pollution, deforestation 22. What is a renewable resource? resource that is virtually inexhaustible or that can be replenished over relatively short time period 23. List 3 renewable resources. Sun, water, plants, wind 24. What is a nonrenewable resource? Resources that take millions of years to form 25. List 3 nonrenewable resources? Coal, oil, natural gas 26. What is a hypothesis? Preliminary untested explanation of something observed 27. What is a scientific theory? Scientific idea that is widely tested and accepted 28. What is the most abundant element in the Earth’s continental crust? Oxygen 29. What are the building blocks of minerals? elements 30. The central region of an atom is called what? nucleus 31. What is an ion? An atom that has lost or gained electrons 32. What is an isotope? The same element that has a different number of neutrons 33. What is a compound?two or more elements bonded together in a definite proportions 34. What subatomic particle is involved in chemical bonding? electrons 35. What is a mineral? Naturally occurring, inorganic solid with an orderly crystalline structure and a definite chemical composition 36. What is the process of mineral formation from magma?crystallization 37. Mineral formation caused by high temperature and high pressure occurs in what type environment?deep within the Earth 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. How are minerals classified?composition of the mineral Minerals in the sulfate and sulfite groups contain what element? sulfur What mineral group is the most common in the Earth’s crust? silicates List 4 properties that are used to identify minerals.hardness, streak, cleavage, color The color of a mineral can change due to what?small amounts of different elements added What is luster?appearance or quality of light reflected from the surface What is the Mohs scale and what does it test? hardness What is cleavage? Tendency of minerals to break along smooth flat surfaces What is fracture? Uneven breakage of a mineral What is density? Mass divided by the volume If a mineral has a mass of 8 grams and a volume of 2 mL, what the density?4g/ml What determines the properties of minerals? composition and structure What is a rock and how is it different from a mineral? Minerals are uniform in composition and the rocks are a mixture of minerals How are rocks classified? How they are formed Look in your textbook at the diagram of the rock cycle on p.67. Study the cycle and stages. You will have a picture of this diagram on the test. What is a sedimentary rock? Rocks formed from the weathered products of preexisting rocks that have been transported, deposited, compacted, and cemented What is a metamorphic rock? Rock formed by the alteration of preexisting rock deep within Earth(but still in the solid state) by heat, pressure, and/or chemically active fluid. What is an igneous rock? Rock formed by the crystallization of molten magma All energy that drives the Earth’s rock cycle comes from where? Earth’s interior and the sun Fossils are only found in what type of rock? Sedimentary rocks What type of fuel is used in nuclear reactors? uranium Look in your textbook at the diagram of the soil layers on p. 138. Study the layers, you will have a picture of this diagram on the test. What is mechanical weathering? The physical breakdown of rock, resulting in smaller fragments. What is frost wedging? Mechanical break up of rock caused by expansion of freezing water in cracks and crevices. What happens to water as it freezes? Volume expands What happens as a result of chemical weathering? The internal structure of the mineral is altered by adding or removing elements. What 3 factors affect the rate of weathering? Chemical composition of the rock, the surface area of the rock that is exposed and the climate What factor has the greatest effect on soil formation? Climate What is a glacier? Thick ice mass that forms over the land from the accumulation, compaction, and recrystallization of snow. What percentage of the Earth’s land surface is covered by glaciers? 10% What is till? Material deposited directly by a glacier What is the name of the process of producing icebergs? Calving Describe the elastic rebound hypothesis. It says that most earthquakes are produced by the rapid release of energy stored in rock. Earthquakes usually occur along faults. What is the most effective way to measure the intensity of an earthquake? Moment magnitude 73. How are travel-time graphs used to find the epicenter of an earthquake? They tell the distance from each seismic station to the earthquake. 74. Label and define: Epicenter- the point on the earth's surface vertically above the focus of an earthquake Focus- is the point beneath Earth's surface where rock breaks under stress and the plates shift-this causes the earthquake Fault-a fracture along which the Earth’s crust on either side have moved relative to one another. 75. What is the minimum number of seismic stations that is needed to determine the location of an earthquake’s epicenter? 3 76. Which seismic waves travel slowest? Surface waves Fastest? Body waves Cause the most destruction? Surface waves (p.223) 77. How many continents did Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis state? 1 major supercontinents 78. What is the name of Wegener’s super continent? Pangaea 79. What is continental drift? Hypothesis states that the continent were once joined to form a single supercontinent 80. What is plate tectonics? Lithosphere is divided into 7 major plates and many smaller plates that move 81. How far does the lithospheric plates move on the average each year? 5 centimeters a year 82. A tectonic plate consists of what parts of the Earth? Crust and uppermost mantle 83. What results when divergence occurs between two oceanic plates? Seafloor spreading 84. What forms when one oceanic plate is forced beneath another plate? A subduction zone 85. The age of rocks in the ocean basins is determined by what? Ocean drilling