Ch 16 Evolution in Populations student
advertisement
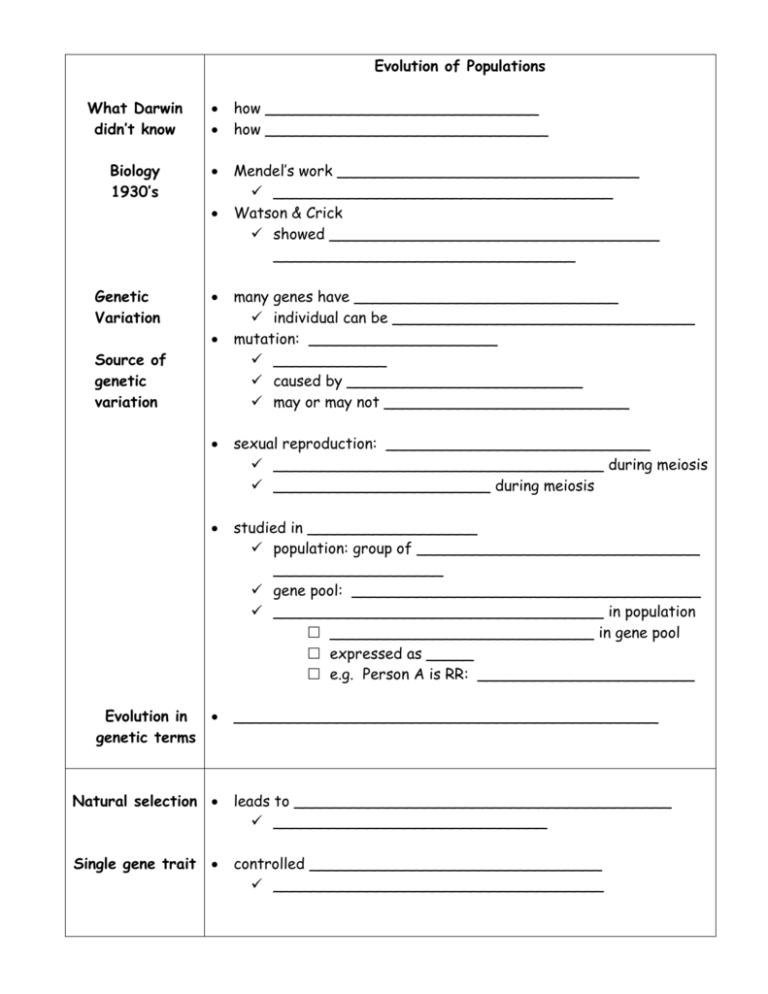
Evolution of Populations What Darwin didn’t know how _____________________________ how ______________________________ Biology 1930’s Mendel’s work ________________________________ ____________________________________ Watson & Crick showed ___________________________________ ________________________________ Genetic Variation Source of genetic variation Evolution in genetic terms many genes have ____________________________ individual can be ________________________________ mutation: ____________________ ____________ caused by _________________________ may or may not __________________________ sexual reproduction: ____________________________ ___________________________________ during meiosis _______________________ during meiosis studied in __________________ population: group of ______________________________ __________________ gene pool: _____________________________________ ___________________________________ in population ____________________________ in gene pool expressed as _____ e.g. Person A is RR: _______________________ _____________________________________________ Natural selection leads to ________________________________________ _____________________________ Single gene trait controlled _______________________________ ___________________________________ Polygenic trait e.g. _____________________________________ present red form _____________________________ black form __________________________________ _____________________________________________ controlled by ________________________________________ _____________________ genotypes and phenotypes ________________ of phenotypes _______________________________ affected in 3 ways: directional selection: individuals at _____________________________ e.g. bird beaks: __________________________ birds with larger beaks ____________________ __________________________ stabilizing selection: individuals ____________________________ e.g. ____________________________ disruptive selection: individuals ______________________________ e.g. bird beaks: ___________________________ birds with ________________________ _______________________. curve splits into ________________________ ______________________ Genetic Drift small populations: ___________________________________. Founder effect small groups of individuals _____________________________ ___________________________ than parent population ________________________ new population frequencies. given enough time: ______________________. How does evolutionary change operate?? What are the conditions where there is no evolution?? Hardy-Weinberg principle: If a population is in genetic equilibrium it means - allele frequencies don’t change = no evolution conditions * to maintain equilibrium from generation to generation there are 5 conditions for no evolution : 1. mating must be random – all members of pop have equal opportunity to produce offspring (doesn’t happen – males compete, females are picky) 2. populaiton must be large - >10,000 or more so genetic drift doesn’t happen (not all populations are that large) 3. no movement into or out of the population – no mixing of gene pool from the bunnies down the meadow (animals do migrate – maybe the clover is sweeter down the meadow) 4. no mutations – if gene mutations happen will = new alleles in the population (mutations (errors) can happen any time) 5. no natural selection – all genotypes must survive and reproduce equally (no advantages) (there is variety in every population = advantages) in some populations these conditions are met if conditions not met = genetic equilibrium dirstrupted =change in allele frequencies = evolution Formation of Species Speciation formation of _________________. Species group of organisms that: ________________________ offspring. shares a ______________. How do new species form? groups of organisms __________________________ that they: can _________________. _________________ a gene pool. Reproductive isolation Behavioral isolation 2 species ________________________________________ rituals e.g. ______________ Geographic isolation 2 species ___________________________________ separated e.g. _______________________, etc. 2 species _______________________________________ at different times e.g. ______________________ at different times Temporal isolation Patterns of Evolution Extinction extinction is a ______________________ on earth _______________________ that ever lived are extinct natural selection: ______________________________ species that _______________________ don’t survive natural disasters ____________________ Adaptive radiation _____________evolves into many _______________ ancient ______________________________ species ancient ______________________________ species Convergent evolution ___________________ evolve with similar _________________ ___________________________ _______ (fish) __________ (bird) __________(mammal) ________ (mammal) Coevolution __________________________________________________ ________________________ ________________________ Punctuated equilibrium ________________ in earth’s history where ______________ in species occurs (________________) ________________ with _______________ in species (evolution)