UNIT PLAN- DNA and MITOSIS
advertisement
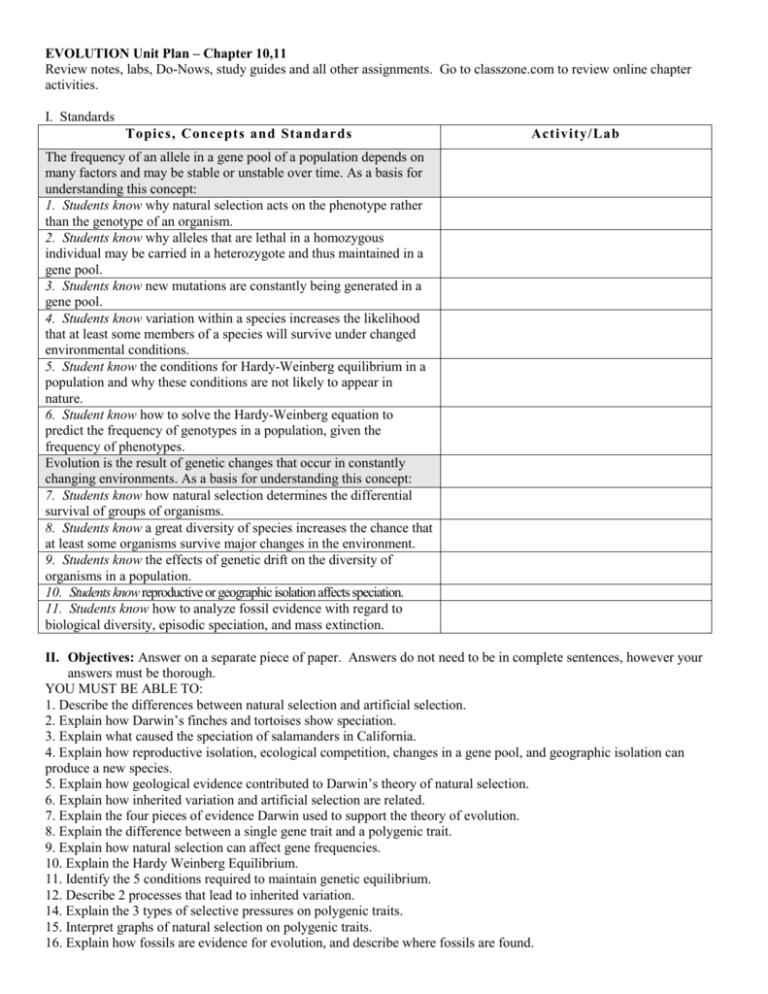
EVOLUTION Unit Plan – Chapter 10,11 Review notes, labs, Do-Nows, study guides and all other assignments. Go to classzone.com to review online chapter activities. I. Standards Topics, Concepts and Standards Activity/Lab The frequency of an allele in a gene pool of a population depends on many factors and may be stable or unstable over time. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1. Students know why natural selection acts on the phenotype rather than the genotype of an organism. 2. Students know why alleles that are lethal in a homozygous individual may be carried in a heterozygote and thus maintained in a gene pool. 3. Students know new mutations are constantly being generated in a gene pool. 4. Students know variation within a species increases the likelihood that at least some members of a species will survive under changed environmental conditions. 5. Student know the conditions for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in a population and why these conditions are not likely to appear in nature. 6. Student know how to solve the Hardy-Weinberg equation to predict the frequency of genotypes in a population, given the frequency of phenotypes. Evolution is the result of genetic changes that occur in constantly changing environments. As a basis for understanding this concept: 7. Students know how natural selection determines the differential survival of groups of organisms. 8. Students know a great diversity of species increases the chance that at least some organisms survive major changes in the environment. 9. Students know the effects of genetic drift on the diversity of organisms in a population. 10. Students know reproductive or geographic isolation affects speciation. 11. Students know how to analyze fossil evidence with regard to biological diversity, episodic speciation, and mass extinction. II. Objectives: Answer on a separate piece of paper. Answers do not need to be in complete sentences, however your answers must be thorough. YOU MUST BE ABLE TO: 1. Describe the differences between natural selection and artificial selection. 2. Explain how Darwin’s finches and tortoises show speciation. 3. Explain what caused the speciation of salamanders in California. 4. Explain how reproductive isolation, ecological competition, changes in a gene pool, and geographic isolation can produce a new species. 5. Explain how geological evidence contributed to Darwin’s theory of natural selection. 6. Explain how inherited variation and artificial selection are related. 7. Explain the four pieces of evidence Darwin used to support the theory of evolution. 8. Explain the difference between a single gene trait and a polygenic trait. 9. Explain how natural selection can affect gene frequencies. 10. Explain the Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium. 11. Identify the 5 conditions required to maintain genetic equilibrium. 12. Describe 2 processes that lead to inherited variation. 14. Explain the 3 types of selective pressures on polygenic traits. 15. Interpret graphs of natural selection on polygenic traits. 16. Explain how fossils are evidence for evolution, and describe where fossils are found. III. Vocabulary: Define vocab words and know how to apply them. Chapter 10,11 evolution Artificial selection Gene pool species Natural selection Allele frequency fossil population Normal distribution gradualism fitness Directional selection variation biogeography Stabilizing selection adaptation Homologous structure Disruptive selection Vestigial structure Genetic drift Analogous structure Founder effect Gene flow Hardy Weinberg equilibrium IV. Labs/Projects/Activities: History of Life timeline Origami birds Now you see, now you don’t Bird beaks Bengal tiger Ch 10 foldable Evolution of a word Fishy Frequencies Salamander Speciation Amino Acid Comparison Ch 11 foldable Reproductive isolation speciation Behavioral isolation Geographic isolation Temporal isolation Convergent evolution Divergent evolution coevolution extinction Punctuated equilibrium Adaptive radiation