6.1: Population Distribution: Density & Global Patterns
advertisement

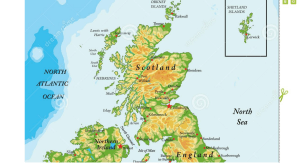
6.1: Population Distribution: Density & Global Patterns Outcomes • 6.1.1 define the terms population density, densely populated, and sparsely populated; (k) • 6.1.2 explain why population density is not always an accurate indicator of population distribution; (k) • 6.1.3 examine patterns in the distribution of population on the earth’s surface; (a) • 6.1.4 analyze the impact of selected factors on the population distribution of a given region. (a) Part A: Important Terminology Population density is a measure of how compact or concentrated a population is. It takes are of land into account as well as population. 1. Describe the difference between each of the following concepts: a). Population Density b). Sparsely Populated c). Densely Populated • It is important to note that these two classifications and the numeric cut off of 100 people / Km² are somewhat arbitrary. Some books use a middle category moderately populated @ 10-100 people / Km² • For example Canada as a whole has a much larger population than St. John's alone. However Canada is spread out over a much larger area than is St. John's. Therefore, St. John's would have a higher population density than Canada. 6.1: Population Distribution: Density & Global Patterns Part B: Global Patterns of Distribution 2. Write a description of population distribution for each region found in the table below Region Population Distribution Description North America South America Europe Asia Africa 3. Describe how each of the following impacts population density and distribution a. Climate b. Economics c. Transportation