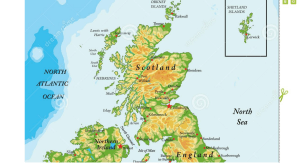
Rural areas (thinly populated)
advertisement

A revised Urban Audit Presenting a harmonised city definition and its application Review process in 2010-2011 • Revise indicators: less and more focussed • Link to official statistics: degree of urbanisation and Europe 2020 • Revise frequency: annual • Revise city selection: all cities instead of sample • Revise city and larger urban zone boundaries: a new OECD-EC definition • Validated by all National Statistical Institutes Two linked local classifications • New degree of urbanisation • Cities (densely) • Towns and suburbs (intermediate) • Rural areas (thinly populated) • Urban Audit 2012 • Cities • Commuting zones • Other areas Replace three conflicting classifications Urban-Rural Typology Rural LAU2 Degree of urbanisation ≠ Urban Audit Thinly populated Intermediate density Densely populated ≠ Cities or Greater Cities New degree of urbanisation • Used in the data collections for reference year 2012 onwards in • • • • • • Labour Force Survey Survey on Income and Living Conditions IT household Survey Safety Survey in 2013 Adult education survey Eurobarometers? • Eurofound European Quality of Life Survey 2011 will also use it EU-OECD definition of a city in four steps 1. Select cells with 1 500 inhabitants per sq km 2. Cluster cells, fill gaps and select those with more than 50 000 inhabitants (urban centre) 3. Select all LAU2s with at least 50% of their inhabitants in the urban centre. 4. Adjust for political level if needed IMPORTANT! Cities are selected on the population of their centre, not total population Creating a Greater City Adjusting the classification • A densely populated LAU2 can be classified intermediate as long as 75% of its high-density cluster population remains in densely populated LAU2s. • A thinly populated or intermediate density LAU2 can be classified as densely populated if it belongs to a group of LAU2s with a political function and if the majority of population of this group of LAU2s lives in a high-density cluster. Toulouse - CU du Grand Toulouse Commuting zone • Check if (greater) cities are ‘connected’ i.e. have at least a one-way commuting intensity of 15%. If so combine cities into a single destination • Identify all LAU2s that send 15% of their employed population to a city • Drop exclaves and add enclaves • If needed approximate with area for which data is available (LAU1, NUTS3) Overall impact • The number of cities in the Urban Audit has increased significantly: from 684 to 828. • 64 cities were dropped, notably in France, but also the UK, Italy and Malta. • A substantial increase in the number of Greater cities to 33 and no longer limited to capitals. They now also include Milan, Naples, Bilbao, Barcelona, Porto, Rotterdam, Manchester… Border cities Other typologies • Harbour cities: Defined by proximity to a harbour and the amount of goods transported through this harbour • Regional capitals: capital or a region with a political function (to be combined with the population of the region and the regional authority index) based on feedback from the NUACs.