Lab 8 Photosynthesis FC
advertisement

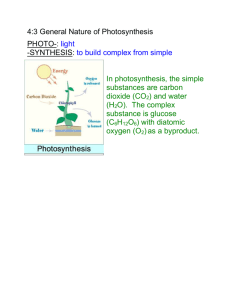
Lab 8 Photosynthesis Flashcards 1) Write the equation for photosynthesis without the numbers of each molecule, and you can write “sugar” instead of the formula 2) Write the equation for photosynthesis 3) What structures in a plant require the Light Dependent reaction? 4) What is the product of a light dependent reaction? 5) What two substances are needed for the light dependent reaction, in addition to sunlight? 6) How are ATP and NADPH used in a plant? 7) What substance is needed from the atmosphere to drive the Calvin Cycle? 8) What substance is produced during the Calvin Cycle which is utilized or stored as starch? 9) What is chlorophyll? 10) What are the two types of chlorophyll molecules? 11) Why do plants appear green? 12) What is the photosynthetic pigment that can be yellow, orange or red in color? 13) What do the photosynthetic pigments do with light energy? 14) Where is chlorophyll a found? 15) Where is chlorophyll b found? 16) What is the function of the antennae assembly? 17) Where is the antenna assembly located? 18) What increases the photo spectrum of the plant? 19) What happens when chlorophyll molecules are exposed to light energy? 20) How can photosynthetic rates be altered? 21) What two components give plants the capacity to undergo photosynthesis and cellular respiration simultaneously? 22) What is formed when combining CO2 with H2O? 23) What happens when CO2 is combined with water? 24) Carbonic Acid may separate into which two ions? 25) What does the following equation describe? 26) Sugars + oxygen <----> CO2 + H2O <---> H2CO3 <---> H+ + HCO3 27) What photosynthetic pigments are utilized most for photosynthesis by green plants? 28) What photosynthetic pigments are utilized least for photosynthesis by green plants? CO2 + H2O + sunlight = sugar + O2 + H2O 6 CO2 + 12 H2O + sunlight = C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O photosynthetic pigments Oxygen (O2) ATP and NADPH to drive the Calvin Cycle to produce chemical energy CO2 GAP The primary photosynthetic pigment of green plants. A and B The chlorophyll molecules absorb the all of the colors of the visible light spectrum except green (which is reflected) Carotenoids They convert light energy to glucose. It is found in the reaction center of a photosystem It is found in the antennae assembly Absorbs light energy and passes high energy electrons to chlorophyll a for energy production It is located in the plant cell membrane the antenna assembly Carbon dioxide and water can be utilized to form sugar and oxygen respectively Change the intensity of light Chloroplasts and Mitochondria. Carbonic Acid (H2CO3) It becomes acidic. Hydrogen ion (H+) and Bicarbonate ion (HCO3) The production and dissociation of carbonic acid chlorophyll a chlorophyll b Carotenoids Lab 8 Photosynthesis Flashcards 29) What method is used in order to saturate a substance in a test tube with CO2? 30) Why do you not want to put test tubes too close to light sources when dealing with photosynthesis? 31) Why is pigment separation possible? 32) How do you handle chromatography strips? 33) Why must you be careful with chromatography strips? 34) What must you allow before adding extra solvent? 35) What is the hypothesis being tested in this experiment? 36) What were the bubbles off by Elodea in this experiment? 37) What can you conclude about the light intensity and the photosynthesis rate? 38) During the summer months, farmers in Alaska can grow much larger (heavier) pumpkins than farmers in California. Explain why this is possible. 39) Graph the effects of light intensity and the photosynthetic rate. Do not forget all the components of a graph. 40) What was the color of the tube with the plant in the light at the end of the experiment? 41) Is the solution acidic or basic? Explain your answer 42) What was the color of the tube with the plant in the dark at the end of the experiment? 43) Is the solution acidic or basic? Explain your answer 44) What is the purpose of the accessory pigments found in plants? Blow through a straw. You may accidentally damage the leaves from the heat. Varying solubility in given solvents. By the edges only. The oils from your fingers will affect the separation of the pigments. Allow drops to dry.