Organic Chemistry
advertisement

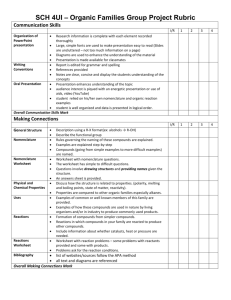
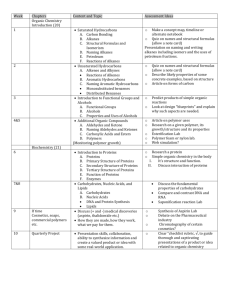
THE SYLLABUS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Applicable students: Six-year system oversea students in the department of clinical medicine. Class hours: It takes 44 hours to study this course. The study of theory needs 24 hours; the study of experimental skill needs 20hours. Course introduction: Organic chemistry is an important major course for the students from the College of Medical. This course is to convey the basic concepts and theories of organic chemistry at an undergraduate level, including nomenclatures, structures, physical properties, preparation, chemical reaction of organic compounds with different functional groups, the conversion between different chemicals, and basic organic synthesis. In “organic chemistry (I)” we mainly talk about the basic theory and concepts of organic compounds, chemistry of alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohols, and ether; basic knowledge about IR, MS, and NMR spectra characterization of organic chemicals. The basic Objectives: The course will help student to develop the following abilities: 1. Understanding the key principles and essential ideas of organic chemistry. 2. Writing correctly the configuration, conformation, stereo-structure or organic chemicals, various chemical reactions such as substitution, addition, elimination, and their typical reaction mechanisms. 3. Understanding the relationship between the structure and properties of important organic chemicals. 4. Applying the knowledge of organic chemistry to understand and solve the related organic synthesis problems. 5. Improving ability on textbook and literature reading. Teaching period plan: Chapter Chapter 1 Contents Hour Alkanes 2 Alkenes , Akynes and Aromatic compounds 4 Chapter 5 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers 2 Chapter 6 Aldehydes and Ketones 4 Chapter 7 Carboxylic acids and their derivatives 4 Chapter 8 Optical Isomerism 2 Chapter 9 Organic compounds containing nitrogen 4 Chapter 10 Carbohydrates 2 Total 24 Chapter 2,3,4 CHAPTER 1: ALKANES [Objectives] 1. Narrate the classification of hydrocarbons. 2. Have knowledge on the structure, nomenclature of alkanes. 3. Describe the conformations of methane and ethane. 4. Explain chemical properties of alkanes. [Contents] 1. Classification of hydrocarbons 2. Alkanes (1) The general formula, structure and homologous series of alkanes (2) The nomenclature of alkanes (3) Conformations of methane and ethane (4) Physical properties of alkanes (5) Chemical properties of alkanes CHAPTER 2, 3, 4: ALKENES, ALKYNES AND AROMATICS [Objectives] 1. Explain structures of alkenes and alkynes, additionally describe sp2, sp Hybridization and the Pi bond. 2. Have knowledge on the isomerism among the alkenes. 3. Narrate the nomenclature of alkenes and alkynes. 4. Explain chemical properties of alkenes and alkynes. 5. Explain the structure of benzene and large π bond in benzene. 6. Narrate the naming derivatives of benzene. 7. Have knowledge on the characteristic reactions of benzene. 8. Describe some common structures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. [Contents] 1. Alkenes (1) The carbon-carbon double bond (2) Isomerism among the alkenes (3) Nomenclature of alkenes (4) Physical properties of the alkenes (5) Chemical properties of the alkenes 2. Alkynes (1) The carbon-carbon triple bond (2) Nomenclature of alkynes (3) Properties of alkynes 3. Aromatics (1) Structure of benzene (2) The pi electrons in benzene (3) Naming derivatives of benzene (4) The characteristic reactions of benzene (5) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons CHAPTER 5: ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS, AND ETHERS [Objectives] 1. Explain the structure, classification and nomenclature of alcohols. 2. Explain the physical properties of alcohols influenced by hydrogen bond. 3. Explain chemical properties of alcohols. 4. Have knowledge on the nomenclature and properties of phenols. 5. Explain the structure and nomenclature of ethers. 6. Describe the principal properties of ethers. 7. Have knowledge on structure and the principal properties of thioalcohols and Disulfides [Contents] 1. Alcohols (1) Structure and subclasses of alcohol, (2) Nomenclature of alcohols (3) Physical properties of alcohols (4) Chemical properties of alcohols 2. Phenols (1) Nomenclature of phenols (2) Properties of phenols 3. Ethers (1) Structure and nomenclature of ethers (2) Properties of ethers (3) Preparations of ethers 4. Thioalcohols and Disulfides CHAPTER 6: ALDEHYDES AND KETONES [Objectives] 1. Explain the Structural features of aldehydes and ketones. 2. Describe the nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones. 3. Explain the principal properties of aldehydes and ketones. [Contents] 1. Structural features and names of aldehydes and ketones (1) The carbonyl group (2) Nomenclature of aldehydes (3) Nomenclature of ketones 2. Physical properties of aldehydes and ketones 3. Chemical properties of aldehydes and ketones (1) The oxidation of aldehydes and kelones (2) The reduction of aldehydes and kelones (3) The reactions aldehydes and kelones with alcohols CHAPTER 7: CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES [Objectives] 1. Describe structures of carboxylic acids and their derivatives. 2. Explain the nomenclature of carboxylic acids and their derivatives. 3. Explain physical properties and chemical properties of carboxylic acids. 4. Describe the physical properties and some reactions of esters. 5. Understand structures of organophosphate ester. [Contents] 1. Occurrence, names, and physical properties of acids (1) Carboxyl group (2) Names of carboxylic acids and their anions (3) Physical properties of acids 1. The acidity of carboxylic acids (1) Neutralization of carboxylic acids by strong bases (2) Carboxylate ions as bases 2. The conversion of carboxylic acids to acid derivatives (1) Acid chlorides (2) Acid anhydrides (3) Amides (4) Esters 3. Occurrence, names, and physical properties of esters (1) Naming esters (2) The effect of the ester group on physical properties 4. Some reactions of esters (1) Hydrolysis of esters (2) Saponification 5. Organophosphate ester (1) Monophosphate esters (2) Diphosphate esters (3) Triphosphate esters CHAPTER 8: OPTICAL ISOMERISM [Objectives] 1. Explain chirality and optical isomerism. 2. Explain Fischer projection formulas and relative configurations. 3. Explain properties of enantiomers. 4. Have knowledge on specific rotation. meso compound and racemic mixtures. [Contents] 1. Types of isomerism 2. Molecular chirality (1) Superimposability (2) The chirality of enantiomers (3) Some difference that chirality makes (4) Deciding molecules are chiral 3. Optical activity (1) Polarized light (2) Polarimeter (3) Optical rotation and specific rotation CHAPTER 9: NITROGEN COMPOUNDS [Objectives] 1. Narrate occurrence, names, and physical properties of amines 2. Explain chemical properties of amines 3. Narrate naming amides and Making amides by acyl group transfer reactions. 4. Explain chemical properties of amides [Contents] 1. Occurrence, names and physical properties of amines (1) Structural features of amines (2) Naming the amines (3) Heterocyclic amines (4) Physical properties of amines 2. Chemical properties of amines (1) Basicity of amines (2) Properties of amines salts 3. Amides of carboxylic acids (1) Naming amides (2) Amides as neutral compounds. (3) Make amides from amines by acyl group transfer reactions. (4) The hydrolysis of amides CHAPTER 10: CARBOHYDRATES [Objectives] 1. Explain classification of carbohydrates. 2. Explain the cyclic structure and mutarotation of Monosaccharides. 3. Describe principal properties of the Monosaccharides. 4. Have knowledge on structures and principal properties of disaccharides. 5. Have knowledge on structures of polysaccharides. 6. Describe some important polysaccharides. [Contents] 1. Classification of carbohydrates 2. Monosaccharides (1) D-and L-families of monosaccharides (2) Glucose (3) Fructose (4) Reactions of the hexoses 3. Disaccharides (1) Maltose (2) Lactose (3) Sucrose (4) Cellobiose 4. Polysaccharides (1) Starch (2) Glycogen (3) Cellulose EXPERIMENTS Experiment Contents Hour 1 Basic Laboratory Techniques 4 2 Determination of Melting Point and Micro scale Determination of Boiling Point 4 3 Operation of Organic Molecular Models 4 4 Paper Chromatography Chromatography 5 Paper Electrophoresis of Amino Acid 4 6 Analysis of Unknown Samples of Organic Compounds 4 and Column 4 24 Total EXPERIMENT 1: BASIC LABORATORY TECHNIQUES [Objectives] 1. To be able to select appropriate methods, apparatus and materials to carry out basic organic laboratory techniques, such as gravity filtration, vacuum filtration, simple distillation, and liquid-liquid extraction and so on. 2. Use common chemical apparatus and instruments correctly and handle chemicals safely. [Contents] 1. Gravity filtration and vacuum filtration 2. Simple distillation 3. Extraction of iodine EXPERIMENT 2: DETERMINATION OF MELTING POINT AND MICROSCALE DETERMINATION OF BOILING POINT [Objectives] 1. Acquire the methods for melting point determination. 2. Acquire the methods for microscale boiling point determination. 3. Learn how to use X-4 digital display melting point meter correctly. [Contents] 1. Determination of melting point 2. Microscale boiling point determination EXPERIMENT 3: OPERATION OF ORGANIC MOLECULAR MODELS [Objectives] 1. Comprehend further the spatial structure of organic molecule. 2. Learn how to assemble the molecular models by using ball-and –stick models. [Contents] 1. Assemble the molecular models of methane and dichloromethane. 2. Assemble the molecular model of ethane. 3. Assemble the molecular models of chair- and boat- conformation of cyclohexane 4. Assemble the molecular models of maleic acid and fumaric acid. 5. Assemble the molecular models of cis-and trans-isomers of 1, 4-cyclohexanedioic acid. 6. Assemble the molecular models of two lactic acids and mark the D-, Lconfigurations. 7. Assemble the molecular models of cis-decalin and trans-decalin. EXPERIMENT 4: PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY AND COLUMN CHROMATOGRAPHY [Objectives] 1. Have knowledge on the principles of paper chromatography and column chromatography. 2. Acquire the methods for paper chromatography and column chromatography. [Contents] 1. Paper chromatography 2. Column chromatography EXPERIMENT 5: PAPER ELECTROPHORESIS OF AMINO ACID [Objectives] 1. Have knowledge on the principle of paper electrophoresis. 2. Acquire the methods for paper electrophoresis of amino acid. 3. Learn how to use DYY-Ⅱtype eletrophoretic apparatus. [Contents] 1. Operation of DYY-Ⅱ type eletrophoretic apparatus 2. Paper electrophoresis of glutamic acid. arginine and mixture of them EXPERIMENT 6: ANALYSIS OF UNKNOWN SAMPLES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS [Objectives] 1. Devise and plan experiment to identify unknown samples of organic compounds. 2. Raise an ability to think scientifically and independently and to make rational decisions according to observations and experimental data. 3. Improve the ability to analyze and solve problems. [Contents] 1. Design experiment 2. Test properties of unknown samples of organic compounds 3. Analysis of unknown samples of organic compounds