File - Ms Hotchin SCSC
advertisement

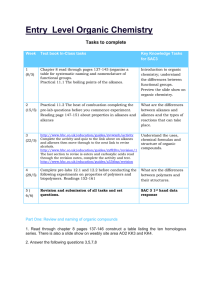
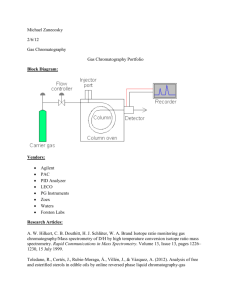
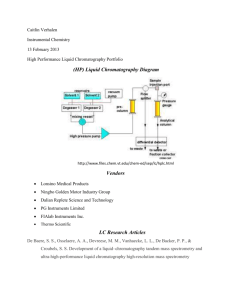
- - - - Principles and application of spectroscopic techniques of data from AAS, mass spectroscopy, IR, NMR and visible-UV Matching analytical techniques to a particular task Be able to describe each technique and explain how it works Analyse(read) all the different technique spectrums to identify the atoms or groups present in the sample Understand what each technique is for and what samples can be used for a particular technique Understand the techniques and principles for , simple titrations, back titrations, acid-base and redox reactions Calculations including the amount of solids, liquids and gases Read and analyse pH curve graphs Explain gravimetric analysis Match techniques to particular tasks Principles and applications of chromatographic techniques and interpretation of qualitative and quantitative data from thin layer chromatography (TLC), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography (GC). Structure and systematic nomenclature of alkanes, amines, chloroalkanes, alkanols and carboxylic acids up to C10 (identify functional groups) Common reactions of organic compounds, addition reactions of alkenes, substitution reactions of alkanes and primary chloroalkanes, oxidation of primary alkanols and esterification. Explain and describe fractional distillation Write and define organic reaction pathways including the production of esters from alkanes, condensation and polymerisation reactions that produce large biomolecules Explain stages for Primary, secondary and tertiary structure of proteins and function of protein catalysts(enzymes) Biochemical fuels including fermentation of sugars to produce ethanol Know The structure of bonding in DNA and its applications in forensic analysis Comprehend the Use of proteins as markers for disease Understand the biological applications for the Function of organic molecules in the design of synthesis of medicines, including the production of aspirin from salicylic acid