Handouts Ch 4

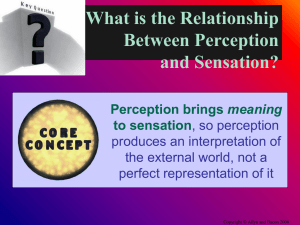
Sensation The process by which receptor cells are stimulated and transmit their information to higher brain centers.
Perception The process that organizes various sensations into meaningful patterns.
The five universal senses: vision, hearing, touch, smell, taste
Depth perception The organization of sensations in three dimensions, even though the image on the eye’s retina is twodimensional.
Source: Shiraev E. and Levy, D. Cross-Cultural Psychology. (2007). Second Edition. Boston: Allyn and Bacon
Altered State of Consciousness (ASC) -
The general name for phenomena that are different than normal, waking flow of consciousness and include mystic experiences, meditation, hypnosis, trance, and possession.
Trance is a sleeplike state marked by reduced sensitivity to stimuli, loss or alteration of knowledge, and automatic motor activity.
Trances are often induced by external sources such as music, singing, and direct suggestion from another person. Trances may provide a sense of protection, wisdom, and greatness.
For the group, it can induce a sense of togetherness and unity.
Source: Shiraev E. and Levy, D. Cross-Cultural Psychology. (2007). Second Edition. Boston: Allyn and Bacon
Meditation is a quiet and relaxed state of tranquility in which a person achieves an integration of thoughts, perceptions, and attitudes. Usually, this state is attained with the cooperation of a special principle or belief. People who meditate often describe their experience as leading to liberation from the self or an expansion of conscious awareness.
Hypnosis is a process of alteration of a person’s consciousness, characterized by willingness to cooperate with a person who conduct hypnosis, heightened suggestibility and receptivity to direction.
Source: Shiraev E. and Levy, D. Cross-Cultural Psychology. (2007). Second Edition. Boston: Allyn and Bacon
Dreams - Story-like sequences of images occurring during sleep.
Monophasic cultures: People in these cultures tend to share materialistic view on psychological experience; they tend to value cognitive experiences that take place only during normal waking phases and do not incorporate dreams into the process of social perception and cognition. Dreams are regarded as indirect indications of the dreamer's concerns, fears, and desires.
Polyphasic cultures: People in these cultures tend to share spiritual or traditional view on psychological experience; they also tend to value dreams and treat them as part of reality.
Source: Shiraev E. and Levy, D. Cross-Cultural Psychology. (2007). Second Edition. Boston: Allyn and Bacon
Aesthetic experience – A term used to identify the feeling of pleasure evoked by stimuli that are perceived as beautiful, attractive, and rewarding. The term also refers to displeasure evoked by stimuli that are perceived as ugly, unattractive, and unrewarding.
Source: Shiraev E. and Levy, D. Cross-Cultural Psychology. (2007). Second Edition. Boston: Allyn and Bacon
The impact of experience on perception:
My wife and my mother-in-law
The impact of experience on perception:
An island…..
A crater….
The impact of experience on perception:
What does the sign say?