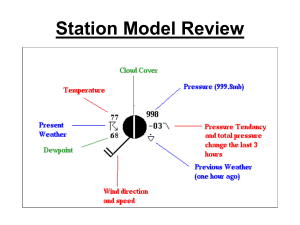
Atsc2000: Homework 3 – Optics, humidity, condensation, cloud types
advertisement

Atsc2000: Homework 2 – Local Temperature, Optics, humidity, condensation, cloud types. Due Feb. 8. 1) a) Which location of the following pairs will be warmer in summer/winter and why? Laramie/Rome, London/Moscow, Mexico City/Mecca, Saudia Arabia, St. Louis/Oslo, Norway. b) Draw a diagram of the Earth’s rotation around the sun showing northern hemisphere summer. Why in this case will it be warmer in southern Mexico than at the equator? 2) What kind of particles and what type of optical phenomena are involved in each of the following observations, blue sky, white clouds, sundogs/haloes, rainbows, coronas, ice pillars? 3. a) During the day, with no change in water vapor content, the radio reports the relative humidity at 6:00 am to be 93%, and at 3:00 pm to be 28%.Explain how this came about. b) Suppose the dew point of cold outside air is the same as the dew point of warm air indoors. If the door is opened, and cold air replaces some of the warm inside air, would the new relative humidity indoors be lower, higher, or the same as before? Explain. c) The average vapor pressure in Laramie is 10 mbar. What is the dew point of this air? The average air pressure in Laramie at an elevation of 2200 m is 780 mbar. If the air over Laramie were brought down to sea level, without any change in the vapor content, what would be the vapor pressure of the air? 4. The dew point and expected minimum temperature are given in the table below. Assume that the dew point remains constant throughout the night as you explain which morning you are most likely to see the following: a) Visible frost c) Frozen dew b) Dew d) Black frost with no sign of visible frost, dew, or frozen dew -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Morning 1 2 3 4 5 Dew Point Temp (C) 2 -7 1 -4 3 Expected Min Temp (C) 4 -3 -1 -5 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------5. The air temperature during the night cools at about 2C per hour until the dew point is reached. A fog then forms and the cooling rate decreases to 0.5C per hour. Give two reasons why the air cooled more slowly after the fog formed. 6. Consider two containers one open and one closed, each containing a layer of water at the bottom. Both containers are allowed to sit at room temperature, 20C, overnight. Compare water amounts, vapor pressures, and relative humidities in the air above the water in each container in the morning. Do you have enough information to say exactly the vapor pressure and RH of the air for either container? If so for which container and what are they? 7. Which cloud types are associated with each of the following characteristics? a) lightning e) wave clouds b) mares' tails f) heavy rain showers c) haloes g) heavy snow flurries d) light continuous snow h) hailstones