Unit: Personal Narrative
advertisement

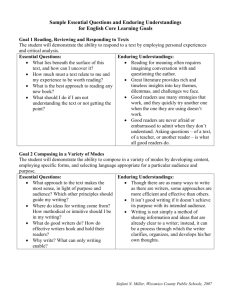
Unit: Personal Narrative Teaching Time: Approx. 2 weeks Objectives: Student will be able to successfully compose a 1st person five paragraph personal narrative. Essential Questions Enduring Understandings How do writers develop a wellwritten product? Why does a writer choose a particular form of writing? Content Statements W.8.3; W8.4; W.8.5; L.8.1; L.8.2; L8.5 Good writers develop and refine their ideas for thinking, learning, communicating, and aesthetic expression. A writer selects a form based on audience and purpose. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Literature Text 2. Write Source 3. Sample writing 4. MOBI activities Desired Results (CPI) CPI: W.8.10 ASSESS final narrative using NJ Holistic 6 point rubric; teacher conferencing Areas of Focus 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Writing process skills Use of organizational graphic organizers Improving and varying sentence structure Brainstorming Peer editing /presentations Model review; use of MOBI Teacher-directed lessons Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: Summer Reading Assessment Teaching Time: Approx. 1 week Objectives: Student will be able to share their selected summer reading title with others and demonstrate their knowledge of the elements of a novel. Essential Questions Enduring Understandings How do readers construct meaning from text? How does fluency affect comprehension? Content Statements RL.8.2; 8.3; SL.8.1; 8.5 Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to text personally relevant and useful. Fluent readers group words quickly to help them gain meaning from what they read. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Choice Summer Reading Title 2. Summer Reading Packet 3. MOBI activities; Power Point, etc. Areas of Focus 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Elements of a novel Oral presentation skills and techniques Persuasive “Book Sell” techniques Various visual aide options Audience participation options MOBI activities Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10 ASSESS by having students present a 1 minute “Book Sell” with audience engaging activities and/or visuals ; Appropriate rubric 2 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: Summer Reading Assessment – Teacher Selected Teaching Time: 1 week Objective: Students will be able to demonstrate their knowledge of the novel elements of The Misfits. Essential Questions How do readers construct meaning from one text? How does fluency affect comprehension? Enduring Understanding Content Statements RL 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 SL 8.1, 8.5 L.8.4, 8.6 Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make connections (text to text, text to world, text to self) to make text personally relevant and useful. Fluent readers group words quickly to help them gain meaning from what they read. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. The novel The Misfits 2. Summer reading packet 3. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Areas of Focus 1. Analyzing/exploring major themes and other elements of a novel 2. Small group/cooperative activities 3. MOBI presentation (varies by teacher) 4. Identifying and using organizational structures to comprehend information 5. Continuing to use structural analysis and context analysis to decode new words. 6. Interpret text ideas through journal writing; writing responses to literature and developing insight into interpretations by connecting to personal experiences and referring to textual information 7. Recall of plot/events 8. Increasing vocabulary development 9. Guided class discussion/questioning Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10 ASSESS by having students complete a group project analyzing the novel elements presented in The Misfits ASSESS through publisher and teacher tests. 3 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: Elements of a Short Story Teaching Time: Approx. 2-3 days Objectives: Student will be able to define and understand the elements of setting, characterization, plot, and story mapping. Essential Questions Enduring Understandings How do readers construct meaning from text? How does understanding a text’s structure help me better understand its meaning? Content Statements RL.8.2; 8.3; 8.4; 8.6 Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to make text personally relevant and useful. Understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Literature Book 2. Outlines and other graphic organizers 3. Story Maps and Character Logs 4. MOBI activities Areas of Focus 1. Define and recognize elements of a short story 2. Locate and analyze the elements of setting, characterization, and plot to construct understanding of how characters influence the progression of the plot and resolution of the conflict. 3. Use literature text as a resource tool 4. Student generated definitions of terms and elements Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10 ASSESS by having students locate definitions and complete outlines, organizers, etc. ASSESS through discussions and teacher generated quiz. 4 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: “Raymond’s Run” Teaching Time: 1 week Objective: Students will be able to locate and analyze the elements of plot, setting, characterization and style. Essential Questions How do readers construct meaning from one text? How does fluency affect comprehension? Why do readers need to pay attention to a writer’s choice of words? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in the text? How do writers develop a wellwritten product? Enduring Understanding Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make connections (text to text, text to world, text to self) to make text personally relevant and useful. Fluent readers group words quickly to help them gain meaning from what they read. Words powerfully affect meaning. Good readers employ strategies to help them understand text. Strategic readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension. Good writers use a repertoire of strategies that enables them to vary form and style, in order to write for different purposes, audiences, and contexts. Areas of Focus 1. Analyze allusion, dialect, author’s style 2. Analyze how style affects characterization and plot 3. Monitor reading for understanding by setting a purpose for reading, making and adjusting predictions, asking questions and making connections 4. Effectively respond to open-ended questions 5. Response and Analysis Questions in textbook at end of story 6. Teacher directed class discussions 7. Teacher directed instruction 8. Student reading and questioning of the text 5 Course: Language Arts Literacy Content Statements RL 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 SL 8.1, 8.4 W 8.2 L 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6 Grade 8 Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. textbook 2. The Holt Reader 3. Holt Reading Solutions 4. Audio CD 5. teacher generated study guide and note-taking sheets 6. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10, W.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to monitoring for understanding,; respond to open opened questions, holt assessment ASSESS through teacher/publishers generated test/quizzes of material; 4 point rubric 6 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: “Broken Chain” fictional short story Teaching Time: Approx. 1 week Objectives: Student will be able to evaluate the plot’s structure and development and the way conflicts are resolved. Essential Questions How do readers construct meaning from text? How does understanding a text’s structure help me better understand its meaning? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in a text? Content Statements RL.8.1; 8.2; 8.3; 8.4; 8.6 Enduring Understandings Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to make text personally relevant and useful. Understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Good readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Literature Book, p. 16 2. Study Guides 3. Story Maps and Character Logs Areas of Focus 1. Read critically by identifying, analyzing, and applying knowledge of theme and literary elements of fiction 2. Locate and analyze the elements of setting, characterization, and plot to construct understanding of how characters influence the progression of the plot and resolution of the conflict. 3. Monitor reading for understanding by setting a purpose for reading, making and adjusting predictions, asking questions, and making connections. 4. Quick Writes 5. Vocabulary review Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to monitoring for understanding; respond to Open-ended Questions; Holt Assessments ASSESS through teacher generated/publisher quizzes and tests; 4 pt OEQ rubric. 7 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: “The Landlady” Teaching Time: 1 week Objective: Students will be able to make predictions and evaluate structural elements of the plot, including foreshadowing. Essential Questions How do readers construct meaning from one text? How does fluency affect comprehension? Why do readers need to pay attention to a writer’s choice of words? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in the text? How do writers develop a wellwritten product? Enduring Understanding Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make connections (text to text, text to world, text to self) to make text personally relevant and useful. Fluent readers group words quickly to help them gain meaning from what they read. Words powerfully affect meaning. Good readers employ strategies to help them understand text. Strategic readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension. Good writers use a repertoire of strategies that enables them to vary form and style, in order to write for different purposes, audiences, and contexts. Areas of Focus 1. Understanding and evaluating elements of plot, including foreshadowing 2. Monitoring reading for understanding by setting a purpose for reading, making and adjusting predictions, asking questions and making connections 3. Avoiding double comparisons 4. Creating a Prediction Chart, Holt Reader 5. Modeling and recognizing of clues that foreshadow future events 6. Teacher directed discussion of plot and characters 7. Response and Analysis Questions 8. Vocabulary review 9. Effectively responding to open-ended questions 10. Teacher directed instruction 11. Student reading and questioning of the text 8 Course: Language Arts Literacy Content Statements RL 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.6 SL 8.1, 8.4 W 8.2 L 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6 Grade 8 Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. textbook 2. Holt Reader 3. Holt Reading Solutions 4. Audio CD 5. teacher generated study guide and note-taking sheets 6. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10, W.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to monitoring for understanding,; respond to open opened questions, holt assessment ASSESS through teacher/publishers generated test/quizzes of material; 4 point rubric 9 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: “The Monkey’s Paw” fictional short story Teaching Time: Approx. 1 week Objectives: Student will be able to identify and analyze story motifs and will be able to compare and contrast characters. Essential Questions How do readers construct meaning from text? How does understanding a text’s structure help me better understand its meaning? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in a text? Content Statements RL.8.1; 8.2; 8.3; 8.4; 8.6 Enduring Understandings Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to make text personally relevant and useful. Understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Good readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Literature Book, p. 85 2. Study Guides 3. Story Maps and Character Logs Areas of Focus 1. Identify and understand the author’s use of idioms, metaphors, and similes. 2. Read critically by identifying, analyzing, and applying knowledge of theme and literary elements of fiction 3. Locate and analyze the elements of setting, characterization, and plot to construct understanding of how characters influence the progression of the plot, development of suspense, and resolution of the conflict. 4. Monitor reading for understanding by setting a purpose for reading, making and adjusting predictions, asking questions, and making connections. 5. Quick Writes 6. Vocabulary review Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to monitoring for understanding; respond to Open-ended Questions; Holt Assessments ASSESS through teacher generated/publisher quizzes and tests; 4 pt OEQ rubric. 10 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: Vocabulary for Success Teaching Time: Daily (warm-ups) Objective: Students will learn new, exciting vocabulary words in order to use them in their everyday and scholastic writing. Essential Questions How does a student figure out a word he/she does not know? Why do readers need to pay attention to a writer’s choice of words? Content Statements L 8.4, 8.6 Enduring Understanding Readers use language structure and context clues to identify the intended meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text. Words powerfully affect meaning. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Vocabulary for Success books 2. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Desired Results (CPI) Areas of Focus 1. Readers use language structure and context clues to identify the intended meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text. 2. Clarify a word’s meaning through the use of a word’s definition, example, restatement or contrast. 3. Clarify pronunciations, meanings, alternate word choice, parts of speech, and etymology of words using the dictionary, thesaurus, glossary, and technology resources 4. utilizing a “Word Wall” within the classroom 5. Encouraging students (even requiring them) to use the new vocabulary words in their own writing ASSESS through teacher generated tests/quizzes of material and through application/usage of new vocabulary words in student writing. 11 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: NJ ASK Open-Ended Questions – Narrative Passage Teaching Time: 1 week + Objective: Students will be able to become familiar with the format of a NJ ASK open-ended question and will complete all requirements and respond with insight. Essential Questions How do good writers express themselves? How do writers develop a wellwritten product? How do rules of language affect communication? Content Statements W 8.2, 8.4 L 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.6 Enduring Understanding Good writers develop and refine their ideas for thinking, learning, communicating, and aesthetic expression. Good writers use a repertoire of strategies that enables them to vary form and style, in order to write for different purposes, audiences, and contexts. Rules and conventions of language help readers understand what is being communicated. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Sample NJ ASK narrative passages/tests 2. Sample open-ended questions 3. Sample open-ended responses (scored) 4. NJ ASK prep. Workbooks 5. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Desired Results (CPI) CPI: W.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to open-ended question timed simulations Areas of Focus 1. Writing a brief multi-paragraph composition that has clear topic development, logical organization, effective use of detail, and variety in sentence structure. 2. Using standard English conventions in all writing, such as sentence structure, grammar and usage, punctuation, capitalization, and spelling. 3. Using supporting evidence/details from the text 4. Providing an insightful explanation/opinion that links to or extends aspects of the text 5. Teacher modeling 6. Timed simulations 7. Reviewing/discussion of open-ended question response 8. Peer assessment of student open-ended question responses ASSESS through 4 point rubric 12 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: NJ-ASK Narrative Passage Teaching Time: Approx. 1 week Objectives: Student will be able to understand the elements of an NJ-ASK narrative passage and successfully respond to multiple choice questions and open-ended questions Essential Questions How do readers construct meaning from text? How does understanding a text’s structure help me better understand its meaning? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in a text? How do readers monitor themselves during a timed NJ-ASK simulation? Content Statements RL.8.1; 8.2; 8.3; 8.4; 8.6; W.8.2; W.8.4; L.8.4 Enduring Understandings Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to make text personally relevant and useful. Understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Good readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension 1. 2. 3. 4. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. State provided samples 2. NJ ASK prep workbooks 3. Constructed Response (Open-ended Questions) Samples 4. State scored samples 5. Areas of Focus Respond to a timed simulation of an NJ-ASK narrative passage by answering multiple choice questions and open-ended questions. Read critically by identifying, analyzing, and applying knowledge of theme and literary elements of a narrative passage. Locate and analyze the elements of setting, characterization, and plot to construct understanding of how characters influence the progression of the plot, development of suspense, and resolution of the conflict. Choose facts, concrete details, dialogue, and other relevant examples to support a written response to an Open-ended Question based on a narrative passage. Use context, a word’s position or function as clues to determine the meaning of a word or phrase. Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10; W.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to a timed simulation of a sample NJ-ASK narrative passage with multiple choice questions and constructed response questions. 13 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: Research Project/Debate Page Teaching Time: Approx. 4 weeks Objectives: Student will be able to research and write persuasive position paper about a controversial issue, citing sources using MLA format and avoiding plagiarism. Essential Questions Why conduct research? How do readers construct meaning from text? How does understanding a text’s structure help me better understand its meaning? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in a text? How do good writers express themselves through well supported persuasive writing? How do good writers cite sources without plagiarizing? How do students argue a position on a controversial issue from the point of view of a created fictional and credible expert? Enduring Understandings Researchers gather and critique information from different sources for specific purposes. Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to make text personally relevant and useful. Understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Good readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension Good writers develop and refine their ideas for effective communication and expression. Good writers are mindful of giving original authors legal and proper in-text credit for their work, as well as citing sources on a works cited page. Good persuasive writers develop and maintain a clear point of view and position on the issue or topic Areas of Focus 1. Read critically by identifying, analyzing, and applying knowledge of the purpose, structure, and elements of non-fiction and persuasive text and provide support from the text as evidence of understanding. 2. Choose facts, concrete details, and other relevant examples to support a position on a controversial issue. 3. Determine an author’s point of view or purpose in a text. 4. Write a multi-paragraph composition with clear position development, logical organization, and effective use of supporting details, examples, and research without plagiarizing. 5. Use basic MLA format guidelines for paper set-up, parenthetical expressions, and a proper works cited page. 6. Use internet, library books, data base sources, and periodicals to research supporting and credible facts and examples relevant to chosen topic. 14 Course: Language Arts Literacy Content Statements RI.8.1; 8.2; 8.6; 8.7; 8.8; 8.9; W.8.1; .8.2; 8.6; 8.7; 8.8; 8.9 Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Instructional packets on the research process and MLA format 2. Instructional packets on avoiding plagiarism. 3. Graphic organizers for multi- phase process. 4. Note cards for organizing research. 5. Model papers 6. Relevant books and periodicals on topics. Grade 8 7. Several, on-going revising and editing conferencing check-points. 8. OPTIONAL: Student dresses in disguise of the credible expert from whose point of view they have chosen to argue their position. Picture of student in disguise is creatively inserted on cover page with a 3rd person “Expert’s Profile”. Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RI.8.10; W.8.10; ASSESS by having students write a well-research and supported persuasive position paper on a controversial issue including a proper MLA works cited page. ASSESS using appropriate rubrics ASSESS by having student verbally debate their position with a student opponent. 15 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: NJ ASK Persuasive Passage Teaching Time: 1 week + Objective: Students will be able to understand the elements of a NJ ASK persuasive passage and successfully respond to multiple choice questions. Essential Questions How does understanding a text’s structure help a student better understand its meaning? How does a student figure out a word he/she does not know? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in the text? Why do readers need to pay attention to a writer’s choice of words? How do readers construct meaning from text? Enduring Understanding The understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Readers use language structure and context clues to identify the intended meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text. Good readers employ strategies to help them understand text. Strategic readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension. Words powerfully affect meaning. Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make connections (text to text, text to world, text to self) to make text personally relevant and useful. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Areas of Focus Identifying and using organizational structures to comprehend information Continuing to use structural analysis and context analysis to decode new words. Monitoring reading for understanding by setting a purpose for reading, making and adjusting predictions, asking questions and making connections Reading critically by identifying, analyzing, and applying knowledge of the purpose, structure, and elements of nonfiction and providing support from the text as evidence of understanding. Recognizing elements of a persuasive passage Establishing author’s point of view, position, and purpose Teacher modeling Practicing tips and strategies for active reading Timed simulations 16 Course: Language Arts Literacy Content Statements RI 8.1, 8.2, 8,3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6, 8.8 LI 8.4 Grade 8 Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Sample NJ ASK persuasive tests 2. NJ ASK prep. workbooks 3. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RI 8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to practice NJ ASK persuasive multiple choice tests 17 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: NJ ASK Open-Ended Questions – Persuasive Passage Teaching Time: 1 week + Objective: Students will be able to become familiar with the format of a NJ ASK open-ended question and will complete all requirements and respond with insight. Essential Questions How do good writers express themselves? How do writers develop a well-written product? How do rules of language affect communication? Enduring Understanding Content Statements W 8.2, 8.4 L 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.6 Good writers develop and refine their ideas for thinking, learning, communicating, and aesthetic expression. Good writers use a repertoire of strategies that enables them to vary form and style, in order to write for different purposes, audiences, and contexts. Rules and conventions of language help readers understand what is being communicated. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Sample NJ ASK persuasive passages/tests 2. Sample open-ended questions 3. Sample open-ended responses (scored) Areas of Focus 1. Writing a brief multi-paragraph composition that has clear topic development, logical organization, effective use of detail, and variety in sentence structure. 2. Using standard English conventions in all writing, such as sentence structure, grammar and usage, punctuation, capitalization, and spelling. 3. Exploring the central idea or theme of an informational text and support analysis with details from the article and personal experiences. 4. Using supporting evidence/details from the text 5. Establishing author’s point of view, position, and purpose 6. Providing an insightful explanation/opinion that links to or extends aspects of the text 7. Teacher modeling 8. Timed simulations 9. Reviewing/discussion of open-ended question responses 10. Peer assessment of student open-ended question responses 18 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 4. NJ ASK prep. workbooks 5. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Desired Results (CPI) CPI: W.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to open-ended question timed simulations ASSESS through 4 point rubric 19 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: Common Novel – The True Confessions of Charlotte Doyle Teaching Time: 3+ weeks Objective: Students will be able to comprehend and understand elements of a novel including setting, theme, characters, plot, and literary devices; students will also develop vocabulary building skills. Essential Questions How does understanding a text’s structure help a student better understand its meaning? How does a student figure out a word he/she does not know? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in the text? Why do readers need to pay attention to a writer’s choice of words? How do readers construct meaning from text? How does fluency affect comprehension? Why does a writer choose a particular form of writing? Enduring Understanding The understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Readers use language structure and context clues to identify the intended meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text. Good readers employ strategies to help them understand text. Strategic readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension. Words powerfully affect meaning. Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make connections (text to text, text to world, text to self) to make text personally relevant and useful. Areas of Focus 1. Identifying and using organizational structures to comprehend information 2. Continuing to use structural analysis and context analysis to decode new words. 3. Monitoring reading for understanding by setting a purpose for reading, making and adjusting predictions, asking questions and making connections 4. Reading increasingly difficult text silently and orally with comprehension and fluency. 5. Interpret text ideas through journal writing; writing responses to literature and developing insight into interpretations by connecting to personal experiences and referring to textual information 6. Analyzing/exploring major themes and other elements of a novel 7. Understanding/identifying literary devices 8. Recall of plot/events 9. Increasing vocabulary development 10. Implementing motivational reading 11. Guided class discussion/questioning 12. Culminating projects/tests (varies by teacher) 20 Course: Language Arts Literacy Content Statements RL 8.1, 8.2, 8,3, 8.4, 8.6 SL 8.1, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6 W 8.2, 8.4, 8.7, 8.8, 8.9 L 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6 Grade 8 Fluent readers group words quickly to help them gain meaning from what they read. A writer selects a form based on audience and purpose. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. The True Confessions of Charlotte Doyle 2. Teacher resource books/materials for novel 3. Study guides 4. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10, W.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to monitoring for understanding ASSESS through teacher generated tests/quizzes of material (containing open-ended questions graded using 4 point rubric) ASSESS through culminating project (varies by teacher) 21 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: Literary Analysis Teaching Time: 2+ weeks Objective: Students will be able to successfully compose a well-developed and organized literary analysis of a common novel (such as, The True Confessions of Charlotte Doyle) Essential Questions How do good writers express themselves? How does process shape a writer’s product? How do writers develop a well-written product? How do rules of language affect communication? Why does a writer choose a particular form of writing? Content Statements W 8.2, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6, 8.9 L 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.6 Enduring Understanding Good writers develop and refine their ideas for thinking, learning, communicating, and aesthetic expression. Good writers use a repertoire of strategies that enables them to vary form and style, in order to write for different purposes, audiences, and contexts. Rules and conventions of language help readers understand what is being communicated. A writer selects a form based on audience and purpose. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Sample literary analysis papers 2. “Writing a Literary Analysis” informative/instructional packets 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Areas of Focus Writing a response to literature and developing insights into interpretations by connecting to personal experiences and referring to textual information. Writing a multi-paragraph composition that has clear topic development, logical organization, effective use of detail, and variety in sentence structure. Using standard English conventions in all writing, such as sentence structure, grammar and usage, punctuation, capitalization, and spelling. Generating and narrowing topics by considering purpose, audience, and form with a variety of strategies (e.g. graphic organizers, brain-storming, etc.) Using personal style and voice effectively to support and engage the audience of a piece of writing. Revising and editing drafts by rereading for content and organization, usage, sentence structure, mechanics, and word choice. Students reflecting on own writing, noting strengths and weaknesses and setting goals for improvement. 22 Course: Language Arts Literacy 3. Graphic organizers 4. rubrics 5. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Desired Results (CPI) CPI: W.8.10 Grade 8 8. Composing, revising, editing, and publishing writing using appropriate word processing software. 9. Using transition words to reinforce a logical progression of ideas. 10. Teacher modeling 11. Teacher-directed instruction 12. Peer-editing ASSESS by having students write and revise several rough drafts their literary analysis; the final draft will be graded Also ASSESS through teacher-student conferencing 23 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: NJ ASK Speculative Writing Prompt Teaching Time: Approx. 1- 2 weeks Objectives: Student will be able to demonstrate their ability to speculate a story based on a given NJ ASK type story starter prompt. Student will be able to write a well-developed and creative narrative that meets the NJ ASK requirements on the state holistic rubric. Essential Questions How do writers develop a well-written product? Why does a writer choose a particular form of writing? How do rules of language affect communication? How does an understanding of figurative language, word nuances and relationships, dialogue, etc. make writing more successful? Content Statements W.8.3; W8.4; W.8.5; L.8.1; L.8.2; L-3; L8.5 Enduring Understandings Good writers develop and refine their ideas for thinking, learning, communicating, and aesthetic expression. A writer selects a form based on audience and purpose. Rules, conventions of language, help readers understand what is being communicated. Good writers take compositional risks and use literary devices to improve their writing. Areas of Focus 1. Examine great beginnings, structure options, compositional risks, vivid verbs, figurative language, etc. 2. Improving and varying sentence structure 3. Use transition words to reinforce a logical progression of ideas 4. Use Standard English conventions 5. Brainstorming 6. Self and Peer editing /sharing Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Sample speculative prompts 2. Scored sample responses 3. Various graphic organizers (e.g. “Somebody-Wanted-ButSo”) 4. MOBI 7. Model review; use of MOBI 8. Teacher-directed lessons 9. Timed simulations using NJ-ASK-type prompts Desired Results (CPI) CPI: W.8.10 ASSESS final narrative using NJ Holistic 6 point rubric; teacher conferencing 24 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: NJ ASK Persuasive Writing Task Teaching Time: 2+ weeks Objective: Students will be able to successfully compose a well-developed and organized 5-paragraph response to a NJ ASK persuasive writing task. Essential Questions How do good writers express themselves? How do writers develop a well-written product? How do rules of language affect communication? Why does a writer choose a particular form of writing? Content Statements W 8.1, 8.4, 8.5, 8.9 L 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.6 Enduring Understanding Areas of Focus Good writers develop and refine their ideas for thinking, learning, communicating, and aesthetic expression. Good writers use a repertoire of strategies that enables them to vary form and style, in order to write for different purposes, audiences, and contexts. Rules and conventions of language help readers understand what is being communicated. A writer selects a form based on audience and purpose. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Sample NJ ASK persuasive writing tasks 2. Sample scored NJ ASK responses 3. Graphic organizers 4. Writers checklists 1. Writing a multi-paragraph composition that has clear topic development, logical organization, effective use of detail, and variety in sentence structure. 2. Stating a position clearly and convincingly in a persuasive essay by stating the issue, giving facts, examples, and details to support the position and argument. 3. Using standard English conventions in all writing, such as sentence structure, grammar and usage, punctuation, capitalization, and spelling. 4. Generating and narrowing topics by considering purpose, audience, and form with a variety of strategies (e.g. graphic organizers, brain-storming, etc.) 5. Utilizing the NJ State Registered 6 point rubric to improve and evaluate a student’s own writing and the writing of peers. 6. Students reflecting on own writing, noting strengths and weaknesses and setting goals for improvement. 7. Using transition words to reinforce a logical progression of ideas. 8. Teacher modeling 25 Course: Language Arts Literacy 5. NJ Holistic 6 point scoring rubric 6. NJ ASK prep. workbooks 7. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Grade 8 9. Teacher-directed instruction 10. Timed and un-timed simulations 11. Peer-editing Desired Results (CPI) CPI: W.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to a NJ ASK Persuasive Writing Task (both timed and un-timed) ASSESS using NJ Holistic 6 point rubric; also through teacherstudent conferencing 26 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: The Diary of Anne Frank historical background connections Teaching Time: Approx. 2-3 days Objectives: Student will be able to make connections between historical events and the literature selection drama Essential Questions How does connecting historical events to a piece of literature improve understanding and appreciation? How does learning about historical background enhance understanding and appreciation of a drama based on a historical event? Content Statements RI.8.3; 8.7; 8.8 Enduring Understandings Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to make text personally relevant and useful. Good readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Textbook p. 364-368 2. A variety of supplemental materials 3. Definitive Edition of The Diary of Anne Frank 4. Critical Ed. Of The Diary of Anne Frank 5. Beyond the Diary 6. Internet websites Areas of Focus 1. Analyze how a text, web site, presentation makes connections among and distinctions between individuals, ideas, or events. 2. Recall and build upon prior knowledge of the Holocaust and WW II 3. Use resources to understand the historical background of the play they are about to read. 4. Attend a presentation by former social studies teacher, then Principal, now Superintendent. Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RI.8.10 ASSESS by having students discuss and write reactions to above activities ASSESS using teacher generated quiz on presented information. 27 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: The Diary of Anne Frank the play: Elements of Drama Teaching Time: Approx. 4-7 weeks Objectives: Student will be able to identify and analyze themes and other elements of drama, including setting, character development, foreshadowing, flashback, and dramatic irony. Essential Questions How does an understanding of how drama is written help us to better understand How do readers construct meaning from text? How does understanding a text’s structure, specifically drama, help me better understand its meaning? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in a text? How does an understanding of figurative language and literary devices enhance understanding and interpretation of dialogue in a drama? How do good writers express themselves? Enduring Understandings Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to make text personally relevant and useful. Understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitates the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Good readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension Good readers appreciate and try to use good writing techniques in their own writing. Analyzing the extent to which a film production of a drama stays faithful to or departs from the script develops critical and analytical thinking. Areas of Focus 1. Identify and analyze elements of drama: themes, flashback, dramatic irony, conflict, foreshadowing, characterizations, set, stage directions, etc. 2. Understanding use of figurative language 3. Make predictions and analyze characters. 4. Grammar links, p. 438 (dangling and misplaced modifiers) 5. Vocabulary development 6. Acting out/reading out loud, staging scenes from the play 7. Teacher directed class discussions 8. Compare and contrast dramatic dialogue to actual diary entries 9. Valentine’s Day project “Anne Frank Style” 10. Journal Writing 11. View and compare an updated and expanded film version of the script. 12. Respond to NJ-ASK type constructed response prompts based on readings. 28 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 How does comparing a film version of this drama enhance our understanding of original written piece? Content Statements RL.8.2; 8.3; 8.4; 8.6; 8.7; RI.8.3; 8.4; 8.6; 8.9; W.8.1 Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Textbook 2. A variety of supplemental materials 3. Definitive Edition of The Diary of Anne Frank 4. Critical Ed. Of The Diary of Anne Frank 5. DVD Beyond the Diary Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RI.8.10; RL. 8.10 ASSESS by having students discuss and write reactions to above activities ASSESS using tests and quizzes on presented information. 29 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: “Walking with Living Feet” (Published student essay, page 463-467) Teaching Time: 2 days Objectives: Students will be able to connect main ideas of this personal narrative to The Diary of Anne Frank and will learn how effective, descriptive literary devices can enhance their own writing Essential Questions Enduring Understandings Areas of Focus How does connecting historical events to a reaction piece of writing by a published student improve understanding and appreciation? How does examining a student sample of descriptive writing and their use of literary devices enhance our own writing? How do writers develop a well written product? How does fluency affect comprehension? Content Statements W.8.5; W.8.3; RL.8.4; RI.8.8 Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to make text personally relevant and useful. Good writers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their own writing style. Good writers use a repertoire of strategies that enable them to vary form and style. Fluent oral reader’s group words using tone and inflection help the listener gain meaning. 1. Make connections between this student’s experience with visiting a concentration camp to the reading of The Diary of Anne Frank and future field trip to the Holocaust Museum, WDC. 2. Motivational oral reading to demonstrate fluency. 3. Recognizing and interpreting literary devices such as similes, metaphor, sensory details, and parallel structure. 4. Understand use of parallelism to present items in a series or to organize ideas for emphasis. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. 2. Textbook p. 463-467 Supplemental Materials about the shoe exhibit in Holocaust Museum, WDC Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RI.8.10; RL.8.10; W.8.10 ASSESS by having students discuss and write reactions to above activities ASSESS using teacher generated quiz on presented information. 30 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: “A Tragedy Revealed: A Heroine’s Last Days” Teaching Time: 2-3 days Objective: Students will be able to use prior knowledge to understand factual reporting. Essential Questions How does understanding a text’s structure help a student better understand its meaning? How does a student figure out a word he/she does not know? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in the text? Why do readers need to pay attention to a writer’s choice of words? How do readers construct meaning from text? How does fluency affect comprehension? Enduring Understanding The understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Readers use language structure and context clues to identify the intended meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text. Good readers employ strategies to help them understand text. Strategic readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension. Words powerfully affect meaning. Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make connections (text to text, text to world, text to self) to make text personally relevant and useful. Fluent readers group words quickly to help them gain meaning from what they read. Areas of Focus 1. Identifying and using organizational structures to comprehend information 2. Continuing to use structural analysis and context analysis to decode new words. 3. Monitoring reading for understanding by setting a purpose for reading, making and adjusting predictions, asking questions and making connections 4. Reading increasingly difficult text silently and orally with comprehension and fluency. 5. Read critically by identifying, analyzing, and applying knowledge of the purpose, structure, and elements of nonfiction and providing support from the text as evidence of understanding. 6. Using prior knowledge to understand factual reporting 7. Analyzing main ideas in factual reporting 31 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 8. Implementing motivational reading Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. textbook RI 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 2. Holt Reading Solutions 8.6, 8.9 3. miscellaneous resource materials Content Statements 9. Guided class discussion/questioning SL 8.2, 8.3 L 8.4, 8.5, 8.6 Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RI 8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to “Response and Analysis” questions at the end of reading; grade responses ASSESS through class discussion 32 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: Edgar Allan Poe: Biography and background information Teaching Time: Approx. 3-4 days Objectives: Student will be able to attain valuable biographical information on Edgar Allan Poe in order to make connections and identify influences between his life and his works. Essential Questions How does connecting historical and biographical events to an author improve understanding and appreciation of his work? How does learning about historical and biographical background of an author enhance understanding and appreciation of literature published by that author? Content Statements RI. 8.6; 8.7; 8.9; RL.8.2; 8.3; 8.5; SL.8.1; 8.2; 8.3 Enduring Understandings Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to make text personally relevant and useful and more meaningful. Good readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension and interpretation of literature. Areas of Focus 1. Analyze how events from an author’s life influence the content, style, and themes of his works. 2. Organize, analyze and respond to information learned and viewed in video. 3. Interpret author’s inspiration from life events. 4. Read and discuss excerpts from “Tell Tale Heart” and “Annabelle Lee” to reveal author’s diverse talent and styles. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Textbook p. 537 2. A & E Biography video 3. Video graphic organizer 4. Various supplemental materials 5. Internet websites. Blogs 33 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RI.8.10 ASSESS by having students discuss and write reactions to above activities ASSESS by having student complete graphic organizer during video ASSESS using teacher generated test/quiz on presented information. 34 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: “The Tell-Tale Heart” Teaching Time: 4-5 days Objective: Students will be able to analyze the narrator and identify literary devices (such as irony) that define a writer’s style. Essential Questions How does understanding a text’s structure help a student better understand its meaning? How does a student figure out a word he/she does not know? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in the text? Why do readers need to pay attention to a writer’s choice of words? How do readers construct meaning from text? How does fluency affect comprehension? Why does a writer choose a particular form of writing? Enduring Understanding The understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Readers use language structure and context clues to identify the intended meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text. Good readers employ strategies to help them understand text. Strategic readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension. Words powerfully affect meaning. Areas of Focus 1. Identifying and using organizational structures to comprehend information 2. Continuing to use structural analysis and context analysis to decode new words. 3. Monitoring reading for understanding by setting a purpose for reading, making and adjusting predictions, asking questions and making connections 4. Reading increasingly difficult text silently and orally with comprehension and fluency. 5. Interpret text ideas through journal writing; writing responses to literature and developing insight into interpretations by connecting to personal experiences and referring to textual information 6. Analyzing and understanding an author’s use of irony and suspense. 7. Understanding/identifying literary devices 8. Recall of plot/events 35 Course: Language Arts Literacy Content Statements RL 8.1, 8.2, 8,3, 8.4, 8.6, 8.7 SL 8.1, 8.3 W 8.4 L 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6 Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make connections (text to text, text to world, text to self) to make text personally relevant and useful. Fluent readers group words quickly to help them gain meaning from what they read. A writer selects a form based on audience and purpose. Grade 8 9. Increasing vocabulary development 10. Implementing motivational reading 11. Guided class discussion/questioning Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. textbook 2. Holt Reading Solutions 3. Holt Reader 4. Audio CD 5. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10, W.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to monitoring for understanding ASSESS through teacher generated tests/quizzes of material (containing open-ended questions graded using 4 point rubric) ASSESS through class discussion ASSESS through graded “Analysis and Discussion” questions at the end of short story in textbook 36 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: Edgar Allan Poe ”The Raven” (Elements of Poetry) Teaching Time: Approx. 6-7 days Objectives: Student will be able to analyze “The Raven” for its poetic structure and use of literary devices. Student will also understand and critique Poe’s inspiration for this poem. Essential Questions How do readers construct meaning from text? How does understanding a text’s structure, specifically poetic structure, help me better understand its meaning and purpose? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in a text? How do an author’s personal life experiences influence his works? How does fluency affect comprehension? Enduring Understandings Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to make text personally relevant and useful. Understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Good readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension Fluent oral readers of poetry group words using tone and inflection help the listener hear the iambic rhythms and rhyming patterns and ultimately gain more meaning. Areas of Focus 1. Analyze how events from an author’s life influence the purpose, content, style, and themes in this famous poem. 2. Interpret author’s inspiration from life events. 3. Select and present one chosen stanza from the poem, identifying various elements and interpretations. 4. Enhance presentation with props, costumes, sound effects, posters, etc. 5. Use of MOBI to model and identify elements of stanza during presentation. 6. Define, recognize and interpret various elements of poetry, such as internal rhyme, allusion, sensory details, alliteration, etc. 37 Course: Language Arts Literacy Content Statements RL.8.2; 8.4; 8.6; SL. 8.3; 8.4; 8.5; 8.6; 8.9 Grade 8 Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Textbook p. 384 (‘93 ed.) 2. Various supplemental materials 3. Internet websites. Blogs 4. MOBI 5. Mock “Bust of Pallas” 6. Various room decorations 7. Supplemental copies of poem and stanza-bystanza interpretations. Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10 W.8.10 ASSESS by having students present their study and interpretation of one stanza from “The Raven” ASSESS by having student complete graphic organizer breaking down the elements of their chosen stanza. ASSESS by engaging audience to clarify and question peer presentations to earn bonus points for their own presentation. ASSESS using teacher generated test/quiz on presented information. 38 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: NJ ASK Explanatory Writing Prompt (with or without a quote in the prompt) Teaching Time: Approx. 1- 2 weeks Objectives: Student will be able to demonstrate their ability to write an explanatory essay based on a given NJ-ASK type prompt of a relatable situation or an interpretation of a famous quote. Student will be able to write a well-developed and informative piece in a timed setting that meets the NJ-ASK requirements on the state holistic rubric. Essential Questions How do writers develop a well-written product? Why does a writer choose a particular form of writing? How do rules of language affect communication? How does an understanding of figurative language, word nuances and relationships, dialogue, etc. make writing more successful? Content Statements W.8.1; W.8.2; W8.4; W.8.5; L.8.1; L.8.2; L-3; L8.5 Enduring Understandings Good writers develop and refine their ideas for thinking, learning, communicating, and aesthetic expression. A writer selects a form based on audience and purpose. Rules, conventions of language, help readers understand what is being communicated. Good writers take compositional risks and use literary devices to improve their writing. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Sample Explanatory prompts 2. Sample quotes 3. Scored sample responses 4. Various graphic organizers 5. MOBI Areas of Focus 1. Write multi-paragraph composition with a clear topic development, logical organization, effective use of detail, and variety in sentence structure. 2. Examine great beginnings, structure options, compositional risks, vivid verbs, figurative language, etc. 3. Improving and varying sentence structure 4. Use transition words to reinforce a logical progression of ideas 5. Use Standard English conventions 6. Brainstorming 7. Self and Peer editing /sharing 8. Model review; use of MOBI 9. Teacher-directed lessons 10. Timed simulations using NJ-ASK-type prompts Desired Results (CPI) CPI: W.8.10 ASSESS final explanatory piece of writing using NJ Holistic 6 point rubric; teacher conferencing 39 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: “Using Documents to Solve a Problem Text pp. 809-817 Teaching Time: Approx. 3 days Objectives: Student will be able to analyze informative and persuasive documents to solve a problem Essential Questions How do readers construct meaning from text? How does understanding a text’s structure help me better understand its meaning? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in a text? How do good writers express themselves through well supported persuasive writing? How do good writers cite sources without plagiarizing? How do students effectively prepare and engage in collaborative discussions on a topic with multiple perspectives? Enduring Understandings Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make various connections to make text personally relevant and useful. Understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Good readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension Good writers develop and refine their ideas for effective communication and expression. Good writers are mindful of giving original authors legal and proper in-text credit for their work, as well as citing sources as needed. Areas of Focus 1. Read critically by identifying, analyzing, and applying knowledge of the purpose, structure, and elements of non-fiction and persuasive text and provide support from the text as evidence of understanding. 2. Choose facts, concrete details, and other relevant examples to support a position on a controversial issue. 3. Determine an author’s point of view or purpose in several documents on the same topic. 4. Compare and analyze several authors’ perspectives of a topic 5. Prepare and discuss possible solutions to the problem presented based on documents examined. 40 Course: Language Arts Literacy Content Statements RI...8.1; 8.2; 8.3; 8.5; 8.6; 8.7; 8.8; 8.9; SL 8.1; 8.4; 8.6; RL.8.5 Grade 8 Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. Elements of Literature text p.809-817 2. Supplemental materials 3. Instructional packets on the research process and MLA format Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RI.8.10 ASSESS by having students complete activities, quizzes in text book ASSESS by having student verbally debate their position with a student opponent. 41 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: Common Novel – The Hobbit Teaching Time: 3+ weeks Objective: Students will be able to comprehend and understand elements of a novel including setting, theme, characters, plot, and literary devices; students will also develop vocabulary building skills. Essential Questions Enduring Understanding How does understanding a text’s structure help a student better understand its meaning? How does a student figure out a word he/she does not know? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in the text? Why do readers need to pay attention to a writer’s choice of words? How do readers construct meaning from text? How does fluency affect comprehension? Why does a writer choose a particular form of writing? The understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Readers use language structure and context clues to identify the intended meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text. Good readers employ strategies to help them understand text. Strategic readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension. Words powerfully affect meaning. Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make connections (text to text, text to world, text to self) to make text personally relevant and useful. Areas of Focus 1. Identifying and using organizational structures to comprehend information 2. Continuing to use structural analysis and context analysis to decode new words. 3. Monitoring reading for understanding by setting a purpose for reading, making and adjusting predictions, asking questions and making connections 4. Reading increasingly difficult text silently and orally with comprehension and fluency. 5. Interpret text ideas through journal writing; writing responses to literature and developing insight into interpretations by connecting to personal experiences and referring to textual information 6. Analyzing/exploring major themes and other elements of a novel 7. Understanding/identifying literary devices 8. Recall of plot/events 9. Increasing vocabulary development 10. Implementing motivational reading 11. Guided class discussion/questioning 42 Course: Language Arts Literacy Content Statements RL 8.1, 8.2, 8,3, 8.4, 8.6 SL 8.1, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6 W 8.2, 8.4, 8.7, 8.8, 8.9 Fluent readers group words quickly to help them gain meaning from what they read. A writer selects a form based on audience and purpose. Grade 8 12. Culminating projects/tests (varies by teacher) Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. The True Confessions of Charlotte Doyle 2. Teacher resource books/materials for novel 3. Study guides 4. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) L 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6 Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10, W.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to monitoring for understanding ASSESS through teacher generated tests/quizzes of material (containing open-ended questions graded using 4 point rubric) ASSESS through culminating project (varies by teacher) 43 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: “Flowers for Algernon” Teaching Time: Short Story – 2 weeks Novel – 3-4 weeks Objective: Students will be able to evaluate structural elements of plot, including sub-plots, parallel episodes, theme, and symbolism. Essential Questions Enduring Understanding How does understanding a text’s structure help a student better understand its meaning? How does a student figure out a word he/she does not know? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in the text? Why do readers need to pay attention to a writer’s choice of words? How do readers construct meaning from text? How does fluency affect comprehension? Why does a writer choose a particular form of writing? The understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Readers use language structure and context clues to identify the intended meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text. Good readers employ strategies to help them understand text. Strategic readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension. Words powerfully affect meaning. Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make connections (text to text, text to world, text to self) to make text personally relevant and useful. Areas of Focus 1. Identifying and using organizational structures to comprehend information 2. Continuing to use structural analysis and context analysis to decode new words. 3. Monitoring reading for understanding by setting a purpose for reading, making and adjusting predictions, asking questions and making connections 4. Reading increasingly difficult text silently and orally with comprehension and fluency. 5. Interpret text ideas through journal writing; writing responses to literature and developing insight into interpretations by connecting to personal experiences and referring to textual information 6. Analyzing/exploring major themes and other elements of a story/novel 7. Understanding/identifying literary devices 8. Recall of plot/events 9. Increasing vocabulary development 10. Implementing motivational reading 11. Guided class discussion/questioning 12. Culminating projects/tests (varies by teacher) 13. Comparing/contrasting story to the video Charly 44 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Content Statements RL 8.1, 8.2, 8,3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7 SL 8.1 W 8.4 L 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6 Fluent readers group words quickly to help them gain meaning from what they read. A writer selects a form based on audience and purpose. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. textbook 2. the novel Flowers for Algernon 3. the video Charly 4. Study guides 5. MOBI (although technology varies by teacher) Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RL.8.10, W.8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to monitoring for understanding ASSESS through teacher generated tests/quizzes of material (containing open-ended questions graded using 4 point rubric) ASSESS through class discussion ASSESS through graded “Response and Analysis” questions at the end of short story in textbook 45 Course: Language Arts Literacy Grade 8 Unit: Pre- Washington DC Trip – research and activities Teaching Time: 1+ weeks Objective: Students will research and complete various projects to establish purpose and meaning for sites to be visited on the Washington DC trip (i.e. Vietnam Memorial, WWII Memorial, Holocaust Museum, Lincoln Memorial, etc.) Essential Questions Enduring Understanding How does understanding a text’s structure help a student better understand its meaning? How does a student figure out a word he/she does not know? What do readers do when they do not understand everything in the text? Why do readers need to pay attention to a writer’s choice of words? How do readers construct meaning from text? How does fluency affect comprehension? Why conduct research? The understanding of a text’s features, structures, and characteristics facilitate the reader’s ability to make meaning of the text. Readers use language structure and context clues to identify the intended meaning of words and phrases as they are used in the text. Good readers employ strategies to help them understand text. Strategic readers can develop, select, and apply strategies to enhance their comprehension. Words powerfully affect meaning. Good readers compare, infer, synthesize and make connections (text to text, text to world, text to self) to make text personally relevant and useful. Fluent readers group words quickly to help them gain meaning from what they read. Areas of Focus 1. Identifying and using organizational structures to comprehend information 2. Monitoring reading for understanding by setting a purpose for reading, making and adjusting predictions, asking questions and making connections 3. Read critically by identifying, analyzing, and applying knowledge of the purpose, structure, and elements of nonfiction and providing support from the text as evidence of understanding. 4. Guided class discussion/questioning 5. Listening to and partaking in various teacher instructed presentations on DC sites/monuments (students rotate to different locations for each presentation) 6. Selecting and researching a name on the Vietnam Wall; completing a “soldier profile”; taking a name rubbing in Washington and presenting his/her profile to the class 46 Course: Language Arts Literacy Content Statements RI 8.2, 8.3, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7, 8.8 W8.7 SL 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6 Researchers gather and critique information from different sources for specific purposes. Materials, Text & Technology Options 1. websites 2. documentary videos 3. “To Heal a Nation” movie 4. newspaper articles 5. travel books 6. postcards, photos Grade 8 7. Researching relevant websites and sharing interesting facts 8. Self-selecting materials appropriately related to a research project. 9. Navigating through informational and interactive websites 10. Locating and organizing relevant information L 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4 Desired Results (CPI) CPI: RI 8.10 ASSESS by having students respond to “Response and Analysis” questions at the end of reading; grade responses ASSESS through class discussion 47