Introduction to Tech Writing

Introduction to
Technical Writing
Why Technical Writing?
In industry, 20-40% of your time will be writing
Career advancement
People judge by communication skills
Many job profiles requires versatility
(more varied responsibilities)
Definition of Technical Writing
Different from literary writing and from normal speech
Normal speech: “I”, “we”
Literary writing: flowery description, quoted speech
Writing with the purpose of communicating a technical idea / process to a specific audience i.e., “Writing to get work done”
Characteristics of Technical Writing
Targeted to particular readers
Helps solve problems
(e.g., instruction manual)
Often created collaboratively
Words + graphics
Uses design to increase readability
(headings, white space, etc.)
Involves high-tech tools
(e.g., CAD snapshots, Powerpoint, Photoshop)
Examples of Technical Writing
In House
Letters, memoranda, e-mail
Reports (project, progress, trip, etc.)
Proposals (to manager, to another department)
Out-of-House
Letters of inquiry, sales, etc.
Reports (to Client)
Articles for publication
Technical Writing Process
Planning and
Prewriting
Writing
(drafting)
Revise and
Edit
-
Purpose? - Write a draft -Proofread
- Audience? Following the - Finalize
-Research outline
- Outline
Process and Guidelines
Process
1. Focus on Why
2. Focus on Readers
3. Accurate Info
4. Outline
Guidelines
Effective Communication
Time is $$$
Step One- Focus on WHY
What is the message?
What do you want audience to do with info?
Inform
Request
Instruct
Propose
Recommend
Persuade
Record
Document Specifications
Expected format e.g., report, email, memo
Specified details:
Length
Headings
Spacing
Margin font type/size, etc.
Step Two- Focus on READERS
Who is intended audience?
Knowledge / ability
Interest
Write at level of audience e.g., technical, layperson, management, in-house, client, general public
Step Three- Collect Accurate Info
“Content is still king”
Do research, check facts
Proof-read
Facts v. opinions
Example:
FACT: The Porsche 911 has a power-to-weight ratio of 0.13, making it one of the fastest cars in its class.
OPINION: The Porsche 911 is undoubtedly the best car in its class.
Step Four- Create an Outline
Logical Flow
Generates ideas
Comprehensive coverage of topic
Like a Table of
Contents
Re-arrange as needed
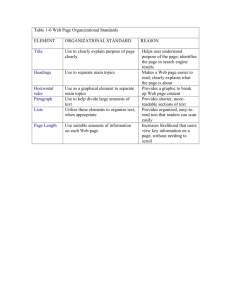
Accessible Document
Sections /subsections
Avoid overly long paragraphs
Use lists (numbered, bulleted, checklist)
Help skimmers!
In Class Activity
1) Complete General Project #1 on page 15 in your text.
2) Complete the Area 51 worksheet on Fact v.
Opinion
-Be sure your name and CRN is on your work
-Turn in your work when you are done
-See you next week!