Final_Draft_NIM_Oxygen_Policy
advertisement
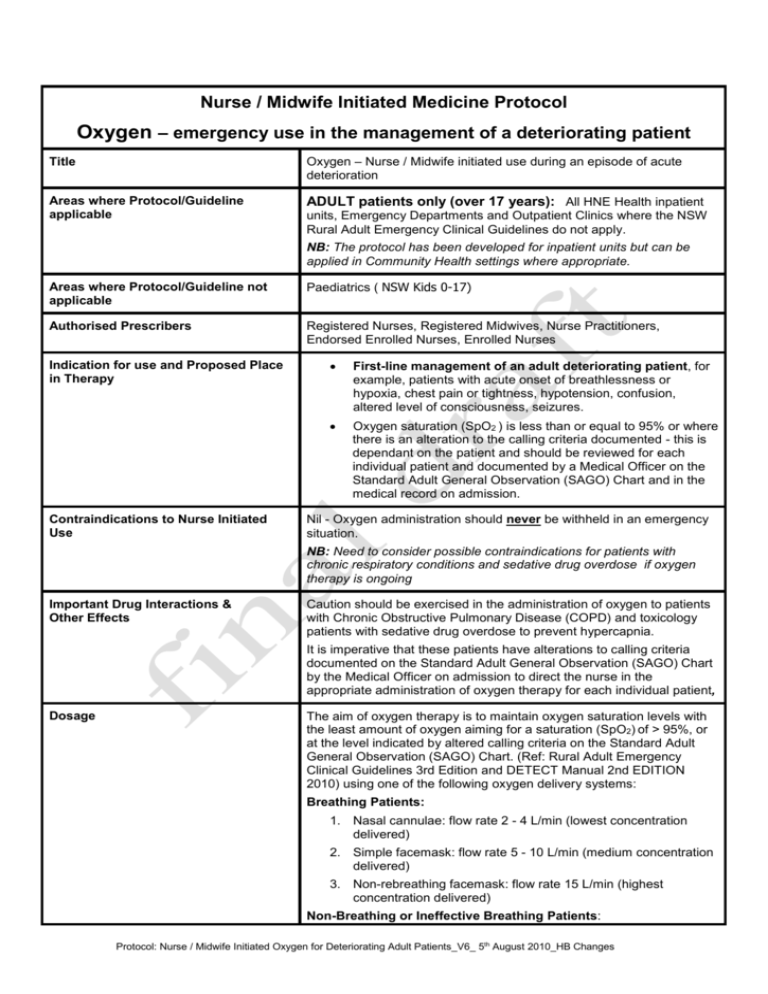
Nurse / Midwife Initiated Medicine Protocol Oxygen – emergency use in the management of a deteriorating patient Title Oxygen – Nurse / Midwife initiated use during an episode of acute deterioration Areas where Protocol/Guideline applicable ADULT patients only (over 17 years): All HNE Health inpatient units, Emergency Departments and Outpatient Clinics where the NSW Rural Adult Emergency Clinical Guidelines do not apply. NB: The protocol has been developed for inpatient units but can be applied in Community Health settings where appropriate. Areas where Protocol/Guideline not applicable Paediatrics ( NSW Kids 0-17) Authorised Prescribers Registered Nurses, Registered Midwives, Nurse Practitioners, Endorsed Enrolled Nurses, Enrolled Nurses Indication for use and Proposed Place in Therapy Contraindications to Nurse Initiated Use First-line management of an adult deteriorating patient, for example, patients with acute onset of breathlessness or hypoxia, chest pain or tightness, hypotension, confusion, altered level of consciousness, seizures. Oxygen saturation (SpO2 ) is less than or equal to 95% or where there is an alteration to the calling criteria documented - this is dependant on the patient and should be reviewed for each individual patient and documented by a Medical Officer on the Standard Adult General Observation (SAGO) Chart and in the medical record on admission. Nil - Oxygen administration should never be withheld in an emergency situation. NB: Need to consider possible contraindications for patients with chronic respiratory conditions and sedative drug overdose if oxygen therapy is ongoing Important Drug Interactions & Other Effects Caution should be exercised in the administration of oxygen to patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and toxicology patients with sedative drug overdose to prevent hypercapnia. It is imperative that these patients have alterations to calling criteria documented on the Standard Adult General Observation (SAGO) Chart by the Medical Officer on admission to direct the nurse in the appropriate administration of oxygen therapy for each individual patient, Dosage The aim of oxygen therapy is to maintain oxygen saturation levels with the least amount of oxygen aiming for a saturation (SpO2) of > 95%, or at the level indicated by altered calling criteria on the Standard Adult General Observation (SAGO) Chart. (Ref: Rural Adult Emergency Clinical Guidelines 3rd Edition and DETECT Manual 2nd EDITION 2010) using one of the following oxygen delivery systems: Breathing Patients: 1. Nasal cannulae: flow rate 2 - 4 L/min (lowest concentration delivered) 2. Simple facemask: flow rate 5 - 10 L/min (medium concentration delivered) 3. Non-rebreathing facemask: flow rate 15 L/min (highest concentration delivered) Non-Breathing or Ineffective Breathing Patients: Protocol: Nurse / Midwife Initiated Oxygen for Deteriorating Adult Patients_V6_ 5th August 2010_HB Changes 1. Mask-to-mouth with supplemental oxygen 2. Bag-valve-mask (BVM) device using high flow oxygen @15 lpm NB: Venturi masks deliver 24 – 50% oxygen concentrations and should be used when accurate oxygen concentration delivery is required in COPD / respiratory patients on an ongoing basis and should be ordered by a Medical Officer or Nurse Practitioner on the National Inpatient Medication Chart / Medical Record. Duration of therapy Nurse/Midwife initiated: Initial management of patients meeting "Clinical Review or Rapid Response" calling criteria (including altered calling criteria) on the Standard Adult General Observation (SAGO) Chart and should be continued until the patient has received a Clinical Review or Rapid Response. NB: Oxygen is a medication and should be prescribed by the Medical Officer or Nurse Practitioner on the National Inpatient Medication Chart / Medical Record if oxygen is used as an ongoing form of treatment. Safety Precautions Administration instructions Monitoring requirements Fire risk is greatly increased where there is a higher than normal oxygen concentration in the environment. Precautions include: No smoking, naked or lighted flames No grease /oil /fat based soaps or lubricants on or near oxygen equipment No use of electrical equipment eg. shaver, hair dryer No use of metal and clockwork toys Ensure correct flow meter is used Oxygen cylinder should be turned off at the valve when not in use Recorded and signed by nurse/midwife on nurse initiated section of the National Inpatient Medication Chart / Medical Record Record date, time, type of device, dosage and evaluation of intervention on Standard Adult General Observation Chart (SAGO) If therapy is to continue the Medical Officer or Nurse Practitioner must order the dose, device and titration instructions in the National Inpatient Medication Chart / Medical Record Frequent clinical re-evaluation as indicated by the patient’s condition including blood pressure, pulse rate, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and where necessary / available Arterial Blood Gas analysis. Review by Medical Officer as soon as possible in accordance with calling criteria for Clinical Review or Rapid Response. Management of complications References Call for immediate Medical Officer review according to the Clinical Review and Rapid Response Calling Criteria and local Clinical Emergency Response Protocols. Document in progress notes. 1. Between the Flags DETECT Manual 2nd EDITION 2010, Clinical Excellence Commission 2. NSW Health. 2010. Rural Adult Emergency Clinical Guidelines 3rd Edition http://www.health.nsw.gov.au/policies/gl/2010/GL2010_003.html 3. Guideline for Emergency Oxygen Use in Adult Patients, Protocol: Nurse / Midwife Initiated Oxygen for Deteriorating Adult Patients_V6_ 5th August 2010_HB Changes October 2008, British Thoracic Society www.brit-thoracic.org.au JBI_HNEH Acute Care Manual 2009. Oxygen Therapy, pp. 597601 Protocol: Nurse / Midwife Initiated Oxygen for Deteriorating Adult Patients_V6_ 5th August 2010_HB Changes










