Deparafinization
advertisement

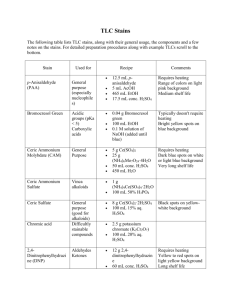
Tissue Staining Deparafinization: The paraffin is removed from the section with xylene. If the tissues are to be stained with an aqueuous solution then the slides must rehydrated in graded ethanol baths. Unless a time is indicated the approach is to gently agitate the slides by repeated immersion ~20x in each bath: Xylene for 2 min. (x3 changes) 100% EtOH (x2) 95% EtOH (x1) 80% EtOH (x1) H2O (x1). Alternative method…….. Immunostaining In Plastic Tubs (200 mL): Deparafinize: 1. Xylene 2' (x3) 2. 100% EtOH 2' (x3) 3. 70% EtOH 2' (x1) 4. PBS 5' (x3). De-Paraffinization of Tissue Sections In order to proceed with sample preparation, paraffin must be removed from tissue sections. Materials Xylene Ethanol Distilled Water Copplin Jars or other solvent containers Procedure 1. Section paraffin blocks at 5-10 microns. 5 microns is optimal for LCM, but the thickness should be dependant on the cell (nuclei) diameter that is being worked on. 2. Place ribbons into a water bath at 42° to smooth out and eliminate folds and wrinkles. 3. Mount sections onto glass slides. Air dry overnight at room temperature. If sections do not adehere to the slide sufficiently they can be baked at 42 C for up to 8 h. 4. Dip the slide containing the tissue section in the following solutions for the specified times. Xylene 5 minutes Xylene 5 minutes 100%Ethanol 30 seconds 95% Ethanol 30 seconds 70% Ethanol 30 seconds Distilled Water 30 seconds Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E): This is the most conventional stain for formalin fixed paraffin sections. The hematoxylin stains negatively charged nucleic acids (nuclei and ribosomes) blue. The eosin stains proteins pink. The hematoxylin or the eosin can also be used by themselves in more dilute form as counterstains for immunoperoxidase staining. To do this dilute the stain 1:4 with H2O or EtOH, respectively. Slides to be stained in eosin must be washed in ethanol first as listed below for the conventional protocol: Reagents: Harris hematoxylin: 1X stock. Anatech Lmtd. Cat #842. (616) 964-6450 Eosin: 1x stock. Cat #837. Acid alcohol: 76.6% EtOH, 1/300 (v/v) conc. HCl. (230 mL EtOH, 70 mL H2O, 1 mL HCl) Ammonia Solution: 0.084 (w/v) NH4OH (1 L H2O 3 mL 28% w/v NH4OH stock). Procedure: Hematoxylin, 2 minutes (x1) Running water (x1) Acid alcohol (x1) H2O (x1) Ammonia solution (x1) Running water 5 minutes (x1) 80% EtOH (x1) Eosin 15 seconds 95% EtOH (x2100% EtOH (x2) Wright Giemsa This is the conventional stain for blood smears and bone marrow cytology. It is usually performed on an automated slide stainer . Methyl Green (2% (w/v) methyl green in 0.1 M NaOAc, pH 4.2) Methyl green is a nuclear counter stain which works nicely for immunoperoxidase stained slides. It is difficult to control the intensity of the stain however since it washes out in both aqueous and organic solutions and this will depend on how quickly you mount the slides. Mix 918 mL of 0.1N acetic acid with 331 mL of 0.1 M NaOAc and adjust pH to 4.2 with NaOH. Add 25 gm of methyl green dye. Filter through Whatman #2 filter paper. H2O x 10-15 sec. Methyl green x 5 min. H2O (x2). Air dry. New Methylene Blue This stain is useful for distinguishing reticulocytes from mature RBCs in the peripheral blood. Mix whole blood 1:1 (v:v) with New Methlylene Blue (Ricca Chemical Co., Arlington Heights, IL). Incubate 10 minutes. Count on hemocytometer. Benzidine Stain This is a specialized stain which identifies erythroid cells (RBCs and their precursors). It gives them a golden brown color. Methanol, 10-15 seconds. Benzidine, 5 min: [1% w/v of 3,3' dimethoxybenzidine in methanol] (This is toxic stuff). Peroxide 2.5 min. (1 vol 30% H2O2 plus 11 vol. 70% EtOH) Dionized water wash, 2.5 min. Hematoxylin stain, 1.5 min. Rinse in tap water, 8 min. Air dry. Acetylcholine esterase (AChE) Stain Fix in 5% glutaraldehyde x 15 min. H2O (x3) Flood slide with fresh AChE stain. (5 mM NaOAc, pH5; 1mM glycine; 0.2 mM CuSO4; 1.15 mg/ml acetylthiocholine iodide: Sigma A5751) Incubate in petri dish o.n. Rinse in H2O (x3), air dry.