End of Chapter 9 Questions and Answers
advertisement

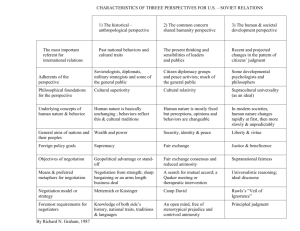
End of Chapter 9 Questions and Answers 1. Explain alternative names for win-lose negotiation. What are the presumptions inherent in this approach? Answer: Win-lose negotiation can also be called “military negotiation” or “power negotiation” This approach is based on the following premises: 1) Current deal is the most important and the only one to concentrate at present. Long-term considerations are not emphasized. 2) The opponent is an adversary and domination (market control) is necessary. 2. What are the assumptions within the win-win approach? What are alternative names? How can this approach backfire? Answer: The win-win approach to negotiation is also known as “principled negotiation”, “ally approach”, “mutual gains approach” and “cooperative method”. Assumptions made while using this approach are: 1) Future deals are as important or even more important than the current deal. 2) Each party is “logical” as defined by objective thinking patterns. 3) Interest-based bargaining is given preference over positional bargaining. 3. Which approach will most people use when they buy a car? Why does this make sense? Answer: Most people will use the “competitive approach” when they buy the car. The buyer knows what model and features of car he wants to purchase and the only issue that needs to be negotiated is price. The seller does not see same buyer purchasing cars in the near future (unless it is a corporate repeat account) and hence is not bothered that much about future deals. Hence the negotiation will often be “adversarial”. 4. Explain some symptoms of confident negotiators? Answer: Confident and self assured negotiators may demonstrate some of the following symptoms: 1) firm hand shake 2) direct eye contact 3) hands together in back while standing 4) hands together in front, elbows bent, 5) with fingers pressed together at the tips 6) standing straight 7) patient and even voice tone 8) little unnecessary movement 5. What are some symptoms of insecure negotiators? Answer: Nervous and Insecure negotiators may display the following symptoms: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) cigarette smoking fidgeting in chair avoiding eye contact perspiring abnormally dry throat or excessive throat clearing 6. Is the place of negotiation important? Answer: The place of negotiation plays an important role in the process by setting the stage. The party using an adversarial approach will like to negotiate at its own location (office or known place, where they can control the setting) to get some extra power over the proceedings. The party using a principled approach will prefer a neutral place and setting. 7. What are the alternatives for dealing with a game player negotiator? Answer: Play games back (win-lose style), ignore them or confront them (win-win style) and state that these games are not acceptable. 8. Why is saying this is my final offer risky? Answer: You will lose credibility if you are not serious and willing to walk. This statement of finality is one of the quickest ways to end a negotiation process. It is one way to increase your perceived power, as the other party may assume that a good BATNA has become available to you, but if no good BATNA exists then it might mean the death of the deal at hand. If you say this is my final offer and yet you continue to negotiate even when the offer is rejected, you have lost all credibility. 9. What is meant by risk shifting in negotiation? Answer: Risk shifting is accomplished by contractual arrangements, which shift risk from one party to another. Anyone involved in the transaction might be affected, including the buyer, seller, landlord, property manager, tenant, agent or banker. In exchange for accepting additional increments of risk, a party might receive a higher return or be able to accomplish another objective. 10. Can you think of some example where you can shift the risk of a changing interest rate to someone else? Or a changing lease rate prior to closing a deal? Answer: A buyer finds the property worth investing only if it can get finance for 75% of the property at a rate of 8% or lower. Due to the volatile market conditions the prospective buyer needs to hedge the risks. The buyer can hedge the risks by negotiating with the seller to lower the price or provide financing if the interest rates exceed 8% at the time financing is approved. There are many other examples. 11. Define ethics and business etiquette? Answer: Ethics are “proper or appropriate behavior”. When behaviors are expected they are called customs or in doing business, etiquette. Expected business etiquette are voluntary courtesies while ethics are appropriate for morale reasons. 12. Are ethics universal over time and among all peoples? Answer: No, ethics vary by country, religion and over time. There are few universal ethics. 13. What are some typical examples of ethical violations by real estate agents? Answer: (1) An agent claiming to be the procuring cause of a sale when in fact they were incidental to the transaction, at best, (2) Exaggerating the market value of a property to a potential seller in order to gain control of the property through an exclusive right to sell listing contract and soon thereafter working on the seller to lower their price aspirations, (3) Suggesting to an owner that the agent is working with a hot prospective buyer who would find their property perfect for their tastes and needs, when in fact no such buyer exists, simply to get an exclusive listing contract, and (4) Keeping an expired listing contract in the multiple listing service in order to attract new potential buyers. Acts of Agency and Fiduciary Violations, such as: (1) Revealing confidential information from the seller or buyer with respect to the lowest/highest acceptable price in the process of single agency negotiations, (2) Avoiding phone messages, faxes, or e-mail messages from other agents with prospects for a listing in order to try and complete a current transaction with an internal prospect that would mean a higher net commission, and (3) Showing a buyer only the firm’s listings while more appropriate listings are available from other firms in order to try and keep more commission fee revenue within the firm or directed towards friends.