Reproduction in Animals

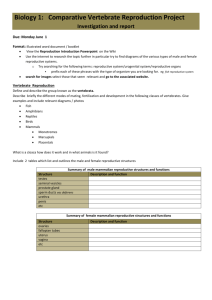
Reproduction in Animals
Learning Objectives:
1) Identify parts on prepared slides
2) Identify human reproductive anatomy
3) Indicate the mode of action and relative effectiveness of birth control methods
Introduction:
Reproduction is necessary for the continuation of all species. There are many strategies that are used in the five kingdoms. Some species use asexual reproduction; fission, budding, pathogenesis and vegetative reproduction. In sexual reproduction, separate sexes are the most common. However, a few species are hermaphrodites, having both male and female sex organs. Some animal species use external fertilization and others use internal fertilization.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction as compared to asexual reproduction?
Lab Activities:
Part I: Male reproductive Anatomy Slides
1)Look at a slide of a cross section of a rat’s testes.
Locate the seminiferous tubules and the interstitial cells.
Identify the different bands of cells in the tubules that give rise to the spermatogonia, primary and secondary spermatocytes, the spermatids and the sperm. Make a sketch of what you see. a)Which cells are going through mitosis, which cells are going through meiosis I, meiosis II? b)What are the functions of seminiferous tubules and the interstitial cells? c) What are the functions of testosterone in the human male?
2)Look at a slide of a human sperm smear. What are its parts? Is it haploid or diploid?
Make a sketch of what you see. If you like, for size comparison, take a piece of your hair and examine it under the microscope to compare sizes.
3)Look at a slide of the Human penis. Make a sketch identifying the urethra and the erectile tissue surrounding it.
Part II: Female Reproductive Anatomy Slides
1 ) Look at a slide of a mammalian ovary. Identify the mature follicle containing the primary oocyte (the oocyte looks like it is on a pedestal of cells). Make a sketch of what you see. a) At what stage is the oocyte ovulated? b) Where does fertilization occur? c) The female reproductive cycle is controlled by several hormones. What hormones are produced by the anterior pituitary that affect this cycle? d)What hormones are produced by the ovaries? e)What is the function of the hormones from the ovaries in the human female?
Part III: Reproduction in Humans:
Examine the plastic modes of human reproductive anatomy
Be sure you can identify the following male structures: testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle, prostate, urethra, bladder, penis, and erectile tissue
Be sure you can identify the following female structures: ovary, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, vagina, labia, bladder and urethra
Examine the various birth control methods set up as a demonstration. Describe how ezch category (barrier, hormonal, spermicidal) works, and give an example for each.
Use your own research, either from the Internet or a book source to determine the effectiveness of the following birth control methods.
Methods Typical Use Rate of Pregnancy
Sterilization
Male Sterilization
Female Sterilization
Hormonal Methods
Implant( Norplant )
Hormone Shot
Combined Pill (Estrogen/Progestin)
Minipill (Progestin only)
Patch
NuvaRing
Barrier Methods
Male Latex Condom
Diaphragm
Cervical Cap ( no previous birth)
Female condom
IUD (intrauterine device)
Spermicide (gel, foam. suppository, film)
Natural Methods:
Withdrawal
Natural Family Planning ( Calendar, temperature, cervical mucus)
No Method: