BIOLOGY Chapter 18 WORKSHEET
advertisement
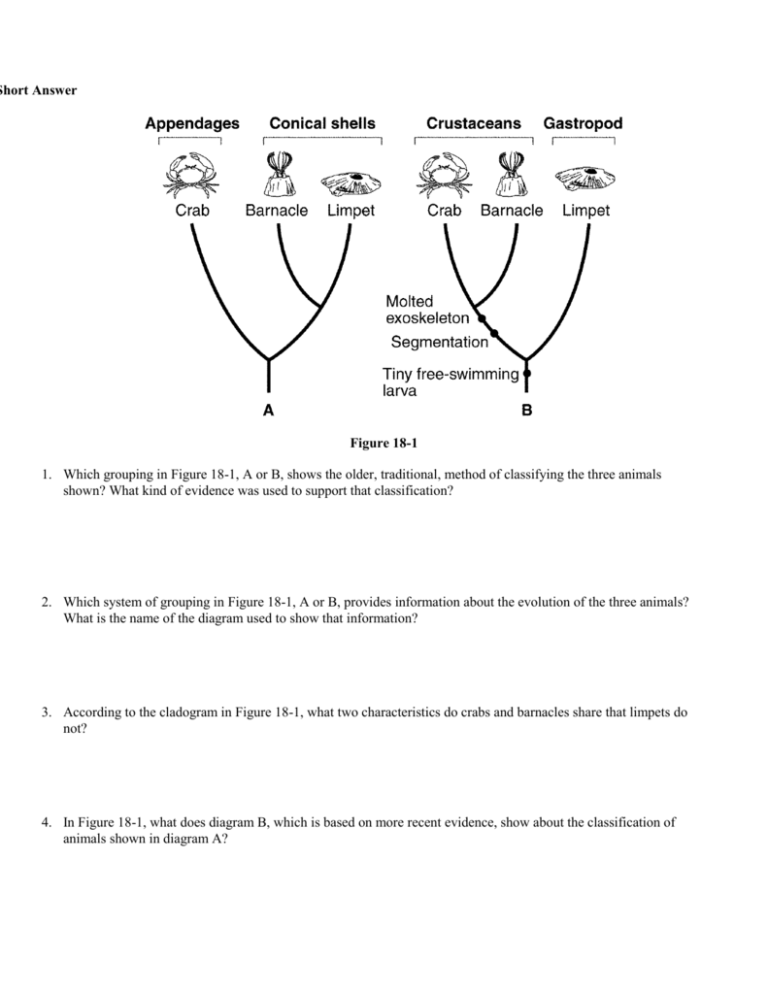
Short Answer Figure 18-1 1. Which grouping in Figure 18-1, A or B, shows the older, traditional, method of classifying the three animals shown? What kind of evidence was used to support that classification? 2. Which system of grouping in Figure 18-1, A or B, provides information about the evolution of the three animals? What is the name of the diagram used to show that information? 3. According to the cladogram in Figure 18-1, what two characteristics do crabs and barnacles share that limpets do not? 4. In Figure 18-1, what does diagram B, which is based on more recent evidence, show about the classification of animals shown in diagram A? USING SCIENCE SKILLS Figure 18-2 5. Interpreting Graphs Which level of taxonomic category shown in Figure 18-2 contains the greatest number of different organisms? 6. Classifying Do all organisms shown in Figure 18-2 that belong to the order Carnivora also belong to the phylum Chordata? Explain. 7. Classifying Do all organisms shown in Figure 18-2 that belong to the class Mammalia also belong to the genus Ursus? Explain. 8. Observing Based on the information in Figure 18-2, describe how the diversity at each level changes from species to kingdom. 9. Inferring Considering the information in Figure 18-2, if you were given a species name and no other information about an unfamiliar organism, what is the largest taxonomic category that you could assign it to? Name _____________________________________ 11/1/10 USING SCIENCE SKILLS Classification of Living Things DOMAIN KINGDOM Bacteria Archaea Eubacteria Archaebacteria Period _________ Eukarya Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia CELL TYPE Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote CELL STRUCTURES Cell walls with peptidoglycan Cell walls without peptidoglycan Cell walls of cellulose in some; some have chloroplasts Cell walls of chitin; no chloroplast Cell walls of cellulose; chloroplasts No cell walls or chloroplasts NUMBER OF CELLS Unicellular Unicellular Most unicellular; some colonial; some multicellular Most multicellular; some unicellular Multicellular Multicellular MODE OF NUTRITION Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or heterotroph Autotroph or heterotroph Heterotroph Autotroph Heterotroph EXAMPLES Streptococcus, Escherichia coli Methanogens, halophiles Amoeba, Paramecium, slime molds, giant kelp Mushrooms, yeasts Mosses, ferns, flowering plants Sponges, worms, insects, fishes, mammals Figure 18-3 10. Using Tables and Graphs According to Figure 18-3, what is the main difference between the domain Bacteria and the domain Archaea? 11. Applying Concepts If you know an organism has a cell wall and is a multicellular autotroph, could you use Figure 18-3 to determine the kingdom to which it belongs? Why or why not? 12. Using Tables and Graphs Can you determine, by examining Figure 18-3, which kingdom contains the greatest number of species? Why or why not? 13. Applying Concepts If you were told only that an organism is unicellular and has chloroplasts and a nucleus, could you use Figure 18-3 to determine the kingdom to which it belongs? Why or why not? 14. Using Tables and Graphs Considering the data presented in Figure 18-3, which characteristic seems more important in assigning an organism to a specific domain—the presence or absence of a nucleus or its mode of nutrition? Why? USING SCIENCE SKILLS Classification of Four Organisms Whale Shark Humpback Whale Spider Monkey Animalia Animalia Animalia Kingdom Corn Plantae Phylum Anthophyta Chordata Chordata Chordata Class Monocotyledones Chondrichthyes Mammalia Mammalia Order Commelinales Squaliformes Cetacea Primates Family Poaceae Rhincodontidae Balaenopteridae Atelidae Genus Zea Rhincodon Megaptera Ateles Species Zea mays Rhinacodon typus Megaptera novaeangilae Ateles paniscus Figure 18-4 15. Using Tables and Graphs Which two organisms listed in Figure 18-4 are most closely related to each other? Explain. 16. Using Tables and Graphs Which level of taxonomic category shown in Figure 18-4 indicates whether an organism is a mammal or not? 17. Using Tables and Graphs How many different kingdoms are represented by the organisms listed in Figure 18-4? What are they? 18. Inferring If you were adding a column to Figure 18-4 for the protist species Amoeba proteus, what taxonomic category, if any, would be the same as for any of the organisms shown in Figure 18-4? Explain. 19. Inferring Consider the following statement: “Size and shape are NOT reliable indicators of how closely different organisms are related.” What information shown in Figure 18-4 supports this statement? BIOLOGY Chapter 18 WORKSHEET Answer Section SHORT ANSWER 1. 2. 3. 4. A; comparisons of body structure A; a cladogram segmentation and a molted exoskeleton Diagram B indicates that the traditional taxonomic grouping shown in diagram A classified less closely related groups together while failing to show a close relationship within the groups. OTHER 5. the kingdom 6. Yes; from the genus through the kingdom, each general category contains the categories shown beneath it. 7. No; the genus Ursus contains the species Ursus arctos and possibly other species, but it does not contain any of the catagories above it. 8. The species has the least diversity. From genus upward, each category has more diversity than the one before it. The kingdom shows the greatest diversity. 9. the genus 10. Bacteria have cell walls with peptidoglycan, while the cell walls of Archaea lack peptidoglycan. 11. No; it could belong to either Protista or Plantae. 12. No; the table gives no information about the number of species in each kingdom. 13. Yes; it could only be a protist because the protists are the only eukaryotic unicellular organisms that have chloroplasts. 14. The presence or absence of a nucleus is more important. All three domains contain both autotrophs and heterotrophs. 15. The humpback whale and the spider monkey are most closely related because they belong to the same class. 16. the class 17. two; Plantae and Animalia 18. None, since this species belongs to the kingdom Protista. 19. The whale and the shark look most alike, yet they belong to different classes. The monkey and the whale are more closely related than any other pair here, yet they differ greatly in size and shape.