Organic Macro
advertisement

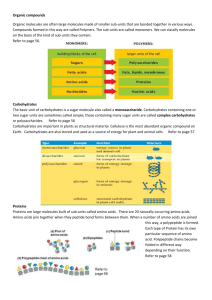
Organic Macro-Molecules --Carbon based molecules --Organic= --great structural (back-bone) molecule. --has e- for 4 covalent bonds to form. -Natural forms of Carbon --Macro-molecule --Monomer= --Polymer= 4 Classes of Macromolecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids -Dehydration Synthesis (Condensation) =for each monomer bonded to a polymer, one water molecule is removed. --Hydroloysis=for each monomer removed from a polymer, a water molecule is added. Carbohydrates (CHO) -most abundant organic molecule --composed of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen. --primarily serves as an energy source molecule. --Quick-use or short-term energy --Storage or long-term energy --some forms serve structural functions --contains many C-H bonds = Types of Carbohydrates: Short-term --Monosaccharides (Simple Sugars) -shape of chain or ring composed of 3 - 9 carbon atoms. -ex: Glucose (C6H12O6)=6 carbon ring or chain molecule. -ex: Ribose & Deoxyribose -5 carbon ring sugars -components of RNA & DNA --Disaccharides=2 monosaccharides bonded together by a Glycosidic bond. -ex: Sucrose =1glucose+1 fructose -used for… -ex: Maltose (Sugar used in alcohol) =1 glucose+1 glucose --used for… -ex: Lactose (Milk sugar) =1 glucose+1galactose -produced by animals Long term Energy Storage Molecules Starch=primary storage form of energy in plants --polysaccharide = --shape is a long highly branched chain. --ex: Amylopectin=most common starch in --Glycogen=“animal starch” Structural Carbohydrates: --Function in support of cells --large, highly branched polysaccharides with complex bonding arrangements . -found in… --ex: Cellulose=polysaccharide of plant cell walls --ex: Chitin=polysaccharide of arthropod exoskeletons Lipids --fatty, greasy, oily, waxy compounds. --insoluble in water=Nonpolar Types of Lipids: 1. Fats --contain more C-H bonds than carbohydrates. --composed of 2 subunits: 1. Glycerol 2. Fatty Acid (3) --Fat=Triglyceride --Fats are Saturated or Unsaturated -Saturated with what? -Characteristics of Fats: --Polyunsaturated fat= --Oil=“liquid fat” liquid @ room temp. --Hydrogenation= --fats yield twice as much energy per gram than carbohydrates. 2. Steroids such as Cholesterol. -important precursor to many hormones. -major component of cell membranes. 3. Hormones 4. Wax such as the cuticle of leaves & fruits. 5. Terpenes=some pigments in plants & animals. 6. Phospholipids=form the cell membrane. Proteins --most diverse molecule type in life. (Humans =50,000-100,000 diff. Proteins) -Important Groups of Proteins: 1. Enzymes=proteins that start or speed-up (catalyze) chemical rxns. -Biological Catalysts 2. Structural proteins -Compose: cartilage, bone, muscle, horn, claw, hooves, nails, scutes, scales, fins, teeth, and feathers. --Collagen=common structural protein in mammals. Protein Structure: --composed of long chains of amino acids. --20 different amino acids in proteins. --Polypeptide bonds link amino acids into a polypeptide chain=protein. 4 characteristics of Shape: -primary = -secondary = -tertiary = -quaternary = -the role of a protein is determined by its shape, which is determined by its amino acid sequence. Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids --Nucleotide composed of: 1. Phosphate group 2. Nitrogenous base -5 types of bases: -2 Purines = Adenine & Guanine -3 Pyrimidines = Thymine, Cytosine and Uracil deoxyribose) Roles of Nucleotides: --function in the packaging of energy. --ex: ATP --linked into nucleic acids --Nucleic Acid=long chain of nucleotides. --ex: DNA & RNA --Phosphodiester bonds link nucleotides into long chains. --nucleic acids determine hereditary information. 3. 5-carbon sugar(ribose /