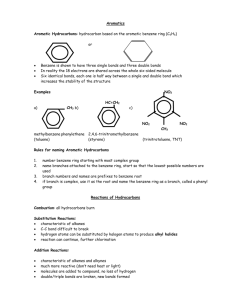
sigma bond Aromatic
advertisement

Chemistry 212 Spring 2009 Aromatic Compounds – 2 Reactions of Substituted Aromatic Compounds – Only organic products given 1. Examples (a.) N C Cl Cl + Cl Cl Cl Cl (c.) FeCl3 Cl NH2 (d.) (e.) (f.) + Cl Cl Cl FeCl3 + CH3 + Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl N Br Br Cl (i.) 3 X 106 H + Cl CH3 + Cl 1.5 X 101 N O Cl Cl (j.) CH3 + Cl Cl (k.) + Cl Cl 4 X 10-4 CH3 3 X 103 Cl O 1 X 10-4 FeCl3 C N FeCl3 Cl O C FeCl3 Cl FeCl3 CH3 O C N H + CH3 H 3 X 102 Cl O C CF3 Cl CH3 C N NH2 Cl O + Cl O 1 X 10-1 NH2 + FeCl3 O (h.) FeCl3 FeCl3 Cl O 5 X 102 OH OH + (g.) Cl Cl Cl Cl O O + FeCl3 Cl CF3 CH3 CH3 + Cl Cl 1 X 10-3 + Br + N Relative Rates Reactions OH O + C FeCl3 CH3 (b.) Relative Rates Reactions CH3 1.5 X 10-3 1 (Rate Standard) 2 1. Analysis of Examples: a. List reactions in (1.) above according to decreasing reaction rate. 1. Rxn D 2. Rxn G 3. Rxn B 4. Rxn I 5. Rxn F 6. Rxn K 7. Rxn C 8. Rxn J 9. Rxn A 10. Rxn E 11. Rxn H Aromatic Compounds-2 b. Group the reactions in (1.) above according to similarities in reaction pattern. Group A, E, H, J (Cl is two carbons away (towards the left) from the original substituent. (Meta) Group B, C and D, F, G, I (forms two product-one where the Cl is directly to the left of the original substituent. (One is Ortho, and the other is Para) K- is standard (rate=1) c. What do the structures of the reactants with rates faster than that of benzene (unsubstituted standard rate =1) have in common? What about the outcomes of the reactions? The reactants(with the rates faster than that of benzene) have 1 extra substituent attached to the benzene ring. These HEE’s on the substituent donate electrons to the electrons on the ring (delocalization donating effect). The reactions that are faster than Benzene, form two products. Products show up in 2 or 3 position (ortho or para position). What do the reactants with rates slower than that of benzene (unsubstituted standard rate =1) have in common? What about the outcomes of the reactions? They all have substituents that have double or triple bonds except reaction e (meta product). The atom with HEE’s are located away from the ring (therefore, electrons are going away from the ring).The reactions with the rate lower than that of benzene, form 1 product except reaction C. It is observed that whenever there’s a withdrawing electron effect, the reaction forms products with substituents present in the meta position. Aromatic Compounds-2 3 d. Are there any reactions that don't seem to fit your general correlations above? Reaction c does not fit the general correlations because it forms two products of para and ortho yet it is slower than the standard reaction. e. Write a mechanism (using arrows) for the formation of at least one product in each reaction in each of the groups that you formed in 2 (b.) above. f. 4 Aromatic Compounds-2 Now try to devise mechanistic arguments to explain: (1.) The variation in the relative rates in (2.a.). (2.) The variation of reaction patterns in the reactions in (2.b.). Reaction c shows a variation of the patterns stated above because of it forms two products yet it goes slower than the standard reaction. This is because bromine has a higher effective nuclear charge than chlorine which lowers the rate. Aromatic Compounds-2 5 Aromatic Compounds-2: Out of Class Applications 1. Predict the products of the following rxns. Explain how your predictions were determined. O CH 3 (a.) (c.) C O + .. NH + HNO 3 N (b.) + + CH 3 (e.) + CH 3 H2C H2SO 4 CH 3 C Cl O AlCl 3 Br AlBr 3 SO3 + (d.) Br CH 3 CH H2SO 4 O CF 3 O- O N C (f.) H2SO4 CH 3 C O + CH 3 H2SO 4 C O O CF 3 (g.) + Cl Cl FeBr 3 CH 3 + C C Cl CH 3 (j.) AlCl 3 H2SO4 N O .. (i.) O + HNO 3 (h.) CH 3 S .. OH S CH 3 + SO 3 H2SO 4 2. Which of the following compounds would be most reactive (give a higher rate) in ring nitration? Which would be least reactive? Explain on the basis of electron energies. O O NH2 3. (a.) CH3 (b.) C (c.) (d.) CH3 C NH CH3 (e.) 3. Which compound in (2.) above would yield the highest percentage of meta-Nitro product? 6 Aromatic Compounds4. Circle the major product(s) of the following rxn and explain the logic of your choice: O NH C Br 2 FeBr 3 NH Br O C NH O C NH (c.) Br O C Br (b.) (a.) NH Br O C NH (d.) O C (e.) Br 5. Which of the following reactions would yield p-Isopropylbromobenzene? Explain your reasoning. Br (a.) + Br (b.) O H2SO 4 + Br (c.) H2SO 4 H Cl + AlCl 3 6. Which one(s) of the following is(are) NOT meta-directing when attached to a benzene ring? Explain how you selected your choice(s). O H N (a.) C O CH 3 O N+ (b.) CH3 CH3 N+ CH3 (c.) H N O C O C (d.) (f.)