Grammar Study Guide for Latin I Stages 1-12
advertisement
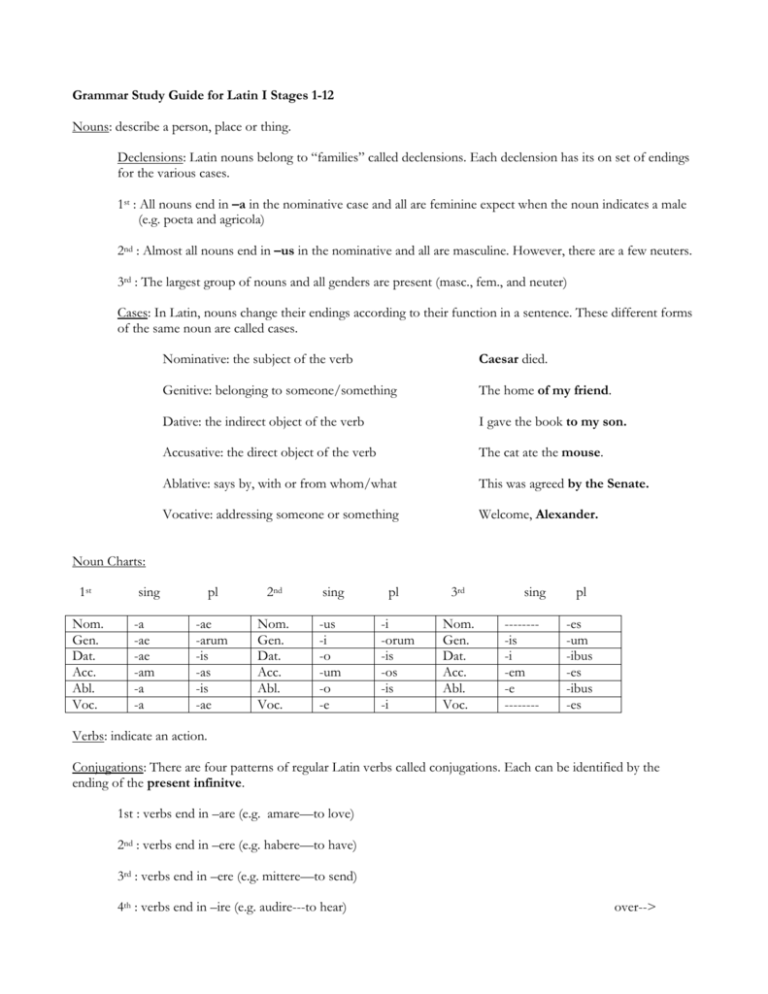
Grammar Study Guide for Latin I Stages 1-12 Nouns: describe a person, place or thing. Declensions: Latin nouns belong to “families” called declensions. Each declension has its on set of endings for the various cases. 1st : All nouns end in –a in the nominative case and all are feminine expect when the noun indicates a male (e.g. poeta and agricola) 2nd : Almost all nouns end in –us in the nominative and all are masculine. However, there are a few neuters. 3rd : The largest group of nouns and all genders are present (masc., fem., and neuter) Cases: In Latin, nouns change their endings according to their function in a sentence. These different forms of the same noun are called cases. Nominative: the subject of the verb Caesar died. Genitive: belonging to someone/something The home of my friend. Dative: the indirect object of the verb I gave the book to my son. Accusative: the direct object of the verb The cat ate the mouse. Ablative: says by, with or from whom/what This was agreed by the Senate. Vocative: addressing someone or something Welcome, Alexander. Noun Charts: 1st Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Voc. sing -a -ae -ae -am -a -a pl 2nd sing pl 3rd -ae -arum -is -as -is -ae Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Voc. -us -i -o -um -o -e -i -orum -is -os -is -i Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Voc. sing --------is -i -em -e -------- pl -es -um -ibus -es -ibus -es Verbs: indicate an action. Conjugations: There are four patterns of regular Latin verbs called conjugations. Each can be identified by the ending of the present infinitve. 1st : verbs end in –are (e.g. amare—to love) 2nd : verbs end in –ere (e.g. habere—to have) 3rd : verbs end in –ere (e.g. mittere—to send) 4th : verbs end in –ire (e.g. audire---to hear) over--> Tenses: These forms of the verb show when an action takes place in the present, in the past or in the future. Present: describes an action that is occurring right now. Imperfect: describes an action that happened in the past but was going on for some time. Perfect: describes an action that happened in the past, but it is a completed action that happened once. Verb Charts Present 1 2 3 Sing -o/-m -s -t Plural -mus -tis -nt Imperfect 1 2 3 Sing -bam -bas -bat Plural -bamus -batis -bant Perfect 1 2 3 Sing -i -isti -it Plural -imus -istis -erunt **Tricky Verbs*** Please refer to p111 and p234-235 for the ways that the perfect tense is formed for these “tricky verbs.” **Irregular Verbs** sum, esse ----to be Present: sum---I am sumus---we are Imperfect: eram---I was eramus—we were es—you are estis---you(pl) are eras—you were eratis—you (pl) were est—He/she/it is sunt---- they are erat--- he/she/it was errant—they were Adjectives: add quality or describe a noun. In Latin they must agree with the noun they modify in case, number, and gender. Positive: the adjective in its simplest form. easy Compartive: the adjective used when things are being compared easier Superlative: the adjective used when things are the most of something easiest Question Words: Refer to p191. qui=who quid=what ubi=where cur=why Also by adding –ne to the end of the first word of a sentence and num indicate questions.