Unit1_Activity4
advertisement

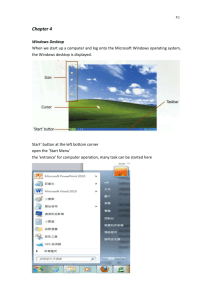
Activity #4 Reading PART A: In order to make good decisions about what computer equipment will best suit your needs for your business, you will need to know about hardware and software. A computer workstation is a stand alone computer generally used in a business or professional setting. These are often personal computers that are connected to a local area network in order to share resources such as a printer. The workstation generally includes the following computer components: These components perform the basic function of a computer: Input: Any device that allows data to be entered into the computer system. Examples include a keyboard, microphone, joystick, light pen, modem. Processing: Completed in the "Central Processing Unit", where the raw data entered into the computer is converted into a usable form and then temporarily stored. This is where all the action takes place. The processing or "system" unit contains a motherboard, microprocessor, power supply, primary memory (RAM), expansion ports or "slots". Storage: Sometimes known as "secondary" or "auxiliary" storage. This is where information can be stored so that it can be retrieved at a later date. Examples include a hard drive, zip drive, floppy disk, USB storage devices. Output: The form by which the result of the process is displayed. Examples of output devices include a monitor, printer, speakers, modem. We will be examining the input, processing and output devices. Input Devices The keyboard The keyboard is a device used to input data by keying it in. Although this is a very tedious method of inputting data, it is a very common one. There are many other types of input devices. Pointing Devices Pointing devices are used to move a pointer around on the screen in order to execute commands. The mouse is a very common pointing device, but there are many others. - mouse, graphic tablets, joysticks, touch pads, track stick, your finger on a touch screen, stylus. Scanners Scanning devices read text or graphics from paper and change it into a format that the computer can use. Although the flatbed scanner to scan pictures is common, there are several other types of scanning devices. Other examples of scanners are Barcode scanners and Magnetic card readers. Image input devices Digital camera, Webcam, Camcorder or digital video camera Audio input devices Audio input devices include the microphone and speech recognition devices. Processing The system unit is where the processing of data is done. When you open the case, you will see a a fan, a power supply and a large circuit board which is called the motherboard. The motherboard holds the microprocessor, main memory, connectors, battery and support chips. Other components such as sound and graphic cards, external storage and peripheral devices can be attached to the motherboard. Click the link below or copy it into your web browser to view the components of the motherboard that you should know. Roll your mouse over the image to view the components. You should be able to find 8. http://download.elearningontario.ca/repository/1058960000/BTA3OPU1/BTA3OPU1A04/mobo. htm Input/Output Ports I/O (Input/Ouput) Ports are used to connect peripheral devices to the motherboard. Serial ports are used for modems and digitizer tablets and parallel ports are used for printers. While serial and parallel ports are still in use, it is becoming more common to connect peripheral devices using a USB (Universal Serial Bus) port. Central Processing Unit (CPU) The CPU is the brain of the computer. It is a small processor (chip) that interprets and executes instructions contained in software. The processor's speed is measured in MHz (megahertz) or GHz (gigahertz). The faster the processor, the faster your computer can process instructions. A desktop processor's speed should be at least 3.4 GHz. Two manufacturers of CPUs are AMD (Athlon) and INTEL (Pentium). Memory - RAM and ROM The computer's main memory is random access memory or RAM. RAM is short term memory in that it is generally erased when the computer is shut down. The RAM memory determines the size and number of programs that it can run. Current PCs generally have of 1 gigabyte (GB) of RAM. A circuit board with additional memory chips can be installed. ROM Read-only memory (ROM) is memory which can be read only and not changed. It is used to store system programs that need to be available to the computer at all times. The BIOS (Basic Input and Output System) chips are an example of ROM memory - the computer uses it in order to boot up. Output Devices An output device receives information from the computer and puts it into a form that a human can use. Output can be in hard copy or soft copy. Hard copy Hard copy output is permanent and can be stored such as a printer or a plotter. Types of printers Laser printers can print 30 ppm (pages per minute) and with 600 dpi (dots per inch). Laser printers use toner which is heated and pressed on the paper. The resolution or clarity of the image is determined by the dots per inch. Ink Jet printers shoot droplets of ink onto the paper into order to create a character or image. Ink Jet printers can print 29 ppm and with 2400 dpi. Dot matrix printers are similar to a typewriter in that print is formed when a pin strikes a ribbon. The dot matrix printer is becoming obsolete. Plotters produce graphic images by using a pen that is attached to a movable arm. Be sure to check out the price of consumables (supplies) when purchasing a printer! Soft copy Soft copy output is transient and lost when the computer is shut off. Some examples of soft copy are the monitor and voice output. Flat top monitors (LCDs or liquid crystal display) have a crisp image and save a great deal of desk space. Traditional monitors (CRTs or cathode ray tube) can handle fast moving graphics better but use much more desk space. Resolution (dots per inch) and screen size are important considerations when purchasing a monitor. PART B - Software Software is a set of instructions that tell the computer what to do. Software can be categorized into: operating system software; applications software. Operating system software A computer requires an operating system (OS) in order to function. The most essential and frequently used items (the kernel) are loaded into the main memory (RAM) and the less frequently used are stored on the hard drive and loaded into memory when needed. The operating system performs the following functions: Job Management determines the order and timing in which programs run; Task Management prioritizes the running of programs; Data Management keeps track of where data is stored; Device Management controls peripheral devices through software called drivers which are installed into the operating system; Security is provided in a multi user environment by providing passwords and scheduling backups. Some operating systems that you might be familiar with are: Windows 8,7 and XP; Mac OS; Unix - used in server systems in business and educational environments; Linux - a free software available to the public to use, modify and redistribute. Application Software Applications software are programs used to perform tasks other than run the computer. It is the applications software that allows the user to accomplish work. The following are some of the applications software that we will be using during this course. Word processing software is used to create and edit text files with basic graphics functions. Spreadsheet software is used to create and edit rows and columns with numbers. Spreadsheets are used for performing calculations such as in budgets or financial analysis. Database software is used to create and edit records in order to sort and filter data according to criteria. Presentation software is used to create slide shows with text, graphics, animations and transitions. Web authoring software is used to create and edit html for a web site. Internet browser software is used to navigate on the web. Adobe Acrobat Reader software used to read portable document files (pdf) files. Some application software that you might be familiar with are: Microsoft Word or Corel Word Perfect Microsoft Excel or Corel Quattro Pro Microsoft Access or Corel Paradox Microsoft PowerPoint or Corel Presentation Microsoft Front Page or Macromedia Dreamweaver Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator PART C - Common Interface Elements Now that you are familiar with the hardware and software, it is time for the CEO to get familiar with the common interface elements. The Desktop The desktop may differ in appearance from one operating system to another. The Windows operating system uses a graphical user interface (GUI), which are graphics to help the user navigate and access programs. When the computer first boots up, the desktop will appear similar to the image below. This is the Windows interface or how you communicate with the computer. The desktop displays: Icons - a picture that represents a program. Double click the icon to open the program. Background - the colour or graphic backdrop on a computer screen. My Computer icon My Computer - gives you access to drives, printers and the Control Panel. The Control Panel gives you access to settings for hardware (mouse, monitor, keyboard, printer and modem) and allows you to Add/Remove Programs. Recycle Bin icon Recycle Bin - a storage area for deleted files. Files in the Recycle Bin can be restored to their original location or permanently deleted by Emptying the Recycle Bin. Task bar A bar at the bottom of a window that displays the Start menu, Quick Launch icons, and a button for open programs so that the user can easily switch between tasks and the Tray. Start Menu gives you access to: Programs - accesses installed programs Favorites - accesses book-marked web pages Documents - accesses the most recently opened documents. Settings - accesses system applications such as Control Panel, printers, task bar and Start Menu options Find - searches for specific files or folders Help - offers helpful topics for computer use Run - user can input commands to run specific programs Log Off - allows a password-protected user to log off and another to log on Shut Down - shuts down or restarts the computer Quick Launch icons give you access to commonly used programs. You can add the programs that you use most often to the Quick Launch. Using the mouse, just drag the desktop icon down to the Quick Launch bar. Open program icons represent the programs or applications that are currently running. This makes it easy for the user to switch between programs. System Tray displays icons for programs that are always running such as the clock and an antivirus program. PART D - Window A window is a box that a that displays a running program or application. You should be familiar with the parts of a window. Parts of a window Title bar - displays the title of the file and program Menu bar - gives you access to all of the functions of the program Status bar - give you information about the open document (such as the page number) Scroll bars - allow you to move through the document or window Minimize - reduces the open window down to the Task bar Maximize/Restore - changes the window between full screen and a window Close - close the window or program Toolbars - give you access to some of the more common program functions. The standard toolbar and the formatting toolbar are common in many programs and are very useful. Standard toolbar- a row of icons displaying some of the common program functions.