softwar and desktop elements
advertisement

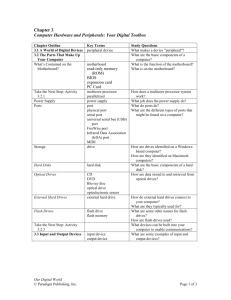
Unit Number 1: Digital Literacy Activity 4: Where will I work? Overview -------------------------------------------------------------------------------In order to work in a digital environment, it is important to have an understanding of and know the terminology associated with the workstation, hardware and software. In order to make good decisions about what computer equipment will best suit your needs for your business, you will need to know about hardware and software. A computer workstation is a standalone computer generally used in a business or professional setting. These are often personal computers that are connected to a local area network in order to share resources such as a printer. The workstation generally includes the following computer components: monitor, keyboard, mouse and system unit. These components perform the basic function of a computer: Input: Any device that allows data to be entered into the computer system. Examples include a keyboard, microphone, joystick, light pen, modem. Processing: Completed in the "Central Processing Unit", where the raw data entered into the computer is converted into a usable form and then temporarily stored. This is where all the action takes place. The processing or "system" unit contains a motherboard, microprocessor, power supply, primary memory (RAM), expansion ports or "slots". Storage: Sometimes known as "secondary" or "auxiliary" storage. This is where information can be stored so that it can be retrieved at a later date. Examples include a hard drive, zip drive, floppy disk, USB storage devices. Output: The form by which the result of the process is displayed. Examples of output devices include a monitor, printer, speakers, modem. We will be examining the input, processing and output devices. Storage devices will be examined in detail later in the unit. Input Devices The keyboard is a device used to input data by keying it in. Although this is a very tedious method of inputting data, it is a very common one. 11 There are many other types of input devices. Pointing devices are used to move a pointer around on the screen in order to execute commands. The mouse is a very common pointing device, but there are many others. - mouse, graphic tablets, joysticks, touch pads, track stick, your finger on a touch screen, stylus. Joystick 12 Touchpad 14 Stylus13 Scanning devices read text or graphics from paper and change it into a format that the computer can use. Although the flatbed scanner to scan pictures is common, there are several other types of scanning devices: barcode scanner, magnetic card reader and fingerprint scanner. Barcode scanner 15 Magnetic card reader 16 Image input devices are as follows: Digital camera and Webcam Camcorder. Digital camera 17 Webcam 18 Camcorder 19 Audio input devices include the microphone and speech recognition devices. Processing The system unit is where the processing of data is done. When you open the case, you will see a a fan, a power supply and a large circuit board which is called the motherboard. The motherboard holds the microprocessor, main memory, connectors, battery and support chips. Other components such as sound and graphic cards, external storage and peripheral devices can be attached to the mother board. Motherboard components long description CPU socket - the connector between the motherboard and the processor RAM slot - the slot for adding and replacing memory chips Floppy disk controller - circuitry to control the reading from and writing to the floppy disk drive IDE (Integrated/Intelligent Drive Electronics) - the hard drive interface PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) slot - connectors to add other devices such as video cards, sound cards, modem. AGP slot - a high speed connection for a video card I/O (Input/Output) ports - ports used to transfer data to and from input and output devices such as the keyboard, mouse and printer Input/Output Ports I/O (Input/Ouput) Ports are used to connect peripheral devices to the motherboard. Serial ports are used for modems and digitizer tablets and parallel ports are used for printers. While serial and parallel ports are still in use, it is becoming more common to connect peripheral devices using a USB (Universal Serial Bus) port. Central Processing Unit (CPU) The central processing unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer. It is a small processor (chip) that interprets and executes instructions contained in software. The processor's speed is measured in MHz (megahertz) or GHz (gigahertz). The faster the processor, the faster your computer can process instructions. A desktop processor's speed should be at least 3.4 GHz. Two manufacturers of CPUs are AMD (Athlon) and the INTEL (Pentium). Memory - RAM and ROM RAM The computer's main memory is random access memory or RAM. RAM is short term memory in that it is generally erased when the computer is shut down. The RAM memory determines the size and number of programs that it can run. Current PCs generally have 1 gigabyte (GB) of RAM. A circuit board with additional memory chips can be installed. ROM Read-only memory (ROM) is memory which can be read only and not changed. It is used to store system programs that need to be available to the computer at all times. The BIOS (Basic Input and Output System) chips are an example of ROM memory - the computer uses it in order to boot up. Output Devices An output device receives information from the computer and puts it into a form that a human can use. Output can be in hard copy or soft copy. Hard copy Hard copy output is permanent and can be stored. Devices such as a printer or a plotter are used to produce a hard copy. Types of printers Laser printers can print 30 ppm (pages per minute) and with 600 dpi (dots per inch). Laser printers use toner which is heated and pressed on the paper. The resolution or clarity of the image is determined by the dots per inch. Ink Jet printers shoot droplets of ink onto the paper into order to create a character or image. Ink Jet printers can print 29 ppm and can with 2400 dpi Dot matrix printers are similar to a typewriter in that print is formed when a pin strikes a ribbon. Plotters produce graphic images by using a pen that is attached to a movable arm. Be sure to check out the price of consumables (supplies) when purchasing a printer! Soft copy output is transient and lost when the computer is shut off. Some examples of soft copy are the monitor and voice output. Flat top monitors (LCDs or liquid crystal display) have a crisp image and save a great deal of desk space. Traditional monitors (CRTs or cathode ray tube) can handle fast moving graphics better but use much more desk space. Resolution (dots per inch) and screen size are important considerations when purchasing a monitor. Software Software is a set of instructions that tell the computer what to do. Software can be categorized into: operating system software; applications software. Operating system software A computer requires an operating system (OS) in order to function. The most essential and frequently used items (the kernel) are loaded into the main memory (RAM) and the less frequently used are stored on the hard drive and loaded into memory when needed. The operating system performs the following functions: Job Management determines the order and timing in which programs run; Task Management prioritizes the running of programs; Data Management keeps track of where data is stored; Device Management controls peripheral devices through software called drivers which are installed into the operating system; Security is provided in a multi user environment by providing passwords and scheduling backups. Some operating systems that you might be familiar with are: Windows NT, ME, 2000 and XP; Mac OS; Unix - used in server systems in business and educational environments; Linux - a free software available to the public to use, modify and redistribute. Application Software Application software are programs used to perform tasks other than run the computer. It is the application software that allows the user to accomplish work. The following are some of the application software that we will be using during this course. Word processing software is used to create and edit text files with basic graphics functions. Spreadsheet software is used to create and edit rows and columns with numbers. Spreadsheets are used for performing calculations such as in budgets or financial analysis. Database software is used to create and edit records in order to sort and filter data according to criteria. Presentation software is used to create slide shows with text, graphics, animations and transitions. Web authoring software is used to create and edit html for a web site. Internet browser software is used to navigate on the web. Adobe Acrobat Reader software used to read portable document files (pdf) files. Some application software that you might be familiar with are: Microsoft Word or Corel Word Perfect Microsoft Excel or Corel Quattro Pro Microsoft Access or Corel Paradox Microsoft PowerPoint or Corel Presentation Microsoft Front Page or Macromedia Dreamweaver Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator