Ancient Rome Vocabulary List | History Terms
advertisement

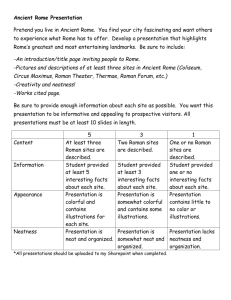
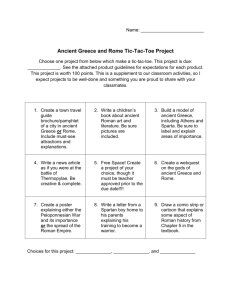
Ancient Rome Vocabulary 1. Agriculture – The raising of crops and animals for human use. 2. Apostle – One of the 12 closest followers of Jesus, chosen by him to help him teach. 3. Aqueduct – A high, arched structure built to carry water over long distances. 4. Bishop – A church official who leads a large group of Christians in a particular region. 5. Christianity – A religion based on the teachings of Jesus, as recorded in the New Testament. 6. Census – A periodic count of all the people living in a country, city, or other region. 7. Civil War – An armed conflict between groups within one country. 8. Consul – One of two elected officials of the Roman Republic who commanded the army and were supreme judges. 9. Dictator – A ruler who has absolute power. 10. Eastern Orthodox Christianity – A branch of Christianity that developed in the Byzantine Empire and that did not recognize the pope as its supreme leader. 11. Elevation – Height above sea level. 12. Gladiator – A Roman athlete, usually a slave, criminal, or prisoner of war, who was forced to fight for the entertainment of the public. 13. Messiah – A special leader the Jewish people believe will be sent by God to guide them and set up God’s rule on Earth. Christians believe Jesus to be the Messiah. 14. New Testament – The second part of the Christian Bible, containing descriptions of the life and teachings of Jesus, and of his early followers. 15. Profile – In geography, a map showing a cross-section of a land surface. 16. Plebeian – A common farmer, trader, or craftworker in ancient Rome. 17. Pax Romana – A period of peace for the Roman Empire that began with the rule of Augustus in about 27 B.C. and lasted around 200 years. 18. Punic Wars – A series of conflicts between Rome and Carthage in the 200s B.C., ending in a victory for Rome. 19. Pope – The bishop, or church leader, of Rome and head of the Roman Catholic Church. 20. Parable – A simple story that contains a message or truth. 21. Representative – A person who is elected by citizens to speak or to act for them. 22. Republic – A form of government in which citizens elect representatives to speak or act for them. 23. Roman Catholicism – A branch of Christianity that developed in the Western Roman Empire and that recognized the Pope as its supreme head. 24. Senate – The lawmaking body and most powerful branch of government in ancient Rome’s Republic. 25. Tribune – An elected leader of ancient Rome who represented the interests of the plebeians. 26. Twelve Tables – The earliest written collection of Roman laws, drawn up by patricians about 450 B.C., that became the foundation of Roman law. Ancient Rome - Places 1. Alps – Europe’s highest mountains, extending in an arc from the Mediterranean coast to the Balkan Peninsula. 2. Apennine Mountains – A mountain range on the Italian peninsula. 3. Byzantine Empire - The name by which the eastern half of the Roman Empire became known some time after A.D. 400. 4. Carthage – An ancient city on the north coast of Africa. 5. Colosseum – A large stadium in ancient Rome where athletic events took place. 6. Constantinople - A city established as the new eastern capital of the Roman Empire by the emperor Constantine in A.D. 300, now called Istanbul. 7. Forum – The city market and meeting place in the center of ancient Rome. 8. Gaul – An ancient region and Roman province that included most of present-day France. 9. Latium - A plain on the west coast of Italy on which the city of Rome was built. 10. Palestine – Region in southwest Asia that became the ancient home of the Jews; the ancient Roman name for Judea; in recent times, the British protectorate that became Israel in 1947. 11. Pantheon - A large, domed temple built in ancient Rome to honor many gods and goddesses. 12. Pompeii – An ancient city in southwestern Italy that was buried by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in A.D. 79. 13. Rome – The former center of both ancient Roman Republic and the Roman Empire; capital of present-day Italy. 14. Sicily – An island in the Mediterranean Sea off the southwest tip of the Italian peninsula. 15. Tiber River – A river flowing southward from north-central Italy across the Latium plain, and into the Tyrrhenian Sea. 16. Zama – Site in northern Africa where the Roman army defeated the Carthaginian army in 202 B.C. Ancient Rome - People 1. Augustus – First Roman emperor; won the civil war following Julius Caesar’s assassination and went on to unify the empire and establish the Pax Romana. 2. Julius Caesar – Roman general who became the republic’s dictator in 45 B.C. 3. Cleopatra – Ruler of the Egyptian government in Alexandria who backed Caesar in the civil was he waged from 49-25 B.C. 4. Christopher Columbus - Italian explorer in the service of Spain who arrived in the Americas in 1492. 5. Constantine – Roman Emperor who founded Constantinople as the new eastern capital of the Roman Empire. 6. Diocletian – Roman Emperor who divided the empire in two and oversaw the eastern part. 7. Galileo Galilei – Italian astronomer, mathematician, and physicist. His telescopes proved the sun is the center of the solar system. 8. Leonardo Da Vinci – Italian Renaissance artist, inventor, and scientist. 9. Hannibal – General of Carthage who marched his army from Spain to Rome in the Second Punic War. 10. Jesus – Religious leader and founder of Christianity. 11. Livy – Historian of the Roman Republic who wrote about the struggle between plebeians and patricians of Rome. 12. Marco Polo – Italian merchant who traveled to China, where he lived for 17 years, at times serving as diplomat for Kublai Khan. 13. Paul – Follower of Jesus who helped spread Christianity throughout the Roman world. 14. Peter – One of the 12 apostles of Jesus; Roman Catholics consider him to be the first pope, or bishop of Rome. 15. Scipio – Roman general who defeated Hannibal in the Battle of Zama outside Carthage, North Africa, in 202 B.C.